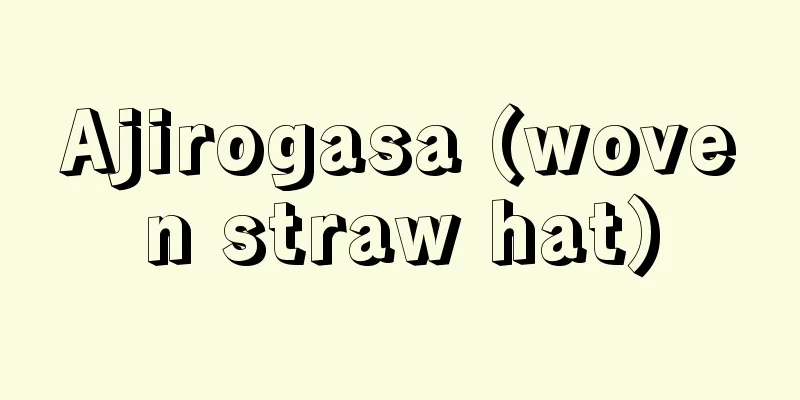Solar spectrum

|
The spectrum of sunlight is a continuous spectrum that stretches from infrared to ultraviolet. However, there are places in this spectrum where light is missing, known as linear absorption spectrum. These are called Fraunhofer lines. When calculated using Wien's displacement law from the wavelength λ m at which the intensity of the continuous spectrum is at its maximum, the temperature of the sun's surface is 5800 K. Since the sun's surface is not a perfect black body, the actual temperature is thought to be slightly higher than this. On the other hand, the temperature of the sun's surface calculated based on the Stefan-Boltzmann law from the radius of the sun, the distance between it and the earth, and the solar constant on the ground is 5700 K, which is in good agreement. Considering Kirchhoff's radiation law, the existence of Fraunhofer lines indicates that the elements that radiate sunlight are in a gaseous state that is slightly cooler than the surface and surround the sun's surface, absorbing the light emitted from the surface. Therefore, from these we can see that the sun contains the most H, followed by He, N, and Ne, as well as metallic elements such as Fe, Mg, Na, K, and Ca. Due to absorption by ozone in the upper atmosphere, the short wavelength limit for sunlight reaching the earth's surface is about 300 nm. [See alternative term] Ozone layer Source: Morikita Publishing "Chemical Dictionary (2nd Edition)" Information about the Chemical Dictionary 2nd Edition |
|
太陽光線のスペクトルは赤外から紫外に及ぶ連続スペクトルを示す.しかし,このなかのところどころに線吸収スペクトルとして光の欠けたところがある.これをフラウンホーファー線という.連続スペクトルの強度最大の波長 λm からウィーンの変位則によって計算すると,太陽表面の温度は5800 K となる.太陽表面も完全な黒体ではないから,実際の温度はこれよりやや高いと考えられる.一方,太陽の半径,それと地球の間の距離,地上における太陽定数からシュテファン-ボルツマンの法則にもとづき算出した太陽表面の温度は5700 K となり,よい一致を示している.キルヒホッフの放射法則から考えるとフラウンホーファー線の存在は,太陽光線を放射した諸元素が表面部よりはやや温度の低いガス状のものとなって太陽表面の周辺をとりまいており,表面から放射されてくる光を吸収してしまっていることを示す.したがって,これらから太陽にはHがもっとも多く,He,N,Neがこれにつぎ,Fe,Mg,Na,K,Caなどの金属元素も含まれていることがわかる.大気上層に存在するオゾンによる吸収のため,地表面に到達する太陽光線の短波長限界は約300 nm である.[別用語参照]オゾン層 出典 森北出版「化学辞典(第2版)」化学辞典 第2版について 情報 |
<<: Sun Bug (Sun Bug) - Sun Bug
Recommend
Terylene
(Terylen) Trade name of polyester synthetic fiber....
Tokudaiji family
This family split off from the Sanjo family, whic...
Theft - Setto Uzai
It is a type of property crime, and is punishable...
Yatsushiro Sea
An inland sea stretching from central to southwes...
Count Gyuragu - Gyuragu Haku
...Even in the 20th century, novels using this te...
The Regional Science Association
…On the other hand, human geography was also lagg...
channel separation
...The ratio of the signal level to the level of ...
Felipe Guamán Poma de Ayala
1534?-1615 Peruvian chronicler. An Indian who clai...
'Abd al‐Rahman I
731‐788 Founder of the Later Umayyad Caliphate. Re...
Akayamaari (English spelling) slave-making ant
An insect belonging to the order Hymenoptera, fam...
Inertial element
…A flywheel is a specially designed and manufactu...
Archaic - Walking
…In addition to pottery, there are also small fig...
Makizono [town] - Makizono
A former town in Aira County in the northeastern p...
Equity - Koheiho (English spelling) equity
The legal principles and remedies developed in the...
Lochia - lochia
This refers to the secretions from the genitals t...