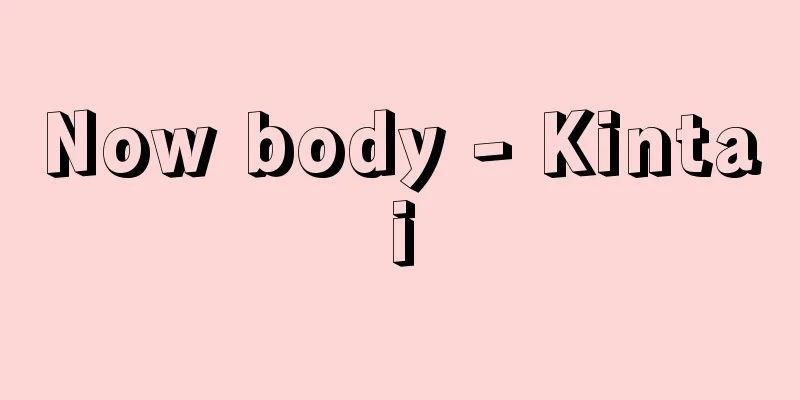Department of Justice

|
An administrative agency in charge of national administrative affairs related to the judiciary. It was established on July 9, 1871 (Meiji 4) to replace the Ministry of Criminal Affairs (Gyobusho) and the Danjodai (Danjodai), and Eto Shinpei was appointed as the first Minister of Justice in April of the following year. Under this Ministry of Justice, the judicial system was gradually improved and systematized, and this was accompanied by frequent reforms of the government system. In December 1885, with the establishment of the Cabinet system to replace the Dajokan system, the position of Minister of Justice was abolished and the Ministry became a ministry under the control of the Cabinet. The following year, February 26th, the "Ministry of Justice Official System" (Imperial Ordinance No. 2) stipulated that the scope and authority of the Minister of Justice was to manage the administration of justice, judicial police, and amnesty affairs, and to supervise the courts below the Daishin-in, and the Minister's Secretariat and the bureaus for general affairs, civil affairs, criminal affairs, and accounting were established as internal bureaus. After that, under the Meiji Constitution system, the government system was reformed several times, but the Ministry of Justice consistently had jurisdiction over judicial administration affairs in general, and the courts below the Daishin-in were under the supervision of the Minister of Justice as far as judicial administration is concerned. After World War II, with the establishment of the Constitution of Japan, the new Ministry of Justice (later renamed the Ministry of Justice and the Ministry of Justice to the present) was established on December 17th, 1947 (Showa 22), and the Ministry of Justice was abolished. There is a big difference in authority between the current Ministry of Justice under the Constitution of Japan, which has the principle of judicial independence. [Yoshii Aio] "The Ministry of Justice compiled the 'Judicial History' (1939, Bar Association)" ▽ "The Ministry of Justice Secretariat Judicial Legislation Research Department compiled the 'Judicial History Continued' (1963, Bar Association)" [References] |This government building is located in Nishi-Hibiya-cho, Kojimachi-ku (currently Kasumigaseki, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo). It was restored to its original appearance in 1994 and designated as an Important Cultural Property of Japan as the "Former Main Building of the Ministry of Justice." "Tokyo Fukei" (Tokyo Landscape) (1911, Meiji 44) National Diet Library Department of Justice Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
司法に関する国の行政事務をつかさどる行政機関。刑部省(ぎょうぶしょう)、弾正台(だんじょうだい)にかわって、1871年(明治4)7月9日に設置され、翌年4月、初代司法卿(きょう)に江藤新平(えとうしんぺい)が就任した。この司法省のもとでしだいに司法制度の整備・体系化が進められ、これに伴ってしばしば官制の改革も行われた。85年12月、太政官(だじょうかん)制にかわる内閣制の創設に伴い司法卿の職制を廃して司法大臣を置き、内閣の統轄下における一省となった。翌年2月26日の「司法省官制」(勅令2号)で、司法大臣の所掌事務の範囲・権限は、司法に関する行政・司法警察および恩赦に関する事務を管理し、大審院以下の諸裁判所を監督することと規定され、内部部局として大臣官房および総務、民事、刑事、会計の諸局が設けられた。その後、明治憲法体制下でいくたびか官制の改革が行われたが、司法省は、一貫して司法行政事務全般を管轄し、司法行政に関する限り大審院以下の裁判所を司法大臣の監督下に置いていた。第二次世界大戦後、日本国憲法の制定に伴い、1947年(昭和22)12月17日、新たに法務庁(のち法務府、法務省と改称して現在に至る)が設置され、司法省は廃止された。司法権の独立を原則とする日本国憲法下における現在の法務省とは、その権限において大きな違いがある。 [吉井蒼生夫] 『司法省編纂『司法沿革誌』(1939・法曹会)』▽『法務大臣官房司法法制調査部編『続司法沿革誌』(1963・法曹会)』 [参照項目] |麹町区西日比谷町(現在の東京都千代田区霞が関)の庁舎。1994年(平成6)に創建当時の姿に復原され、「法務省旧本館」として国の重要文化財に指定された。『東京風景』(1911年〈明治44〉)国立国会図書館所蔵"> 司法省 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
<<: Ministry of Justice Law School
Recommend
Bunkuen - Bunkuen
Land managed by public or private organizations is...
Phenyllithium
A colorless solid organometallic compound obtained...
Network modifying oxide - Network modifying oxide
… SiO2 , B2O3 , P2O5 , As2O3 , Sb2O3 , GeO2, etc....
Informal group
It refers to a spontaneous, long-term relationship...
Centaurus
A constellation that appears only with its upper ...
Commercial location - Shogyorich (English spelling) commercial location
It refers to the occupation of a specific spatial ...
Karo
The area includes Tottori Port (Karo Port) at the...
Guinea Current - Guinea Current
A warm current that flows eastward in the Gulf of ...
dipavali (English spelling)
…It is a Hindu festival held every year on the ne...
Time division multiplex communication
A method of multiplexing communication. It is also...
Hospitalitas (English spelling) [Latin]
Originally meaning "hospitality for guests,&q...
Ada
A programming language designed by the US Departme...
Coefficient of parentage
…Here, F I and F J are the inbreeding coefficient...
Blastomere
A cell that is produced by cleavage from a fertili...
Rotten City - Rotten City
〘 noun 〙① A market where waste and junk are bought...