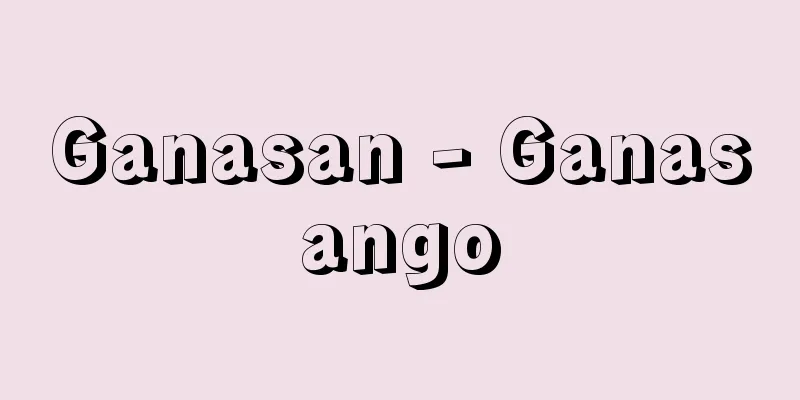Ra - Ra (English spelling)

|
In ancient Egyptian religion, he was the original god and the sun god. He is the creator of all things, including gods and humans, and is considered the source of life and crops. When written in cuneiform texts, it is written as Ri-e (which represents the sound of Rē) when romanized, so he is sometimes written as Re. During the Fifth Dynasty (after 2500 BC), the southern Delta region, today's Innu (Hebrew name On, or Bet Shemesh "House of the Sun", Greek name Heliopolis "City of the Sun") on the outskirts of Cairo, became the center of Ra worship, and Ra came to occupy the position of the chief god. After this, the title of pharaoh (Egyptian king) also included "son of Ra", and later names such as Ramses (Ra-mes "one born of Ra") were also used. During the Middle and New Kingdoms, Amon (Amun)-Ra, who merged with Amon (Amun), the earth-dwelling god of Thebes, became powerful as the supreme god. As a sun god, Ra was believed to travel from east to west across the sky in a sun boat during the day, and return to the east again at night through the body of the sky goddess Nut. Ra is often depicted as a hawk as a sky god, or as a hawk-headed figure with a solar disk on its head. The sun that appears above the horizon is called Ra-her-huti (Ra-Harmachis in Greek), and the sphinx, bearing this name, is believed to represent it. Pyramids and obelisks are also thought to be related to the worship of Ra. [Yajima Fumio] Late Period - Ptolemy period (4th century BC) Faience Height 8.2cm Collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art Rah Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
古代エジプト宗教における原初の神で太陽神。神々や人間を含む万物の創造者であり、生命や作物の源泉とされる。楔(くさび)形文字文書での表記をローマナイズするとRi-e(これはRēの音を表す)であるところから、レーと書かれることもある。第五王朝(前2500以降)にデルタ地帯南部、今日のカイロ市郊外のインヌ(ヘブライ名オン、あるいはベート・シェメシュ「太陽の館」、ギリシア名ヘリオポリス「太陽の都」)がラー崇拝の中心地になり、ラーは主神の位置を占めるようになった。こののちにはファラオ(エジプト王)の称号にも「ラーの息子」が加えられるようになり、のちにはラムセス(ラー・メス「ラーから生まれたもの」)のような名も使われた。中・新王国時代にはテーベの地着きの神であるアモン(アメン)と合体したアモン(アメン)・ラーが最高神として勢力をもった。太陽神としてのラーは、昼は太陽船に乗って東から西へと天空を移動し、夜は天空の女神ヌトの体内を通ってふたたび東方へ戻ると考えられていた。ラーはしばしば天空神としての鷹(たか)、あるいは太陽円盤を頭上にのせた鷹の頭をした人像として表現される。地平線上に姿を現した太陽はラー・ヘル・フティ(ギリシア語でラー・ハルマキス)とよばれ、この名でよばれたスフィンクスはこれを表現するものとされた。ピラミッドやオベリスクも、ラー神崇拝と関係があると考えられている。 [矢島文夫] 末期王朝時代~プトレマイオス朝時代(紀元前4世紀) ファイアンス 高さ8.2cmメトロポリタン美術館所蔵"> ラー 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
<<: La Harpe (English spelling)
>>: Luo - ra (English spelling)
Recommend
Keihan Electric Railway
A private railway company. Keihan Electric Railway...
The Nagayao Incident
A political upheaval occurred in February 729 (Te...
Kioi
〘 noun 〙 When the eaves are double -eavesed , this...
Equus
A play by Peter Shaffer that premiered in 1973. Or...
Wehnelt, B.
...They said that there are two types of substanc...
Isherwood, JW
…This was the prototype of modern tankers, and wa...
Meteor shower
〘 noun 〙 When the Earth encounters a meteor shower...
Book design (binding)
This word refers to the shaping of a book and the ...
Wei River
A river in China. It is the largest tributary of ...
Illumination - Irumine-shion (English spelling) illumination
Originally a word meaning illumination, it refers...
automatic radar plotting apparatus
…Current devices are automated to a certain exten...
Dahlem Museum of Art - Dahlem Museum (English name)
A national art museum in Berlin. It is the common...
Skilled worker - Ginousi
Based on the Human Resources Development Promotion...
Pneumatolytic deposit
…For this reason, in recent years, the fluids tha...
Donatist - Donatus (English spelling)
A sect of Christians in North Africa in the 4th ce...