Megar - Megar (English spelling)
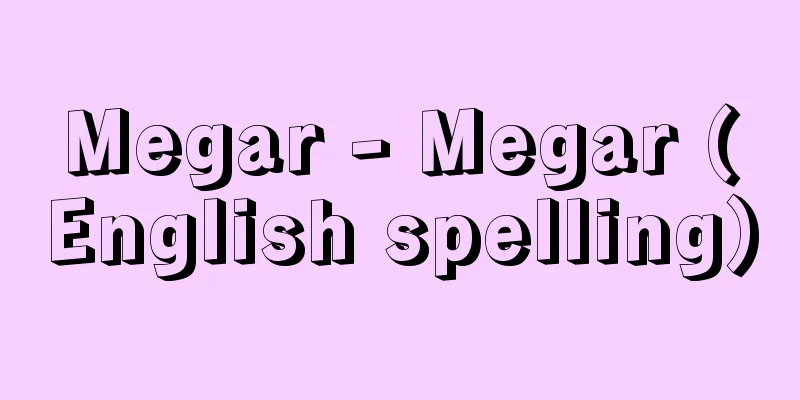
|
A general name for a portable instrument used to measure high resistance or insulation resistance of electrical materials of 5000 megaohms or less. In JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards), it is called an insulation resistance meter, but of all the instruments of this type ever made, this one designed and manufactured by the American company Evershed was the most famous and widely used, so it became the general name. The principle is an application of the moving coil ratio ohmmeter, and there are types that use a hand-cranked built-in magneto generator as a power source, types that use a dry cell battery and a transistor-type DC converter, and types that combine an electronic circuit with a moving coil type. The current coil I is the same as that of a normal moving coil meter, and the voltage coil V rotates through the iron ring. If nothing is connected to terminals E and L, which connect the unknown resistance, the current generated by the voltage generated by the generator M with a centrifugal clutch for constant speed rotation flows only through the voltage coil V (parallel to the power supply), the coil stops at the air gap position of the iron core, and the needle points to ∞. Next, if an unknown resistance is connected between E and L, a current also flows through the current coil I (series to the power supply) through the unknown resistance X, and the needle stops at the position where the torque caused by that and the torque caused by the voltage coil are balanced, and the value of the unknown resistance can be known. In this way, the moving mechanism moves as a function of voltage/current = resistance, but the scale graduated in resistance value (ohms) is almost logarithmic. [Yamazaki Shukai] I = current coil V = voltage coil E, L = terminals M = generator X = unknown resistance ©Shogakukan "> Megger's principle (Evershed type) Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
電気材料の5000メガオーム程度以下の高抵抗あるいは絶縁抵抗を測定するための携帯用計器の一般名。JIS(ジス)(日本工業規格)では絶縁抵抗計と称するが、かつてつくられたこの種の計器のなかでアメリカのエバーシェッドによって設計製作されたこのものがもっとも著名であり、またよく使用されたので一般名化した。 原理は可動コイル比率計型抵抗計を応用したもので、電源が手回しの内蔵磁石発電機のものと、乾電池とトランジスタ式の直流コンバーターとを利用したものとがある。また、電子回路と可動コイル型を組み合わせたものもある。 電流コイルIは普通の可動コイル型計器のそれと同じで、電圧コイルVは環状鉄を突き抜けて回るようになっている。未知抵抗を接続する端子EとLになにも接続されていないと、定速回転用遠心クラッチ付き発電機Mによって発生した電圧による電流は、電圧コイルV(電源に並列)にのみ流れ、コイルは鉄心のエアギャップの位置に静止し、指針は∞を指示する。次に、EとLの間に未知抵抗を接続すると、未知抵抗Xを通じて電流コイルI(電源に直列)にも電流が流れ、それによるトルクと電圧コイルによるトルクが平衡する位置で指針が静止し、未知抵抗の値を知ることができる。このように可動機構は、電圧/電流=抵抗の関数として動くが、抵抗値(オーム)で目盛った目盛りは、ほぼ対数目盛りに近くなっている。 [山崎修快] I =電流コイル V =電圧コイル E、L =端子 M =発電機 X =未知抵抗©Shogakukan"> メガーの原理(エバーシェッド型) 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
<<: Megaklēs (English spelling)
Recommend
short take-off and landing aircraft
...An aircraft that has a short runway distance f...
Kitsuki Castle Town
...Tourist attractions include the well-preserved...
Enjugahama Beach
This coastline is in Mihama Town, in the mid-west...
blastomere
… The egg cytoplasm already contains a large amou...
Syrian Desert - Syrian Desert
In Arabic, Badiyat al-Sham means Eastern Desert. I...
Barlow, T.
...Scurvy, a disease caused by vitamin C deficien...
Jan Gossaert
A Flemish painter who lived from about 1478 to abo...
Mucous membrane
This refers to the parts of the inner wall surfac...
Volcanic bomb - Kazandan (English spelling) bomb
This refers to volcanic lapilli and volcanic block...
Matsuyama
[1] 〘Noun〙 A mountain with many pine trees. Shozan...
Shirasuka
The name of a place in Fuchi District, Totomi Prov...
Soloist
…sujet: A dancer who dances in small groups or so...
Peacock King
One of the Myo-o. A statue of the Peacock Buddha ...
Chopinel, J.
…French poet and translator. His real name was Je...
Birds - English
A general term for animals belonging to the phylu...









