Pharynx - Intestine
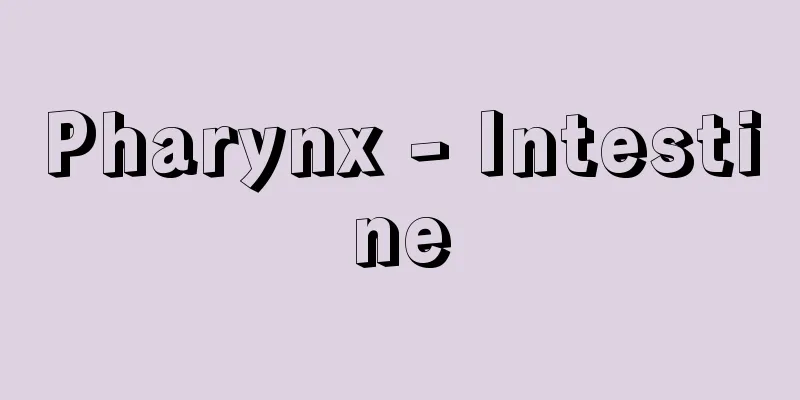
|
It is part of the digestive tract, but also part of the respiratory tract, and is located behind the nasal cavity and oral cavity. Straight below it connects to the esophagus, and the lower front also connects to the larynx. The pharyngeal cavity is divided into three parts: the nasal, oral, and laryngeal parts. It is about 12 centimeters long and has a cylindrical shape that is slightly flattened from front to back. If you open your mouth wide, you can see an arch-shaped mucosal fold at the rear and upper part of the oral cavity. This fold is called the palatine pharyngeal arch, and the area behind this pharyngeal arch becomes the pharynx. The mucosal wall at the end of the oral cavity is the posterior pharynx. The nasal pharynx is the rear part of the nasal cavity, and is above the soft palate. The nasal pharynx and nasal cavity are connected by the posterior nares. The upper end of the nasal pharynx is at the base of the skull, and is called the pharyngeal vault. On the outer wall of the nasal pharynx, at the level of the inferior turbinate, there is the Eustachian tube pharyngeal opening, which is the opening of the Eustachian tube that connects the middle ear to the pharynx. When we yawn or swallow saliva, the Eustachian tube opens, connecting the middle ear to the pharynx, and at that moment the internal pressure of the middle ear changes. The pharyngeal opening is from the soft palate to the level of the hyoid bone, and the laryngopharynx is from the hyoid bone to the part that transitions to the esophagus. In front of the part that transitions to the esophagus is the entrance to the larynx, which is closed by a lid called the epiglottis that protrudes from the anterior wall of the larynx. When a swallowing movement occurs, such as when food is swallowed, the epiglottis acts to close the larynx. This action is reflexive, occurring when food stimulates the mucous membrane of the posterior wall of the pharynx, and preventing food from entering the larynx. The inner wall of the pharynx is covered by the pharyngeal mucosa, which contains many pharyngeal glands that secrete mucus. In addition, there are protuberances of lymphatic tissue on the mucosa of the side and posterior walls of the pharynx, called pharyngeal tonsils. These tend to enlarge during infancy, and when they reach a considerable size they are called adenoids. If the adenoids become too large, they are easily irritated and often cause tonsillitis. Between two mucosal folds at the border between the pharyngeal and oral cavities are the relatively large palatine tonsils, which are also prone to inflammation. Pharyngeal muscles related to the function of the pharynx are well developed around the pharynx and are made up of striated muscle fibers. In particular, the posterior wall of the pharynx has three muscle layers that encase the pharynx from the posterior wall, running from the inner upper to the outer lower to the left and right from the midline of the posterior pharynx, and are divided into the upper, middle and inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscles, but the borders between these three layers overlap. Other pharyngeal muscles include the stylopharyngeus, eustachian tube pharyngeus and palatopharyngeus. Pharyngeal muscles not only work to help swallow food, but also to facilitate vocal cord movement during speech production. When swallowing occurs, that is, when food touches the pharyngeal mucosa and the pharyngeal muscles contract reflexively, the pharynx is pulled upward. In particular, the stylopharyngeus pulls the pharyngeal wall upward and outward, expanding the pharyngeal cavity and increasing its horizontal diameter. At the same time, the soft palate adheres to the posterior wall of the pharynx, closing the passage to the nasal pharynx, and the base of the tongue moves anteriorly and upward, causing the epiglottis to close the entrance to the larynx. Food is sent straight from the expanded pharynx into the esophagus. If the nasal pharynx and larynx are not completely closed at this time, food or liquid may enter the nasal cavity or larynx. The pharyngeal muscles are controlled by the vagus nerve, sympathetic nerve, glossopharyngeal nerve, etc., so if the vagus nerve or glossopharyngeal nerve is damaged, swallowing will not be smooth as well as speech disorders. [Kazuyo Shimai] Animal pharynxAs in humans, it generally refers to the ampulla between the oral cavity and the esophagus. Its form and function vary depending on the animal group. The pharynx of Turbellaria is enclosed in a muscular wall called the pharyngeal sheath, which inverts when feeding and comes out of the mouth to encase food and swallow it. In fish, there are gills on both sides of the pharynx, so it is also called the gill-enteric. Even in higher vertebrates, gill slits form on both sides of the pharynx during development, and the lungs also develop from this area. As the pharynx is also the area between the nasal cavity and trachea, it also serves as part of the respiratory tract. [Seiichiro Kawashima] [References] |©Shogakukan "> Names of parts of the pharynx Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
消化管の一部であるが、気道の一部にもなっている部分で、鼻腔(びくう)、口腔の後方にあって、まっすぐ下方は食道につながり、下前方は喉頭(こうとう)にも通じる。咽頭腔は鼻部、口部および喉頭部の3部に区分されるが、長さ約12センチメートルで、多少前後に圧平された円筒形状である。口を大きく開けると、口腔の後上方にアーチ形の粘膜ひだがみえる。このひだを口蓋咽頭弓(こうがいいんとうきゅう)とよび、この咽頭弓を境として後方が咽頭になる。口腔の突き当たりの粘膜壁が咽頭後壁である。咽頭鼻部は鼻腔の後方部分で、軟口蓋より上方になる。咽頭鼻部と鼻腔とは後鼻孔によって連絡している。咽頭鼻部の上方端は頭蓋底にあたり、咽頭円蓋とよんでいる。咽頭鼻部の外側壁では、下鼻甲介(かびこうかい)の高さのところに耳管(じかん)咽頭口があり、中耳と咽頭とを結ぶ管である耳管の開口部になる。あくびをするとか、唾液を飲み込む動作によって耳管が開き、中耳と咽頭とが連絡して、その瞬間に中耳の内圧が変化する。咽頭口部は軟口蓋から舌骨の高さまでをいい、咽頭喉頭部は舌骨から食道に移行する部分までをいう。食道に移行する部分の前方には喉頭の入口があり、喉頭の前壁から出ている喉頭蓋という蓋(ふた)によって、この入口はふさがれている。食物を飲み込むような嚥下(えんげ)運動がおこるときには、喉頭蓋が喉頭を閉じるように働く。この働きは反射的で、食物が咽頭後壁の粘膜を刺激することによっておこり、食物が喉頭に進入するのを防いでいる。 咽頭内壁は咽頭粘膜に覆われるが、この粘膜には粘液を分泌する咽頭腺が多数存在する。また咽頭側壁や後壁粘膜にはリンパ組織の隆起があり、咽頭扁桃(へんとう)とよぶ。これは幼児期には肥大しやすく、かなりの大きさになったものをアデノイドとよぶ。あまりアデノイドが著しいと、刺激を受けやすく、扁桃炎をしばしばおこす。咽頭口腔と口腔との境にある2枚の粘膜ひだの間には比較的大きな口蓋扁桃がある。これも炎症をおこしやすい。 咽頭周囲には、咽頭の働きに関係する咽頭筋群が発達しており、横紋筋線維からなっている。とくに咽頭後壁には、咽頭を後壁から包むように3種の筋層があり、咽頭後面の正中線から左右に向かって内上方から外下方に走り、上・中・下咽頭収縮筋に区別されるが、この3層の境は重なっている。このほかに、咽頭筋として茎突咽頭筋、耳管咽頭筋、口蓋咽頭筋などがある。咽頭筋は、食物を飲み込むときに、これを助けるように働くだけでなく、発声のときにも、声帯の運動を助けて発声を容易にするように働く。 嚥下運動がおこるとき、つまり食物などが咽頭粘膜に触れて反射的に咽頭筋の収縮がおこるときには、咽頭は上方に向かって引き上げられる。とくに茎突咽頭筋は咽頭側壁を上外側方に引き上げ、咽頭腔を拡張し、横径も増大する。同時に軟口蓋が咽頭後壁に密着して咽頭鼻部への通路を閉じ、舌根は前上方に移動するので、喉頭蓋が喉頭の入口を閉じる。食物は、拡張した咽頭から食道にまっすぐに送り込まれる。このとき、咽頭鼻部や喉頭への閉鎖が完全に行われないと、食物や液体が鼻腔や喉頭に入ることがある。咽頭筋は迷走神経、交感神経、舌咽神経などの支配を受けるから、迷走神経、舌咽神経などの傷害があると、発声障害とともに嚥下作用も円滑に行われなくなる。 [嶋井和世] 動物の咽頭ヒトの場合と同様に、一般には口腔(こうこう)と食道の間にある膨大部をいう。動物群によってその形態や働きに違いがある。渦虫類の咽頭は咽頭鞘(しょう)という筋壁に包まれているが、摂食時には反転して口外に出て食物を包んで飲み込む。魚類では咽頭の左右にえらがあるので鰓腸(さいちょう)ともよぶ。高等脊椎(せきつい)動物でも、発生の途中で咽頭の両側壁に鰓裂を生じ、肺もこの部位から発生する。咽頭は鼻腔と気管との間にある部位でもあるから、呼吸道の一部を兼ねることとなる。 [川島誠一郎] [参照項目] |©Shogakukan"> 咽頭の各部名称 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
>>: Indian medicine - Indian medicine
Recommend
masking
Also called shielding. Eliminating interference b...
Seeber, LA (English spelling)
…In 1830, mineralogist JFC Hessel succeeded in de...
Pros Thessalonikeis; Letters to the Thessalonians
Two letters in the New Testament written by Paul f...
Parliamentary policy faction
…(1) On June 22, 1908, at Kinkikan in Kanda, Toky...
Current account balance
This refers to the total of the trade balance, non...
Ley Lerdo (English spelling)
The Law on the Dissolution of Perpetual Property ...
Ponti, G. (English notation) PontiG
...The bentwood furniture by Thonet, which was po...
Akitsushima
〘Noun〙 (Misreading of " shima " in "...
blackfin tuna
...In Japan, tuna usually refers to a large macke...
Bardulia
…Its origins lie in the Villarcallo area on the u...
Ninth day - Okunchi
There is a custom in various regions of holding an...
Yamato binding - Yamato binding
A binding method. Several or several dozen sheets...
Eneida
…(5) Galicia became part of Austria after the par...
Rheumatic fever - Rheumatic Fever
◎A type of allergic reaction [What kind of disease...
Sueuji
A powerful clan in Suo during the Muromachi and Se...







![Aru [Islands] - Aru](/upload/images/67cadd30011b9.webp)
