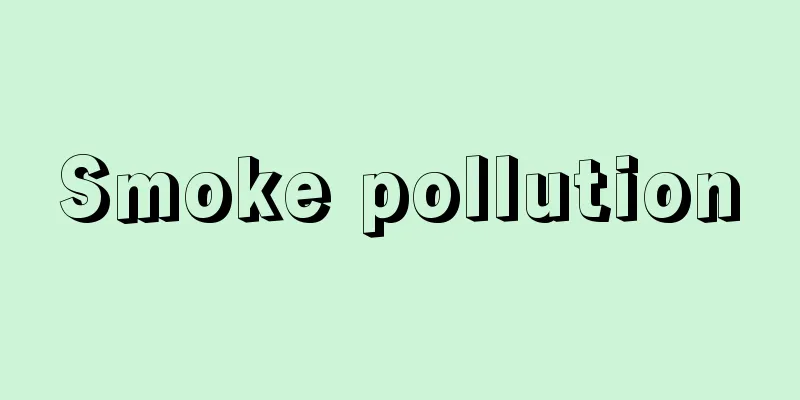Prism (English spelling) prism

|
A transparent body with two or more smooth, uniform, optically flat surfaces, at least one pair of which is not parallel. It is used to bend, disperse, or totally reflect light. In addition to optical glass, quartz is used for ultraviolet rays, and rock salt is used for infrared rays. (1) Devices that disperse light and split it into spectra are often triangular prisms with two polished faces, and are used in spectroscopes, spectrometers, refractometers, etc. In the figure, α is called the apex angle, and light that enters one side at an incidence angle i is split into monochromatic rays and exits in the direction of different deviation angles δ, because the refractive index n of the medium varies depending on the wavelength, resulting in dispersion. δ also changes depending on the incidence angle i , but when monochromatic light is used and incident at various incidence angles i , the deviation angle never becomes smaller than a certain value δ 0 , no matter how i is changed. δ 0 is called the minimum deviation angle, and its value is determined only by the refractive index n and the apex angle α, as shown in the following equation. This relationship is used to measure the refractive index of a medium. The resolution of a spectroscope using a prism is proportional to the size of the prism, so a large material is required to achieve high resolution. For this reason, diffraction gratings and interferometers are more effective at increasing resolution. (2) Erecting prisms and pentagonal prisms are used to change the direction of a bundle of light rays or to erect an image using total reflection. Erecting prisms include the Porro type, the Appe type, the Amici type, and the Hensorth type, and are used in telescopes to flip inverted images. The telescope body can be made shorter than when erecting images using a lens system. Pentagonal prisms reflect a bundle of light rays and change their direction of travel by a uniform 90°, and the image is not inverted. Since they do not perform total reflection, they are silver-plated to increase reflection. They are used in rangefinders and single-lens reflex cameras. (3) Polarizing prisms, which create polarized light, are made from birefringent crystals such as calcite and quartz, and are used to extract linearly polarized light. Examples include the Nicol prism and the Rochon prism. Source: Encyclopaedia Britannica Concise Encyclopedia About Encyclopaedia Britannica Concise Encyclopedia Information |
|
なめらかで均質な,光学的平面を二つ以上もつ透明体で,少なくともその1組の面が平行でないもの。光を屈曲,分散,全反射させるために用いる。光学ガラスのほか,紫外線には水晶,赤外線には岩塩などが使用される。 (1) 光を分散させてスペクトルに分けるものには,二つの面を研磨した三角柱状のものが多く,分光器,分光計,屈折計などに用いられる。図においてαを頂角といい,入射角 i で一辺に入射した光は,媒質の屈折率 n が波長によって異なるため,各単色光に分かれて異なった偏角δの方向に出てゆき,分散が生じる。δは入射角 i によっても変化するが,単色光を用いていろいろの入射角 i で入射させるとき,i をいかに変化させても偏角はある一定の値 δ0 より小さくはならないという性質がある。 δ0 を最小偏角と呼び,その値は次式のように屈折率 n と頂角αの大きさのみで決まる。この関係式は媒質の屈折率の測定に利用される。プリズムを使った分光器の分解能はプリズムのサイズに比例するので,高い分解能を得るためには大きな素材を必要とする。このため分解能を上げるには回折格子や干渉計のほうが有効である。 (2) 全反射を利用して,光線束の方向を変え,または像を正立させるためのものには,正立プリズムと五角プリズムがある。正立プリズムには,ポロ型,アッペ型,アミーチ型,ヘンスオルト型などがあり,望遠鏡などで倒立像を反転させるために用いる。レンズ系で正立させる場合よりも,望遠鏡体を短くできる。五角プリズムは光線束を反射させて,進行方向を一様に 90°変え,像は倒立しない。全反射をしないので,反射を増すため銀メッキする。測距儀,一眼レフカメラなどに用いられる。 (3) 偏光をつくる偏光プリズムは,方解石,水晶など複屈折性の結晶を使ってつくり,直線偏光を取り出すのに用いる。ニコルのプリズム,ロションプリズムなどがある。
出典 ブリタニカ国際大百科事典 小項目事典ブリタニカ国際大百科事典 小項目事典について 情報 |
<<: Friesland - Friesland (English spelling)
Recommend
Vaal River
A river that flows through northeastern South Afri...
Idori
A form of extreme fighting in judo. It is used to ...
Kiwa [town] - Kiwa
A former town in Minamimuro District, southern Mie...
Rakusho-Kan - School custody
...A place for studying Tang music and music from...
Bishamonten
A Buddhist guardian deity. The Sanskrit word Vaiś...
Seebeck - Thomas Johann Seebeck
German physicist. Born in Tallinn, Estonia. He st...
Repair job - Repairman
An extra-office official established in 818. The J...
Mount Katsuragi
One of the main peaks of the Kongo Mountains, loca...
Bambusa vulgaris (English spelling)
…[Ueda Koichiro]. … *Some of the terminology that...
Column - Eiren
A couplet on the Bo Zhu. A couplet. A Bo Chronicle...
Sansa Dance - Sansa Dance
This dance is mainly performed during the Bon Fest...
Estigarribia, JF (English spelling) EstigarribiaJF
...World War I brought a lull, but in 1932 a bord...
Sentoku
A haiku poet of the mid-Edo period. Mizuma, who w...
Civil Engineering Change - Doboku no Hen
This is an incident in which Emperor Zhengtong of...
Walpurgis Night - Walpurgisnoyol
The night before May Day in Europe. In folklore, i...