Bassoon - fagotto (English spelling) Italian

|
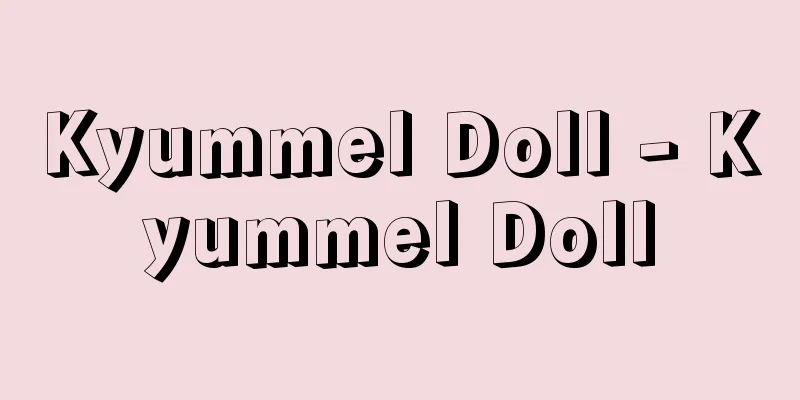
A type of double-reed aerophone, also known as the bassoon. A woodwind instrument based on a conical tube, it usually has a range of B ♭ 1 to F5 and plays an important role in the orchestra as the low-pitched woodwind instrument. The total length of the tube is 2.54 meters, but the length of the instrument itself is about 1.3 meters because it is made up of two tubes bundled together. A double reed, larger than that of an oboe or English horn, is attached to a metal blowing tube (crook), which is connected to the body. The crook has a very small hole near the body, which makes overblowing easier. Modern instruments can be disassembled into four parts. Starting from the crook, they are the wing joint, double joint, long joint, and bell joint. The wing joint has a thickened part of the tube wall to allow three of the finger holes to be drilled at an angle. This is because if they were drilled vertically, the fingers would not be able to reach them. The double joint has two tubes passing through it, which are connected at the bottom by a metal U-shaped tube. A metal cover is placed on top of the U-shaped tube to protect it. The keys are gathered at these two joints, and the left hand opens and closes the wing joint, while the right hand opens and closes the double joint. Many keys are assigned to both thumbs. The inside diameter of the tube gradually increases, widening to a long joint and a bell joint. Maple is the most common wood used for the body. There used to be five types of this type of instrument, but now there are two: the bassoon mentioned above and the contrabassoon, which has a range one octave lower than the bassoon and has the same basic structure as the bassoon, but since it requires a longer tube, it is folded multiple times to make it easier to handle. [Ryūji Uta] ©Yamaha "> bassoon Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
ダブルリードの気鳴楽器の一種。バスーン(英語ではbassoon)ともよばれる。円錐(えんすい)管を基本とする木管楽器で、通常B♭1~F5の音域をもち、木管群の低音楽器としてオーケストラで重要な役割を果たしている。 管の全長は2.54メートルだが、2本の管を束ねたような形にして楽器自体の長さは1.3メートルほどになっている。オーボエやイングリッシュ・ホルンよりも大型のダブルリードを金属製の吹き込み管(クルック)に取り付け、これを本体につなぐ。クルックにはごく小さい孔(あな)が本体に近いほうにあけてあり、これによってオーバーブローを容易にしている。現在の楽器は、本体を四つに分解できる。クルックのつくほうから順に、ウィング・ジョイント、ダブル・ジョイント、ロング・ジョイント、ベル・ジョイントである。ウィング・ジョイントは、指孔のうち三つを斜めにあけるために管壁の一部が分厚くなっている。これは、垂直にあけると指が届かなくなるためである。ダブル・ジョイントは2本の管が通っており、その2本が下端で金属のU字管によってつながれている。そしてその上から、U字管を保護するために金属のカバーがつけられている。この二つのジョイントにキーが集められており、左手でウィング・ジョイント、右手でダブル・ジョイントの指孔とキーを開閉する。多くのキーが両親指に割り当てられている。管の内径は徐々に大きくなり、ロング・ジョイント、ベル・ジョイントへと広がっていく。本体の木はカエデを用いるのがもっとも一般的である。 この種の楽器はかつては5種類あったが現在では2種類で、前述のファゴットのほかにコントラ・ファゴットがある。これはファゴットよりも1オクターブ低い音域の楽器で、基本構造はファゴットと同じだが、さらに長い管を必要とするため、操作しやすいように何重にも折り曲げた形になっている。 [卜田隆嗣] ©ヤマハ"> ファゴット 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
<<: Phacolith (English spelling)
Recommend
Responsibility for starting the war
…World War I showed the appearance of a total war...
Gaya pottery
…From the second half of the 4th century to the 5...
Billiton
…An island in the western part of Indonesia. It i...
Yoshiaki Ashikaga
The 15th Shogun of the Muromachi Shogunate. Son o...
Michiyasu Inoue
Poet and Japanese literature scholar. Born in Him...
Glass Screen
...In this way, the screen functions to change th...
Consumer Reports
...In 1891, the Consumers' League was formed ...
Grasshopper - Grasshopper
An insect belonging to the family Scutellaria in ...
Mendes, M.
…The main composers of the 16th century were the ...
Maria I
1734‐1816 Queen of Portugal. Reigned 1777-1816. Da...
Pledging - Tong-yue
A humorous piece from the Western Han Dynasty in C...
internal desynchronization
…Therefore, there is a discrepancy in rhythm betw...
Sakartvelo
…Official name: Republic of GeorgiaSakartvelos Re...
mousetail
…Perennial aquatic plant of the Equisetaceae fami...
Zeune, JA (English spelling) ZeuneJA
… [Name and its scope] The peninsula we now call ...