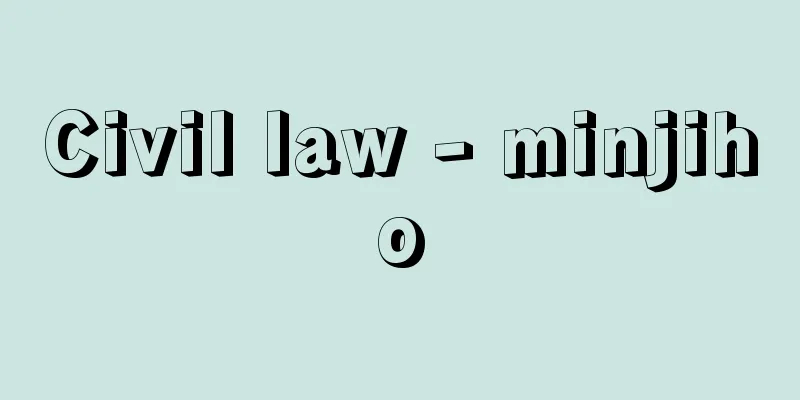Tosa School

|
This is the school of painting that inherited the traditions of Yamato-e and dominated its style for the longest time. In the "Tosa Family Trees" that are in circulation, the school dates back to the Heian period, but the parts before the Kamakura period are less reliable. The person who is definitely known as the founder of the school is Fujiwara no Yukimitsu (Nakamikado Yukimitsu), who is thought to have become the head of the art school around 1352 (Bunwa 1, Shohei 7). The name Tosa was first used in documents by Fujiwara no Yukihiro (possibly Yukihiro's grandson). After that, successive generations of people were appointed as heads of the art school, but the Tosa school developed significantly when Yukihiro's successor Mitsuhiro and then Mitsunobu appeared. Mitsunobu was a central figure in the production of Yamato-e paintings during the Muromachi period, painting for the Imperial Court and the Shogunate from the mid-15th century to the beginning of the 16th century, when he was in charge of the Imperial Court Paintings. His son Mitsushige also succeeded Mitsunobu as the head of the Imperial Court Paintings, leaving behind works such as "Kuwano-dera Engi". However, in 1569 (Eiroku 12) towards the end of the Muromachi period, Mitsushige's eldest son Mitsumoto was killed in battle, leaving the Tosa school without a successor and forced to retreat from the central art world. The school moved to Sakai, where it maintained its lineage as town painters, centered around Mitsuyoshi (perhaps a disciple of Mitsushige), but his son Mitsunori moved to Kyoto in 1634 (Kan'ei 11) and attempted to revive the school. His son Mitsuoki was finally appointed head of the Imperial Court Paintings in 1654 (Shoo 3), and revived the school. Afterwards, Mitsunari, Mitsuyoshi and others emerged and maintained the traditions of Yamato-e throughout the Edo period. The Tosa school was an important presence as the bearer of Yamato-e in the Middle Ages, and is also notable for encouraging the new rise of town-e in the early modern period. Jokei, who emerged from the same school in 1662 (Kanbun 2), founded the Sumiyoshi school and was active in Edo. [Etsuko Kato] "Tosa School Paintings" (1982), edited and published by Suntory Museum of Art [Reference] | |©Shogakukan "> Tosa School / Brief family tree Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
大和絵(やまとえ)の伝統を継承して、もっとも長くその主流を占めた画派。数種類流布する「土佐系図」などでは、その画系は平安時代にまでさかのぼるが、鎌倉時代以前の部分は信憑(しんぴょう)性が薄い。画系の祖として確実に知られるのは1352年(文和1・正平7)ごろに絵所預(えどころあずかり)となったと考えられる藤原行光(ふじわらのゆきみつ)(中御門行光(なかみかどゆきみつ))である。また、土佐の呼称は藤原行広(ゆきひろ)(行光の孫か)が文献上の初出である。以後代々絵所預に任じられたりしているが、行広の次代の光弘(みつひろ)、ついで光信(みつのぶ)が輩出するに及んで、土佐派は著しく発展した。光信は宮廷絵所預であった15世紀なかばから16世紀初めまで、宮廷・幕府などのために絵画活動を行い、室町時代の大和絵制作の中心的存在であった。子の光茂(みつしげ)も、光信を継承して絵所預を務め『桑実寺縁起(くわのみでらえんぎ)』などを残している。しかし室町末期の1569年(永禄12)に光茂の長男・光元が戦死したため土佐派は後継者を失い、中央画壇からの後退を余儀なくされた。堺(さかい)に下った同派は、光吉(みつよし)(光茂の弟子か)を中心に町絵師として画系を維持したが、子の光則(みつのり)は1634年(寛永11)京都に移り、同派の再興を企てた。その子光起(みつおき)は1654年(承応3)ついに宮廷絵所預に任じられ、同派を復興した。以後、光成(みつなり)、光芳(みつよし)らが出て、江戸時代を通じて大和絵の伝統を遵守した。土佐派は中世における大和絵の担い手として重要な存在であり、また近世においては町絵の新しい興隆を促したことも特筆される。なお1662年(寛文2)に同派から出た如慶(じょけい)は住吉派(すみよしは)をおこして、江戸で活躍した。 [加藤悦子] 『サントリー美術館編・刊『土佐派の絵画』(1982)』 [参照項目] | |©Shogakukan"> 土佐派/略系図 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
Recommend
Ligurian Sea - Ligurian Sea
An inlet in the western Mediterranean Sea, northwe...
Simushir Island (English spelling)
A volcanic island under Russian rule in the centra...
Hong Gai - Hong Gai (English spelling)
The capital of Quang Ninh Province in northern Vi...
Kato Kyodai - Kato Kyodai
Year of death: January 20, 1792 (February 12, 1792...
Akayu [Hot Spring] - Akayu
...A city in the southeastern part of Yamagata Pr...
Zakariyā ibn Muammad ibn Mamūd, abu Yayā al-Qazwīnī
A Persian-born Arabic encyclopedia writer, he was...
Sophistikē; sophistry
It refers to a deliberately false argument. The em...
Tarudama [Hot Spring] - Tarudama
A hot spring located on the southwestern slope of ...
Age - Dai
[1] 〘noun〙① The period during which one holds a po...
Akai Tozen - Akai Tozen
...Early modern Tokoname ware was mainly made up ...
Cache memory - Cache memory
A small memory (storage device) that is installed...
Mikamo [town] - Mikamo
An old town in Miyoshi County, western Tokushima P...
Umbilical cord
Umbilical cord. Umbilical cord blood is, as the na...
Air bubbling device
...In addition, fuel and fresh water tanks that a...
Yoshiro Sakatani
Born: January 16, 1863 (Bunkyu 3) in Okayama [Died...