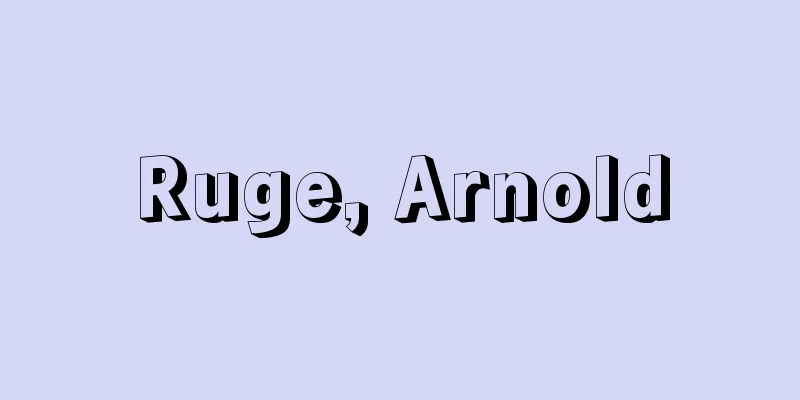Ammeter - Ammeter

|
An instrument that measures DC or AC current. Ideally, the voltage drop inside the meter should be zero, so the internal impedance is extremely small. DC ammeters generally use instruments known as moving coil types. This is based on the principle that a coil placed in a uniform magnetic field generates a rotational torque proportional to the current flowing through the coil. A spring and a pointer are attached to this coil, and when the torque of the coil and the spring are balanced, the coil comes to rest and the angle of rotation is proportional to the current, so the current can be measured by the scale indicated by the pointer. The most common AC ammeter is an instrument called the moving iron type. The principle is that two iron pieces, one fixed and the other movable, are placed in a magnetic field generated by a coil through which a current to be measured flows, and the torque generated by their repulsion or attraction is utilized. Other AC ammeters in use include electrodynamometer type instruments that utilize the force acting between two types of air-core coils, one fixed and the other movable, connected in series, thermocouple type instruments in which a measurement current flows through a hot wire and a DC meter is connected to a thermocouple joined to the hot wire, and rectifier type instruments that combine a rectifier and a DC meter. Ammeters for measuring currents larger than the meter's specific current range have a resistor (shunt) connected in parallel to shunt currents other than the meter's specific current in the case of direct current, and for alternating current they use a current transformer that converts the magnitude of the current by a coil wound around the same iron core. A digital ammeter works by passing a measurement current through a built-in standard resistor and digitally measuring the voltage drop across it. [Yamazaki Shukai] ©Takashi Aoki Principles of ammeters (moving coil type and moving iron type) Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
直流あるいは交流の電流を測定する計器。理想的には計器内部での電圧降下が0であることが望ましいので、その内部インピーダンスがきわめて小さくなっている。 直流電流計には、一般に可動コイル型とよばれている計器が用いられている。これは、均一磁界中に置かれたコイルには、そのコイルに流れる電流に比例する回転トルクが発生するという原理に基づいている。このコイルにはスプリングと指針が取り付けられており、コイルとスプリングのトルクが平衡したときコイルは静止し、その回転角は電流に比例することになるので、指針が示す目盛りによって電流が測定されるようになっている。 交流電流計としてもっとも一般的なものは可動鉄片型とよばれている計器である。原理は、測定電流が流れるコイルによって発生する磁界の中に、一方は固定で他方が回転できるようになっている二つの鉄片を配し、それらが反発あるいは吸引するトルクを利用している。交流電流計には、このほか、直列接続された一方が固定で他方が可動の2種の空心コイル相互間に働く力を利用する電流力計型計器、また熱線に測定電流を流しその熱線に接合した熱電対に直流計器を接続した熱電対型計器、あるいは整流器と直流計器を組み合わせた整流型計器などが利用されている。 計器固有の電流範囲より大きい電流を測定するための電流計には、直流の場合、計器固有の電流以外の電流を分流させるための抵抗器(分流器)が並列接続されており、交流に対しては同一鉄心に巻かれたコイルによって電流の大きさを変換する変流器を利用している。 デジタル電流計は、内蔵の標準抵抗器に測定電流を流し、そこにおける電圧降下をデジタル測定することによっている。 [山崎修快] ©青木 隆"> 電流計の原理(可動コイル型と可動鉄片型… 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
Recommend
smoothhaired fox terrier
…It stands about 45cm tall and weighs about 7-9kg...
Austrian Slavism
...The number of participants was about 360, incl...
The Japan Foundation
An independent administrative institution establis...
Abnormal birth - Ijōtanjō
…In the Petition, the child is banished to an isl...
Epirus Empire - Epirus (English spelling)
A Greek state (1204-1340) established by Michael I...
Sulfate resisting cement
...Used for bulking, port construction, etc. Sulf...
Aikawa [town] - Aikawa
A former town in Kitaakita County in northern Akit...
Ivor - Ivor
…Suspension bridges are a typical example of cabl...
Heliant - Heliant (English spelling)
This gospel of unknown authorship is said to be t...
"The Imitation of Christ" - The Imitation of Christ
…Completed around 1427, many copies were immediat...
Chemical prevention - KAGAKUYOBO
…However, chemotherapy is now being attempted for...
Yusuke Arimura
1833-1860 A samurai from the late Edo period. Bor...
Sayasan
Leader of the peasant uprising in Myanmar. In 1928...
Wholesale store - Gyohanten
…As of the end of 1983, the number of sales affil...
Ustad Sea Rebellion - Ustad Sea Rebellion
...The beginning of the Abbasid movement was when...