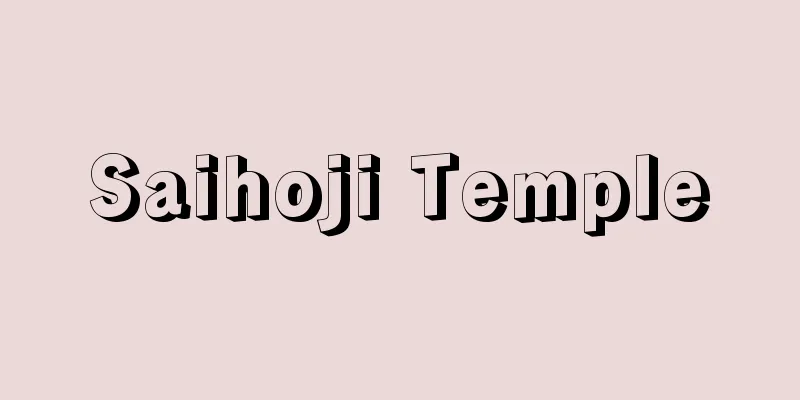
The Sixteen Provinces of Yanyun

|
This refers to the 16 prefectures in northern China that were ceded to the Liao Dynasty by Shi Jingtang, the first emperor of the Later Jin Dynasty (936-946). These are the 16 prefectures in Hebei Province: You (Beijing), Ji (Ji County), Ying (Hejian County), Mo (Renqiu County), Zhuo (Zhuo County), Dan (Miyun County), Shun (Shunyi County), Ji (Huailai County), Ru (Yanqing County), Xin (Zhuolu County), Wu (Zhangjiakou City), and Wei (Wei County); and Yun (Datong County), Ying (Shanyin County), Shuo (Shuo County), and Huan (near Mayi, northeast of Shuo County) in Shanxi Province. Yanyun is a name that dates back to the time of Huizong of the Song dynasty, and was previously called Yandai, Youkei, Youyan, etc. In 933, when Li Congke, the adopted son of Emperor Mingzong of the Later Tang dynasty (923-936), seized the Later Tang dynasty, Mingzong's son-in-law Shi Jingtang raised an army in Taiyuan and asked Emperor Taizong of the Liao dynasty for help, on the condition that he cede the prefectures north of Yanmen Pass. In 936, the Liao dynasty sent an army to destroy the Later Tang dynasty and had Shi Jingtang establish the Later Jin dynasty, so Shi Jingtang became a vassal to the Liao dynasty and handed over the 16 prefectures of Yanyun to the Liao dynasty in November of the same year. The Liao Dynasty designated Youzhou as Nanjing and Yunzhou as Xijing, appointed Chinese scholar-officials as government officials, and worked to maintain order. In China, the Great Wall was considered the boundary between the two worlds, and the area south of the wall was considered Chinese territory, so they tried to recapture lost territories whenever they had the chance. Emperor Shizong of the Later Zhou Dynasty recaptured Yingzhou and Mozhou in 959. The Song Dynasty also made the recovery of lost territories a national policy, and Emperor Taizong launched an expedition to the north, but to no avail. When the Jin Dynasty was founded in 1115, Emperor Huizong of the Song negotiated with the Jin Dynasty to use their power to recover lost territories, and agreed to cede the lost territories to the Jin Dynasty on the condition that the Song capture Yanjing (Beijing) and give the Jin the silver and silk that it had previously given to the Liao Dynasty. However, the Jin occupied Yanjing by themselves, so the conditions changed, and in 1123, the Song ceded Yanjing and the six prefectures of Ji, Jing, Tan, Shun, Zhuo, and Yi to the Jin in exchange for giving annual offerings and rice. However, the Jin, accusing the Song of violating the treaty by not sending annual offerings, sent troops to North China in 1125 and occupied Yanjing, and the following year occupied the Song capital of Kaifeng, so the North China Plain, including the prefectures of Yanyun, became Jin territory. [Yoshihiro Kawachi] ©Shogakukan "> The Sixteen Provinces of Yanyun Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
中国、後晋(こうしん)(936~946)の高祖石敬瑭(せきけいとう)が遼(りょう)に割譲した華北の16州をいう。河北省内にある幽(ゆう)(北京(ペキン))、薊(けい)(薊県)、瀛(えい)(河間県)、莫(ばく)(任邱(じんきゅう)県)、涿(たく)(涿県)、檀(だん)(密雲県)、順(順義県)、嬀(ぎ)(懐来県)、儒(延慶県)、新(涿鹿(たくろく)県)、武(張家口市)、蔚(うつ)(蔚県)と、山西省の雲(うん)(大同県)、応(おう)(山陰県)、朔(さく)(朔県)、寰(かん)(朔県東北馬邑付近)の16州である。燕雲とは宋(そう)の徽宗(きそう)時代からの呼称で、それまでは燕代、幽薊(ゆうけい)、幽燕などとよばれた。933年後唐(こうとう)(923~936)の明宗の養子李従珂(りじゅうか)が後唐を奪うと、明宗の女婿石敬瑭は太原で挙兵し、雁門関(がんもんかん)以北諸州を割譲することを条件に遼の太宗に援助を求めた。遼は936年、軍を送って後唐を滅ぼし、石敬瑭に後晋(こうしん)を建てさせたので、石敬瑭は遼に臣礼をとり、同年11月燕雲十六州を遼に譲った。遼は幽州を南京とし、雲州を西京とし、中国人士大夫を官吏に任用し、治安の維持に努めた。 中国では長城をもって華夷両世界を分かつ境界と考え、長城以南は中華の地としていたから、機会あるごとに失地を奪回しようとした。後周(こうしゅう)の世宗は959年、瀛州、莫州を奪回した。宋でも失地回復を国是とし、太宗は北伐軍をおこしたが効果はなかった。1115年、金が建国すると、宋の徽宗(きそう)は金の勢力を用いて失地を回復しようと金と交渉し、宋が燕京(北京)を攻略しかつ宋がこれまで遼に与えていた銀と帛(はく)を金に与えることを条件に、失地を譲り受けることとした。しかし金は自力で燕京を占領したので条件が変わり、1123年、宋は歳幣や銭米を金に与えるかわりに燕京と薊、景、檀、順、涿、易の6州を譲り受けた。しかし金は、宋が歳幣を送らず約に背いたとして、1125年華北に出兵して燕京を占領し、翌年宋都開封(かいほう)を占領したので、燕雲の諸州を含む華北平野は金の領土となった。 [河内良弘] ©Shogakukan"> 燕雲十六州 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
Recommend
Bonifatius (English spelling)
A Christian saint. Born to an aristocratic family...
The Last Judgement
The idea of the "Last Judgment," in w...
Ørsted, Hans Christian
Born: August 14, 1777, Rooskebing, Langeland Died ...
mashhad
...Architecturally, they have a similar structure...
Gill worm - Gill worm
An aquatic earthworm of the Oligochaeta class of ...
Zhou Zuoren - Shu Sakujin
A Chinese prose writer. He was known by many pen ...
Audubelle, JP - Audubelle
...The period from 1780 to 1830 was the golden ag...
Potentilla chinensis (English spelling) Potentilla chinensis
…[Naruhashi Naohiro]. . … *Some of the terminolog...
Arikbüge (English spelling)
?-1266 A man who competed with Kublai Khan for the...
Tokoutei
A Chinese Taoist priest of the Five Dynasties in ...
Fugger, A.
...He became one of the wealthiest men through lo...
Tomb of King Muryong (English: Muryǒng-wang-rǔng)
This ancient tomb is one of the Songsan-ri ancient...
The tale of the past - Kyoraishou
This is Kyorai's treatise on haiku. It was co...
Perugino - Perugino (English spelling)
Italian Renaissance painter. His real name was Pi...
ghaṣba (English spelling) ghasba
...In addition to this common style, Iranian clas...