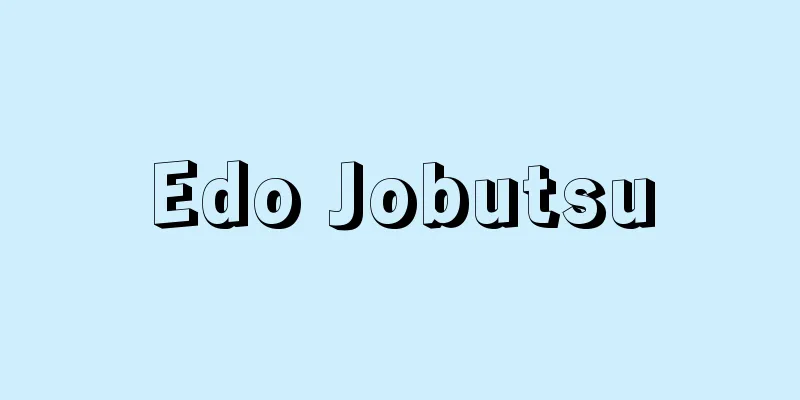
Egyptian alphabet - Ejiputomoji

|
The ancient Egyptian characters. There are three types: hieroglyphs, priestly characters, and common characters. The oldest is hieroglyphs, which show pictures of the human body, birds, animals, fish, and other natural objects. This character was created in the Predynastic period, but the writing system was not established until the beginning of the First Dynasty. The writing system combines phonetic characters (alphabet) and semantic characters, and the same character can sometimes be phonetic and sometimes semantic. Even though they are phonetic characters, some characters do not represent one sound, but two or three sounds. Also, the written phonetics do not have vowels, only consonants. Therefore, Egyptologists today pronounce them by adding e or o between consonants. There are about 700 hieroglyphs in total. The writing system is similar to the Japanese "Kanji-Kana mixed writing". This hieroglyphic writing was laborious and time-consuming, so a hieratic script was developed to write faster. This new script was a significant simplification of the pictures. While hieroglyphic writing was consistently used in temples, pyramids, tombs, and royal decrees, hieratic writing was mainly used for administrative documents, literary works, and letters. With the spread of papyrus paper, hieratic writing came into widespread use. Then, the Egyptians devised a way to write it even faster, creating demotic writing. This was in the 7th century BC. This script completely abandoned the pictographical remains of hieratic writing and wrote groups of letters together, and was mainly used for administrative documents. After Egypt became a Roman territory in 30 BC, Egyptian writing declined significantly, and finally disappeared when the temples were closed by decree of the Byzantine Emperor Justinian in the 5th century AD. The hieroglyphics were deciphered by the Frenchman Champollion in 1822, but the key to this was provided by an inscription on the Rosetta Stone written in hieroglyphics, demotic script, and Greek characters from the 2nd century BC. [Denroku Sakai] [References] | |Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
古代エジプトで使われた文字。聖刻文字、神官文字、民衆文字の3種がある。いちばん古いのが聖刻文字(ヒエログリフ)で、人体、鳥、獣、魚、その他自然界のものを絵として示した。この文字はすでに先王朝時代に生まれていたが、書記法が整ったのは第1王朝が始まってからである。その書記法は、音韻文字(アルファベット)と意味文字を組み合わせるということであり、同じ文字が場合によって音韻文字になり、また意味文字にもなった。音韻文字といっても1文字1音だけではなく、2音、3音を表すものがあった。また表記音韻には母音はなく、子音だけである。そこで今日のエジプト学者は、子音の間にeまたはoの音を補って発音している。聖刻文字の数は約700である。その書記法は日本の「漢字仮名交じり文」に近い。 この聖刻文字は筆記に手数がかかり、したがって多くの時間を要するので、早く書くための神官文字(ヒエラティック)が生まれた。この新しい文字は、絵を著しく簡略化したものである。聖刻文字が神殿、ピラミッド、墓、勅令などに一貫して用いられるのに対し、神官文字は行政上の文書、文学作品、書簡におもに用いられた。パピルス紙の普及とともに神官文字は多用された。ついでエジプト人は、それをさらに早く書くくふうをし、民衆文字(デモティック)をつくりだした。紀元前7世紀のことである。これは、神官文字の象形的な名残(なごり)をまったく捨てるとともに、文字のグループをまとめて記すという文字で、行政上の文書に主として用いられた。 前30年にエジプトがローマ領になってから、エジプト文字は著しく衰え、紀元後5世紀にビザンティン皇帝ユスティニアヌスの勅令によって神殿閉鎖が命ぜられたときをもって決定的に消えた。聖刻文字は1822年にフランスのシャンポリオンによって解読されたが、この鍵(かぎ)を与えたのは前2世紀の、聖刻文字、民衆文字、ギリシア文字で書かれたロゼッタ石の碑文である。 [酒井傳六] [参照項目] | |出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
<<: Egyptian Calendar - Ejiputoreki
Recommend
Theodore II
… [Toshi Okakura]. … *Some of the terminology tha...
Kyoto sweets - Kyogashi
Japanese sweets made in Kyoto. Both fresh and dri...
Drainage system
A general term that includes the main stream and ...
Japanese ground beetle
...A species endemic to Japan. Its head and thora...
depot fat
...Cholesterol is an important component of anima...
Laconia - Lakonia (English spelling)
A region in southern Greece, southeastern Pelopon...
Zermelo, Ernst Friedrich Ferdinand
Born: July 27, 1871, Berlin Died: May 21, 1953. Fr...
Chomel, N.
...Dutch interpreter and physician Narabayashi Ch...
Boioi
…It is a hilly highland located almost in the cen...
Kanbun Kosode - Kanbun Kosode
…Following the example of Koetsu, Korin also demo...
Tabula smaragdina (English spelling)
…The oldest alchemical document inscribed on an e...
Cour d'appel (English spelling)
… [In Europe and the US] A three-tiered court sys...
Politics as a profession - Politik als Beruf German
Written by M. Weber. Published in 1919. A passion...
Anglo-Boer War
…an imperialist war fought between the British an...
Taku Oe
Year of death: September 12, 1921 Year of birth: 2...