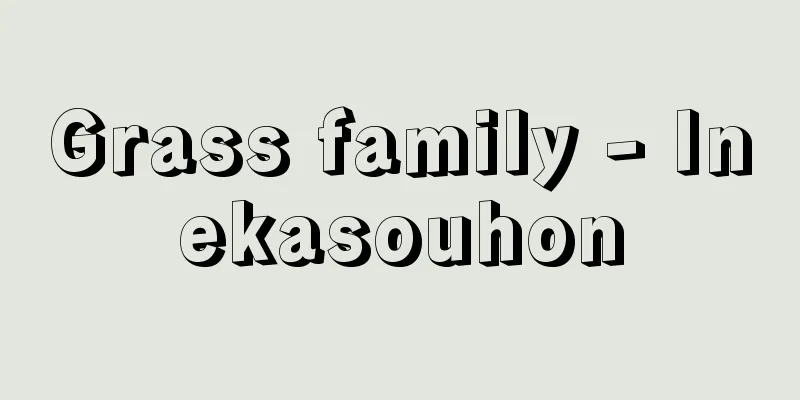Hop - Hop (English spelling)

|
A perennial vine of the Mulberry family (APG classification: Cannabaceae). The stems grow to over 10 meters, entwining with other plants, and the leaves are deeply lobed in 3 or 5 parts, with the blade and petiole each about 10 cm long. Both the stems and leaves are densely hairy. Dioecious, the flowers appear in the leaf axils in summer. The male flowers are pale green, small, and many are borne in panicles, with 5 petals and 5 stamens. The female flowers grow in oval, pine-cone-shaped spikes about 3 cm long, pale green, and hang down on long stalks. Each flower is surrounded by scaly bracts, and at the base of each bract there are many tiny yellow secretory organs called hop glands. Two small achenes form for each bract in autumn, but in cultivation, only female plants are planted, so they do not bear fruit. Native to Europe and Western Asia, hop cultivation spread in Europe as a flavoring agent with the development of beer. It was introduced to Japan in 1876 (Meiji 9) from the United States and Germany to Hokkaido. The hop glands of young, unfertilized ears secrete humulone and lupulone, which give beer its unique bitterness, and also have the effect of adding aroma and clarifying the beer. The ears are collected and dried over fire for storage. Currently, most of this dried hops are imported from Europe and other places, but they are also produced domestically under contract with beer companies in Hokkaido, Yamagata, Iwate, Nagano, and other prefectures. In addition, many wild yeast fungi grow on the female ears of hops, which are used for making yeast for bread, etc. Hop fields are created in cold mountainous areas, where iron poles and wires are set up to entangle the vines that sprout in the spring. In summer, the vines are cut and pulled down, and the ears are picked. The remaining stalks are fertilized to fertilize the roots and maintain an increased production volume the following year. [Hoshikawa Kiyochika December 13, 2019] [Reference] |The stems grow to over 10 meters and are entangled with other plants, and the flowers bloom in summer. The female flowers are pine cone-shaped and about 3 cm long, and are used in brewing beer . hop Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
クワ科(APG分類:アサ科)の多年生つる草。茎は他物に絡まって十数メートルに伸び、葉は深く3または5裂して葉身、葉柄ともに約10センチメートル。茎、葉ともに毛を密生する。雌雄異株で、花は夏に葉腋(ようえき)につく。雄花は淡緑色で、円錐(えんすい)花序に多くつき小さく、5弁で、雄しべは5本。雌花は長さ約3センチメートル、楕円(だえん)形の松かさ形の花穂となり、淡緑色で長い柄で垂れ下がる。各花は鱗(うろこ)状の包葉に包まれ、各包葉の基部に、多数の黄色で微小なホップ腺(せん)とよぶ分泌器官がある。包鱗(ほうりん)ごとに小さい2個の痩果(そうか)が秋に結実するが、栽培上は雌株のみを植えるので、結実することはない。 ヨーロッパ、西アジア地域原産で、ヨーロッパでビールの発達とともに、その付香料として栽培が広まった。日本へは1876年(明治9)にアメリカやドイツから北海道に導入された。若い未受精の雌穂のホップ腺からは、ビール特有の苦味成分となるフムロン、ルプロンなどが分泌され、それらはまたビールに香りをつけたり、ビールを清澄させる効果ももつ。雌穂を摘み集め、火力で乾燥して保存する。この乾燥ホップは現在大部分はヨーロッパその他から輸入されているが、国内でも北海道、山形、岩手、長野県などで、ビール会社との契約栽培で生産されている。 なおホップの雌穂には野生の酵母菌が多く繁殖するので、これをパン用酵母などに用いられる。 ホップ畑は寒冷な山間地などにつくられ、鉄柱や鉄線を設置して、春に芽生えたつるを絡ませ、夏につるごと切って引き下ろし、雌穂を摘み取る。残株には施肥し、根の肥培に努めて、翌年の生産量の増大維持を図る。 [星川清親 2019年12月13日] [参照項目] |茎は他物に絡まって十数mに伸び、花は夏に開花する。雌花は長さ約3cmの松かさ形で、ビールづくりに利用される©Shogakukan"> ホップ 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
Recommend
Teton Dakota (English spelling)
...Leather products were decorated with beads, wh...
Jumping Response - Jumping Response
...(3) Skin reflexes If a cat is supported in the...
Bran (fu) - Bran
It is a by-product of wheat flour production, cons...
Nanocnide japonica Bl.
A perennial plant of the Urticaceae family that gr...
Product differentiation
It is a marketing strategy that aims to give a co...
Kuttāb (English spelling)
An Arabic word meaning "school." It gene...
Face Index - Ganshisuu
A percentage value that indicates the ratio of the...
normative standard of living
…they correspond to standard of living and level ...
Odate Jōkō Diary - Odate Jōkō Diary
The diary of Odate Hisauji (Buddhist name Tsuneok...
Tournai (English spelling)
A city in the province of Hainau in southwest Belg...
Glubb Pasha
1897‐1981 John Bagot Glubb was a British soldier w...
Campbell Plateau
...A wide plateau that appears on the edge of a c...
Jubulaceae
…General term for liverworts of the family Jubula...
Ergosterol
…Cholesterol is almost nonexistent in plants, and...
Clay tablet document - Nendobanmonjo (English spelling) clay tablet
A general term for clay tablets, which were used a...
![Tagami [town] - Tagami](/upload/images/67cc1e26f095a.webp)