Bandage - Houtai
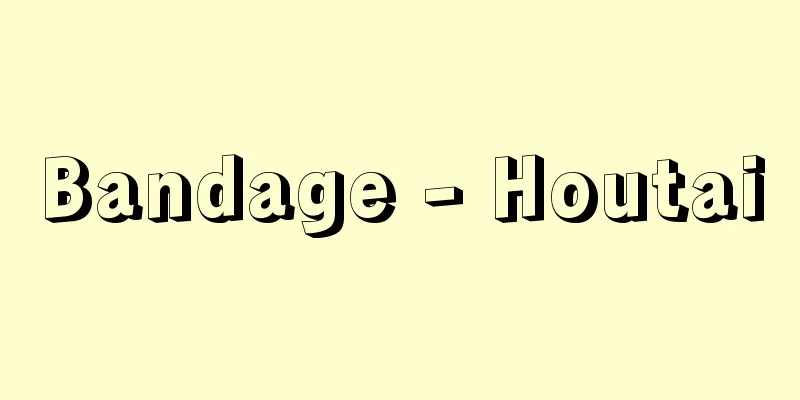
|
This refers to the mechanical operation of applying bandage materials to the body for a relatively long period of time to treat or treat wounds, fractures, or illnesses. Bandage materials refer to all items used in bandaging, and the techniques used are called bandaging methods. Therefore, the purposes are also diverse, as described below. That is, (1) covering and protecting wounds and superficial diseases, (2) preventing the slippage of drugs and equipment applied locally, (3) rest and protection, (4) maintaining the reduction of fractures and dislocations, (5) preventing dehiscence of surgical wounds, (6) keeping lesions in their normal position, (7) preventing pressure from being applied to pathological protrusions, (8) stopping bleeding, (9) treating morphological abnormalities, (10) filling in missing parts of the body, (11) emergency treatment for injuries and illnesses, and (12) applying heat, cold, or moisture to the body. Depending on their purpose, bandages may also be classified as covering bandages, support bandages, immobilization bandages, pressure bandages, traction bandages, corrective bandages, compensation bandages, and emergency bandages. Furthermore, depending on the material used, bandages can be classified as roll bandages, cloth bandages (triangular cloth, square cloth, T-shaped bandage, etc.), replica bandages, bandage plaster bandages, splint bandages, and plaster bandages. In medical terms, the term bandage in the narrow sense refers to covering bandages, while the term bandage in general often refers to roll bandages. Only gauze is regulated by the Japanese Pharmacopoeia as a bandage fabric, while the others are not. Generally, gauze and bleached cotton are widely used. A bandage measuring 30 centimeters wide and 10 meters long is called a tan, and half a tan is torn into 1 to 8 equal-spaced pieces to make bandages. Bandages torn into two pieces are called bilobal bandages, and those torn into three pieces are called trilobal bandages. Four-, five-, or six-lobed bandages are commonly used, and these bandages are made by rolling one end of the fabric into a cylindrical shape. [Yamane Nobuko] BandagingUsing the example of a roll bandage, we will touch upon the basics of bandaging. The basic techniques for roll bandages include circular bands, spiral bands, serpentine bands, folded bands, tortoiseshell (gathering/separating) bands, ear of wheat (ascending/descending) bands, three-section bands, and repeated (cap-shaped) bands, and by combining these appropriately, it is possible to bandage various parts of the body. The principles and precautions for bandaging are as follows. (1) Stand in front of the patient and wrap the bandage from left to right, rolling it over the skin with even pressure, without letting it come off. (2) The general rule is to wrap from the periphery to the center. (3) If it is too loose, it will not serve its purpose, and if it is too tight, it will cause blood circulation problems. (4) In order to detect circulatory disorders early and prevent blood congestion, it is necessary to observe changes in the skin of the extremities. For this reason, the fingertips and other parts of the body should be exposed and wrapped. (5) In order to avoid causing pain from the bandage, wrap only the minimum amount of area necessary, support the necessary areas, and wrap quickly. (6) The wrapping should be in the natural anatomical position of the human body, and the two surfaces of the skin should never be touched together. (7) When attaching the bandage, avoid areas near wounds or pressure points. (8) When removing a bandage, be sure to protect the wound to avoid causing pain to the patient. There are also elastic bandages made of elastic synthetic fibers woven into the fabric, which come in strips and bags (nets), and the bags come in several sizes and are cut to the appropriate length for the purpose and then used. There are also plastic bandages, which are sprayed directly onto the wound and then covered with a disinfectant, transparent plastic film. [Yamane Nobuko] "How to Wrap a Bandage" by Fumio Fujiwara (1980, Nanzando) ©Shogakukan "> Basic techniques for roll bandaging Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
創傷や骨折、病気の治療・処置のため、比較的長時間にわたって包帯材料を身体に装着する器械的操作をいう。包帯材料とは包帯に使用される物品のすべてをいい、その手技を包帯法とよぶ。したがって、その目的も、次に述べるように多岐にわたっている。すなわち、(1)創傷や表在性疾患の被覆保護、(2)局所に貼布(ちょうふ)する薬剤・器材の滑脱防止、(3)安静保護、(4)骨折・脱臼(だっきゅう)の整復維持、(5)手術創の離開防止、(6)病変部の正常位整復保持、(7)病的突出部の防圧、(8)止血、(9)形態異常の治療、(10)身体一部の欠損補填(ほてん)、(11)損傷・疾病の救急処置、(12)温熱・寒冷・湿気を身体に適用する場合などである。また、これらの目的に応じて、包帯を被覆包帯、支持包帯、固定包帯、圧迫包帯、牽引(けんいん)包帯、矯正(きょうせい)包帯、代償包帯、救急包帯の呼称で区別することもある。さらに包帯材料によって、包帯は巻軸(けんじく)包帯、布帕(ふばつ)包帯(三角布(巾(きん))、四角布、丁字帯など)、複製包帯、絆創膏(ばんそうこう)包帯、副子(ふくし)包帯、ギプス包帯に分類される。なお、医療のうえで、狭義に包帯という場合は被覆包帯をさし、一般に包帯という場合は巻軸包帯をさす場合が多い。 包帯の生地は、ガーゼのみが日本薬局方で規定されているが、ほかは規定外となっている。一般的には、ガーゼと晒(さらし)木綿が多く使用されている。幅30センチメートル、長さ10メートルのものを一反といい、半反のものを等間隔に1~8つに裂いて包帯とする。二つに裂いたものを二裂包帯、三つに裂いたものを三裂包帯とよんでいる。普通には四、五、六裂包帯がよく使用されており、これらの生地を一方の端から巻いて円柱状にしたものが巻軸包帯である。 [山根信子] 包帯法巻軸包帯を例に、包帯法の基本について触れる。巻軸包帯の基本手技には、環行帯、螺旋(らせん)帯、蛇行帯、折転帯、亀甲(きっこう)(集合・離開)帯、麦穂(ばくすい)(上行・下行)帯、三節帯、反復(帽状)帯があり、これらを適当に組み合わせることによって身体各部の包帯が可能となる。巻き方の原則と注意については次に述べるとおりである。 (1)患者の前に立ち、包帯を左から右へ向けて、皮膚から離さないように、転がすようにして平均した圧迫で巻いていく。 (2)末梢(まっしょう)から中枢に向けて巻くのを原則とする。 (3)緩ければ目的を果たさないし、きつすぎれば血液の循環障害をおこす。 (4)血行障害を早く発見して、うっ血を予防するためには、末梢部の皮膚の変化を観察しなければならない。このため指先などは出して巻く。 (5)包帯による苦痛を与えないために、巻く部位は必要最低限の範囲とし、必要な箇所を支えて迅速に巻く。 (6)人体の自然の解剖的位置を維持して巻き、皮膚の2面は、けっしてつけて巻かない。 (7)包帯を止める位置は、創傷の部位や圧迫部位を避ける。 (8)包帯を解くときは、苦痛を与えないように創傷面を保護して解く。 また、伸縮性のある合成繊維を生地に織り込んだ伸縮(弾性)包帯もあり、これには、帯状と袋状(ネット状)があり、袋状のものは大きさが何種類かに分かれ、用途に応じた長さに切ってかぶせて使うようになっている。このほか、プラスチック包帯といって、創面に直接スプレーをし、殺菌性の透明なプラスチック膜で覆うようなものもある。 [山根信子] 『藤原文夫著『包帯の巻き方』(1980・南江堂)』 ©Shogakukan"> 巻軸包帯の基本手技 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
Recommend
bur marigold (English spelling) burmarigold
...The bracts are arranged in two rows, one insid...
Blue Whale Unit (English)
... In the 1970s, anti-whaling movements grew wor...
Shinwa [town] - Shinwa
A former town in Amakusa County, eastern Amakusa S...
Angelus - Otsuge no Inori
Angelus is also called Angelus. It is a Roman Cath...
sputtering
...(3) Vapor deposition: In a high vacuum, the me...
Fundamental Theology - Theologia Fundamentalis
It is a branch of Catholic theology that actively ...
Maritime Disaster Prevention Center
A general incorporated foundation established in ...
Mannoike Pond
This reservoir is located in Mannou Town, Nakatad...
Üsküdar (English spelling)
It is one of the five districts of Greater Istanbu...
Kafir Wars
...Furthermore, in 1834, the separation of the le...
Galtieri, LF (English spelling) GaltieriLF
...However, inflation and other economic problems...
Hypogastrula
…They become adults after molting about 5 to 7 ti...
Karagasy
…Turkic-speaking herders who live in the area of ...
Hosho - Hosho
A document issued by a vassal to convey the will ...
Kaufmann, A.
…After the war, G. Radbruch of the Neo-Kantian sc...