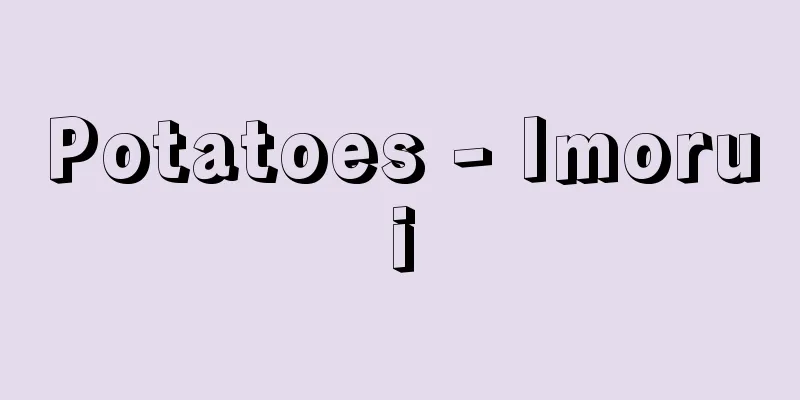Pork - Butaniku

|
A type of meat. It is also widely used as a raw material for processing into ham, sausages, etc. Its fat is used as lard. [Tomomi Kono] historyWild boars, the ancestors of pigs, were widely distributed in Asia and Europe. Therefore, the practice of eating wild boars and capturing and raising them simultaneously began in China, Egypt, Greece, and other countries from early times. In China, pigs were already being raised around 2200 BC, and pork, along with mutton, became an important meat. Wall paintings also show that pig farming was practiced in ancient Egypt during the primitive agricultural period (after 5000 BC). In ancient Greece (around 2000 BC), eating pork became widespread, and processed meat products such as ham and sausages were also made. On the other hand, pork is considered taboo in Islam, Judaism, and Hinduism, and pork is thoroughly avoided. In countries where pork is eaten a lot, such as China, there are restaurants that specialize in Muslims, and they mainly use mutton and beef. In Japan, wild boar bones have been excavated from shell mounds from the Jomon and Yayoi periods, including some with arrowheads still stuck in them. Bronze bells depict hunting wild boars with dogs and bows and arrows. In this period, wild boar meat, along with deer meat, was the most commonly eaten animal meat. The Kojiki contains a legend about the Yamashiro Ikai who stole the Emperor's meals, suggesting that the Ikaibe people raised wild boars and served them to the Emperor. There are various theories as to whether the "wild boars" raised at this time were domestic boars, i.e. pigs, or wild boars, i.e. wild boars, but it is likely that wild boars were not domesticated, and therefore pigs were not raised. Under Chinese influence, pork was eaten in the Okinawa region from an early stage (records show that Okinawan cuisine using pork existed in the mid-Muromachi period). During the Edo period, pig farming was introduced to Kagoshima from Okinawa, and pork was also eaten in Kagoshima. Pig farming was also introduced to Nagasaki from China, and pig farming and the eating of pork became quite commonplace for foreigners residing in Nagasaki. In the Meiji period, meat consumption was encouraged, but beef was more prevalent than pork, and it was not until the middle of the Meiji period that pork became widespread nationwide. [Tomomi Kono] Characteristics and parts of porkPork is light pink in color, has a soft texture, and has fat layers. It is generally thought to be fattier than beef or chicken, but in recent years, due to changing tastes, pork varieties have been bred to be leaner, and if you choose parts such as the fillet or thigh, it will actually be less fat than other meats. Pork fat has a low melting point, so it feels smooth in the mouth. Good pork has a white layer of fat that is mochi-like. The parts are usually classified as shoulder, shoulder loin, loin, belly (also called sanmainiku), fillet, thigh, and outer thigh. The fillet is the most tender part and has the least fat. The belly has the most fat and is the part that is processed into bacon. In places where pork is used a lot, such as China and Okinawa, all parts of the pork are used in addition to the above. The ribs (also called spare ribs), feet, head, skin, ears, nose, internal organs, and blood are used in various unique dishes. [Tomomi Kono] nutritionIt is a good source of fat and protein, and contains more vitamin B1 than beef or chicken. The lean parts of the meat, such as the fillet and thighs, contain a lot of vitamin B1 , about 10 times as much as beef or chicken. The fat is characterized by having more linoleic acid than beef. [Tomomi Kono] cookingDue to the risk of parasitic worms such as the solium tapeworm, pork should be thoroughly cooked and not eaten raw. Common dishes include pork cutlets, steaks, roast pork, butter-fried pork, ginger-fried pork, yakiniku, sweet and sour pork, pork soup, stir-fried pork, and stewed pork. Yakiniku (roasted pork) is roasted pork loin or thigh meat seasoned with soy sauce, sake, and spices. There are many pork dishes in Okinawa, but the most representative are rafu-tee (Okinawan-style braised pork cubes), soki-bone soup made with kelp and rib bones, and ashi-tebichi (foot and kelp stewed in a light sauce). Pork is also salted to preserve it and used in cooking. There are pork dishes in each country, such as Eisbein (salted thigh meat) in Germany and pork and beans in America. [Tomomi Kono] "Supervised by Katsuji Hatada, compiled and edited by the Meat Communication Publishing Department, 'Dividing and Cutting Pork Carcasses: Until Pork is Commercialized' (2002, Meat Communication)" ▽ "Mastering Pork: Betting on Producing Delicious Pork" by Teizo Ishikawa (2004, Graph Publishing) 1. Shoulder: The area centered around the arm 2. Shoulder loin: The area between the shoulder and the loin 3. Loin: The center part of the back. The area following the shoulder loin 4. Fillet: The finest part of the inside of the loin. Also called tenderloin 5. Belly: The belly part below the loin. It has alternating layers of lean meat and fat, and is also called sanmainiku 6. Thigh: The area near the base of the leg 7. Outer thigh: The area near the buttocks © Takashi Aoki "> Pork cuts 1. Liver: Liver 2. Heart: Heart 3. Mame: Kidney 4. Gatsu: Stomach 5. Himo: Small intestine 6. Daicho: Large intestine 7. Tan: Tongue 8. Tonsoku: Leg 9. Kopukuro: Uterus In addition, tontoro (the part of the arm meat close to the neck), net fat (net-like fat between the intestines), and mimi (ear) are also edible. © Takashi Aoki "> Pig by-product parts Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
食用肉の一種。ハム、ソーセージなどの加工原料としての用途も大きい。脂肪はラードとして利用される。 [河野友美] 歴史ブタの先祖である野生のイノシシは、アジア、ヨーロッパに広く分布していた。そのため、イノシシを食用にすること、また、イノシシを捕らえて飼育することは早くから中国やエジプト、ギリシアなどで同時発生的に行われている。中国では紀元前2200年ごろにはすでにブタが飼育され、豚肉は羊肉とともに重要な食肉となっている。また、古代エジプトの原始農耕時代(前5000以降)に養豚が行われていたことが壁画にうかがえる。古代ギリシア(前2000ころ)では豚肉を食べることが一般的に広がり、ハムやソーセージのような肉加工品もつくられている。一方、イスラム教やユダヤ教、ヒンドゥー教では豚肉をタブー視し、徹底して豚肉を避けている。中国のように豚肉を多く食べる国では、イスラム教徒専門の飲食店が存在し、主として羊肉や牛肉を用いている。 日本では、縄文・弥生(やよい)時代の貝塚からイノシシの骨が出土しており、なかには鏃(やじり)の刺さったままの骨片もあった。銅鐸(どうたく)には、イヌを使い、弓矢でイノシシを狩る図も描かれている。この時代、イノシシの肉はシカの肉とともにもっとも多く食用とされていた獣肉である。『古事記』には、天皇の食事を奪った山代(やましろ)の猪甘(いかい)の伝承があり、猪甘(猪飼)部の部民がイノシシを飼養しながら天皇の食事にも奉仕していたことを思わせる。このとき飼養された「猪(いのしし)」が、家猪(かちょ)すなわちブタ(豚)であったか、野猪すなわちイノシシであったのか諸説あるが、おそらくはイノシシは家畜化に至らず、したがってブタの飼養も行われなかったと思われる。中国の影響を受けて、沖縄地方で早くから豚肉が食用とされていた(室町中期には豚肉を用いた沖縄料理のあったことが記録にある)。江戸時代には、沖縄から養豚が鹿児島に伝わり、鹿児島でも豚肉を食用とすることになった。また、とくに長崎では中国から養豚が伝わり、長崎に在留する外国人のためにも養豚と豚肉を食べることがかなり一般化していた。明治になって肉食が奨励されたが、豚肉よりも牛肉が中心で、豚肉が全国的に普及したのは明治中ごろからである。 [河野友美] 豚肉の特徴と部位豚肉は淡紅色で肉質が柔らかく、脂肪が肉と層状になっている。牛肉や鶏(とり)肉に比べ一般に脂肪が多いと思われているが、近年は嗜好(しこう)の変化から脂肪の少ない品種に改良され、ヒレ、もも肉など部位を選べば、むしろ他の肉より脂肪は少ない。豚肉の脂肪は融点が低いので、口中で滑らかな感触がある。脂肪層が白くて餅(もち)状のものがよい豚肉である。部位は通常、かた肉、かたロース、ロース、ばら肉(三枚肉ともいう)、ヒレ、もも、そとももに区分される。ヒレはもっとも柔らかい部分で、脂肪も少ない。ばら肉は脂肪がもっとも多く、ベーコンに加工される部分である。中国、沖縄など豚肉の利用の多い所では、以上の肉のほかにあらゆる部分が利用される。あばら骨(スペアリブともいう)、足、頭、皮、耳、鼻、内臓、血液などいろいろに特有な料理にされる。 [河野友美] 栄養脂肪、タンパク質のよい給源で、ビタミンでは牛肉や鶏肉に比べB1が多い。とくにヒレ、もも肉など脂肪の少ない部位にビタミンB1が多く、牛肉や鶏肉の約10倍含まれる。脂肪は牛肉に比べ、リノール酸が多いのが特徴。 [河野友美] 調理有鉤条虫(ゆうこうじょうちゅう)などの寄生虫の心配があるので生食を避け、よく火を通す必要がある。料理にはカツレツ(とんかつ)、ステーキ、ローストポーク、バター焼き、しょうが焼き、焼き肉、酢豚、豚汁、炒(いた)め物、煮込みなどが一般的。焼き豚(または焼き肉)は、しょうゆ、酒、スパイスで調味したロースまたはもも肉をあぶり焼きしたもの。沖縄料理には数多くの豚肉料理があるが、代表的なものは、らふてー(沖縄風ブタの角煮)、コンブとあばら骨を煮込んだそーき骨の汁物、足てびち(足とコンブを薄味に煮込んだもの)などがある。また、保存のため塩漬け豚肉をつくり、これを料理に用いる。ドイツ料理のアイスバイン(もも肉の塩漬け)、アメリカ料理のポークビーンズなど各国に豚肉料理がある。 [河野友美] 『畑田勝司監修、食肉通信社出版局構成・編『豚枝肉の分割とカッティング 豚肉を商品化するまで』(2002・食肉通信社)』▽『石川楨三著『豚肉を極める――おいしい豚肉づくりに賭ける』(2004・グラフ社)』 1 かた:腕を中心とした部分2 かたロース:かたとロースの間の部位3 ロース:背中の中央部分。かたロースから続く部位4 ヒレ:ロースの内側のもっともきめが細かい部位。テンダーロインともいう5 ばら:ロース下の腹部分。赤身と脂肪が交互に層をなしており、三枚肉ともいう6 もも:脚の付け根に近い部位7 そともも:ももの尻に近い部位©青木 隆"> 豚肉の部位 1 レバー:肝臓2 ハツ:心臓3 マメ:腎臓4 ガツ:胃5 ヒモ:小腸6 ダイチョウ:大腸7 タン:舌8 トンソク:足9 コプクロ:子宮ほかに、トントロ(腕肉の頸に近い部位)、網脂(腸の間にある網状の脂)、ミミ(耳)を食用とする©青木 隆"> ブタの副生物の部位 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
>>: Butana (English name) Hypochoeris radicata L.
Recommend
Chivalry - Today
… [China] In ancient China, among the vagabond cl...
Brown tussock moth (Euproctis pseudoconspersa)
An insect of the Lepidoptera family, Lymantriidae ...
Cell engineering
A field of study that studies and develops techniq...
Chuo Koronsha - Chuo Koronsha
A general publisher centered on the magazine Chuok...
Fat - shibou (English spelling) fat
A general term for ester compounds (glycerides) o...
Incirrata
...In addition to this, experiments have been con...
Kosrae Island
Kosrae is also called Kusaie. It is a volcanic isl...
Makkari
〘Noun〙 (maggərri)⸨Makgeolli⸩ A cloudy alcoholic dr...
Holt, T.
…The seminary (1483), along with Oxford Cathedral...
Landscaping
…Official name: Swiss Confederation Schweizerisch...
Lake Tahoe (English spelling)
A lake on the border between California and Nevada...
Robinson, R.
…Similarly to Woodward, he worked on the total sy...
Palmitic acid - Parumichinsan (English spelling) palmitic acid
It is a straight-chain, higher saturated fatty ac...
Idola (English spelling)
Idol. (1) An image made to represent a god and to ...
Cheleutoptera
...They live on food trees. The order Cheleutopte...