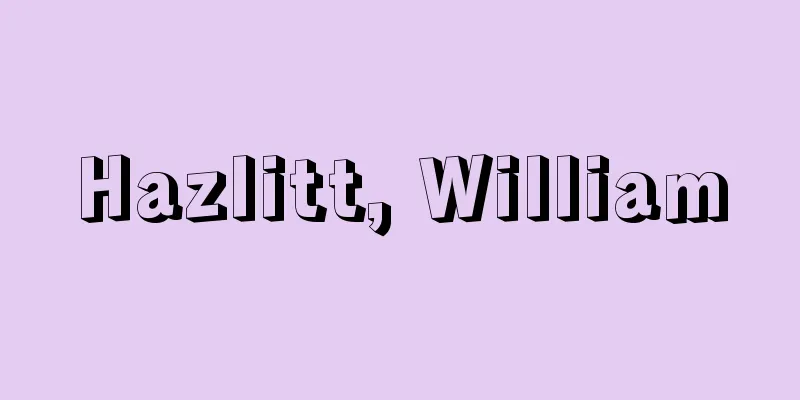Antennae

|
The first appendage on the head of many arthropods, it is the organ of touch and smell. Chilopoda (centipedes, house centipedes), Diplopoda (millipedes), Oligopoda (scorpions), Sympetrum (combined worms), and insects have one pair of antennae and are called horned worms. In contrast, Xiphopoda (horseshoe crabs) and Arachnids (spiders, scorpions, ticks) do not have antennae and are called anantenata. On the other hand, Crustaceans (crabs, shrimps) have two pairs of antennae: the small antennae (first antennae) and the large antennae (second antennae). Insect antennae basically consist of a stalk (first segment), a pedicel (second segment), and a flagellum (third segment and beyond), but the shape varies depending on the species. These include whip-shaped (grasshoppers and dragonflies), thread-shaped (stink bugs), bead-shaped (termites), saw-toothed (fallen spider webworms), rod-shaped (butterflies), and comb-shaped (mountain saturday moths). There are also many species with different shapes between males and females. Antennae have numerous sensory hairs and pores, and some insects have the Johnston organ, a mechanoreceptor, in their rachis segments. Furthermore, some crustaceans have antennal glands, which are excretory organs, at the base of the large antennae, and slime tube insects (collembolans) have post-antennal organs at the base of the antennae that are thought to be humidity receptors. In invertebrates other than arthropods, antennae are a pair of projections that protrude from the front end of the body in gastropod mollusks and turbotidae flatworms. Some gastropods have two pairs of antennae, and the second pair has eyes at the tip (snails) or base (Lymnaea). [Takeo Machida] ©Toshio Sekiguchi "> Insect Organs (Antennae) Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
多くの節足動物の頭部第1付属肢をいい、触覚および嗅覚(きゅうかく)器官である。唇脚類(ムカデ、ゲジ)、倍脚類(ヤスデ)、少脚類(ヤスデモドキ)、結合類(コムカデ)および昆虫類は1対の触角をもち、有角類とよばれる。これに対し、剣尾類(カブトガニ)、クモ形類(クモ、サソリ、ダニ)には触角がないので無角類とよばれる。一方、甲殻類(カニ、エビ)には小触角(第1触角)および大触角(第2触角)の2対の触角がある。昆虫類の触角は、基本的には柄節(へいせつ)(第1節)、梗節(こうせつ)(第2節)および鞭節(べんせつ)(第3節以降)からなるが、種によってさまざまの形に変化している。すなわち、鞭(むち)状(バッタ、トンボ)、糸状(カメムシ)、数珠(じゅず)状(シロアリ)、鋸歯(きょし)状(ハラアカヒトリ)、球桿(きゅうかん)状(チョウ)、櫛(くし)状(ヤママユガ)などがある。また、雌雄で形の異なるものも少なくない。触角には多数の感覚毛、感覚孔などがあり、また、昆虫には梗節に機械受容器のジョンストン器官をもつものがある。さらに、甲殻類では大触角基部に排出器官の触角腺(せん)をもつものがあり、また、粘管類昆虫(トビムシ)には触角基部に湿度の受容器と思われる触角後器官がある。 なお、節足動物以外の無脊椎(むせきつい)動物では、軟体動物の腹足類や扁形(へんけい)動物の渦虫類などの体の前端に突出した1対の突起を触角という。腹足類には触角が2対あるものもあり、第2対の先端(カタツムリ)や基部(モノアラガイ)に目がある。 [町田武生] ©関口俊雄"> 昆虫の器官(触角) 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
>>: Position classification plan
Recommend
Brain hormone - Brain hormone
In insects, this hormone stimulates the prothoraci...
Bongo, AB (English spelling) BongoAB
During this time, Gabon's abundant mineral re...
Kinokawa Plain
Please see the "Wakayama Plain" page. S...
Alnus pendula (English spelling) Alnuspendula
… [Okamoto Motoji]. … *Some of the terminology th...
Hierarchical structure (botany) - Plant biology
…In forests, the distribution of leaves in a comm...
《Des réactions politiques》 (English notation) Desreactions politiques
…This ideological revolution, which was carried o...
Izu Senryo (Izu Senryo) - Izu Senryo (English spelling) Maesa japonica
An evergreen shrub of the Ardisiaceae family. It g...
Men's Assembly Hall - danshi shuukaijo
A communal house for men of an age group or a men...
Gakusando Inpu - Gakusando Inpu
…The Qing Dynasty had Wu Guanjun’s 10 volumes of ...
Jinbaori - Jinbaori
This garment was worn by military commanders over...
Levitan, II (English spelling)
...As a result of being liberated from academic c...
Kingdom of East Anglia
…the name of a historical region in the eastern p...
Ain Jalut - Ain Jalut
…He continued his conquests and went to Syria, wh...
flight shooting
…[Ban Shimizuo] [Takayanagi Noriaki]. … *Some exp...
Sakigahana Ruins - Sakigahana Ruins
A Jomon archaeological site in a sea cave in Komak...