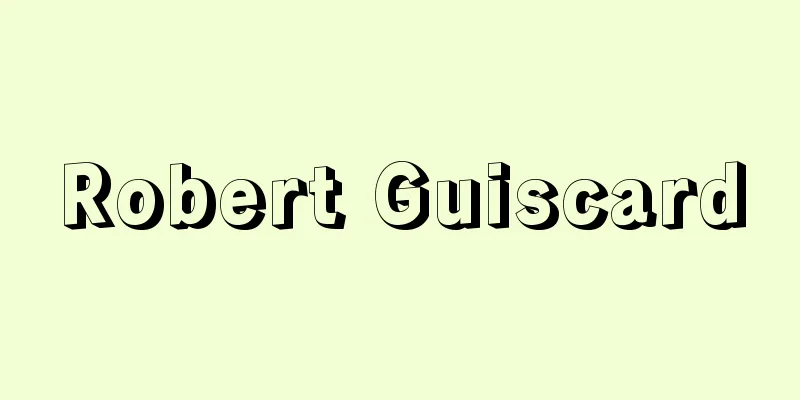Fire extinguisher - introduction

|
A portable device that uses the cooling, smothering or suppression effects of an extinguishing agent to extinguish a fire in the very early stages of the fire. There are various types of extinguishers depending on the agent or mechanism used, and the extinguisher must be selected according to the object to be extinguished. The following types of fire extinguishers are currently in use: White, yellow and blue circular signs are used to indicate the compatibility of the extinguisher with the type of flammable material that is the source of the fire. [Kishiyama Koichi] Water Fire ExtinguisherWater extinguishers come in three types: manual pump type, gas pressurized type, and pressure storage type, and are suitable for ordinary fires involving wood, textiles, paper, etc., but are not suitable for oil, electrical, or chemical fires. For manual pump type extinguishers, the handle on the top is raised and lowered about 10 times to increase the internal pressure, and then the nozzle is opened to spray water on the fire surface. The circular sign is white. [Kishiyama Koichi] Acid-alkali fire extinguisherAcid-alkali extinguishers release extinguishing agents by the pressure of carbon dioxide produced by the combination of sulfuric acid and sodium bicarbonate. The carbon dioxide released at the same time as the cooling effect of the water also has a suffocating effect. Although it is designed for use on ordinary fires, it can also be used for electrical fires by switching the nozzle and discharging the mist. The circular sign is white and blue. [Kishiyama Koichi] Reinforced Liquid Fire ExtinguisherReinforced liquid fire extinguishers use a concentrated aqueous solution of potassium carbonate as the extinguishing agent, and are available in pressurized and pressurized (reactive and gas pressurized) types. Of these, reactive types involve crushing a glass bottle containing concentrated sulfuric acid, causing a chemical reaction between the sulfuric acid and the reinforced liquid, and releasing the reinforced liquid using the pressure of the carbon dioxide that is produced. These are suitable for use on ordinary fires, but if you switch the nozzle and spray the liquid in a mist, they can also be used on oil and electrical fires. The circular sign is blue, yellow, and white. [Kishiyama Koichi] Foam fire extinguisherFoam extinguishers generate foam by combining two types of chemicals, cutting off the air supply. They can be used for ordinary fires, but are particularly suitable for gasoline and other flammable oil and chemical fires. They are not suitable for electrical fires. The circular sign is white and yellow. [Kishiyama Koichi] Carbon Dioxide Fire ExtinguisherCarbon dioxide fire extinguishers compress carbon dioxide under high pressure to liquefy it, then spray it in gas form from the nozzle. 1 kilogram of liquefied carbon dioxide normally expands to 534 liters of gas at 15°C, expelling the air from the fire and suffocating it to extinguish it. It is highly effective at extinguishing fires indoors, but care must be taken to prevent the user from suffocating. An advantage is that it does not get wet or dirty after being put out. It is suitable for oil and electrical fires. The circular sign is yellow and blue. [Kishiyama Koichi] Halide Fire ExtinguisherHalide extinguishers use three types of extinguishing agents: Halon 1011, Halon 2402, and Halon 1301. The agent discharged has suffocating and suppressing properties, and is suitable for oil and electrical fires. The circular sign is yellow and blue. [Kishiyama Koichi] Powder fire extinguisherPowder fire extinguishers are broadly classified into four types based on the components of the extinguishing agent. (1) Powder (ABC) Fire Extinguisher: This extinguisher is made of ammonium phosphate as its main ingredient, and is made by treating the dried fine powder with silicone resin and other materials to make it moisture-proof. It is colored pale red. The agent sprayed out covers the burning surface and extinguishes the fire by suffocating and suppressing it. It is suitable for ordinary fires (A), oil fires (B), and electrical fires (C). The circular sign is white, yellow, and blue. (2) Powder (Na) Fire Extinguisher: A fine powder whose main component is sodium bicarbonate, which extinguishes fires by suffocating and suppressing them. It has the same moisture-proofing treatment as the powder (ABC). It is not suitable for ordinary fires, but is suitable for oil and electrical fires. The circular sign is yellow and blue. (3) Powder (K) Fire Extinguisher This is a fine powder whose main component is potassium carbonate, and its moisture-proofing treatment is the same as (1) and (2). Its fire-extinguishing action and applications are the same as (2). (4) Powder (KU) Fire Extinguisher: It is called KU because its main ingredient is a reaction product of potassium bicarbonate and urea. It is suitable for oil and electrical fires, and the powder is gray in color. The circular mark is yellow and blue. [Kishiyama Koichi] General precautions regarding fire extinguishersThe best place to install an extinguisher is in a place that is easy to see, does not get in the way of people passing by, has little vibration, and is not too humid or hot. Also, because fire extinguishers cannot be used forever, they should be inspected about once every six months to replenish any pressure that is lacking, replace the chemicals, and check for any damage to the hose. Furthermore, fire extinguishers that pass the standards of the Fire and Disaster Management Agency of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (formerly the Ministry of Home Affairs) are required to bear a certification mark from the Japan Fire Equipment Inspection Association, so it is necessary to have extinguishers bearing these marks. [Kishiyama Koichi] [Reference] |©Shogakukan "> Structure of a powder fire extinguisher Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
火災におけるごく初期の段階において、消火剤のもつ冷却、窒息または抑制などの効果を利用して消火する持ち運びのできる器具のこと。使用する薬剤、あるいはその機構によって種類はいろいろあり、消火の対象物に応じて、消火器を選ばなければならない。現在使用されている消火器の種類には次のようなものがある。消火器と火源となっている可燃物の種類との適合性を表すものとして、白・黄・青の円形標識が用いられている。 [岸谷孝一] 水消火器水消化器は、水を放出する方式として手動ポンプ式、ガス加圧式、蓄圧式があり、木材、繊維、紙類などの普通火災に適しているが、油、電気、化学薬品火災には不適当である。なお、手動ポンプ式の消火器は、上部のハンドルを10回近く上下させ、内圧を上昇させてからノズルを開いて火面に放射させる。円形標識は白。 [岸谷孝一] 酸アルカリ消火器酸アルカリ消火器は、硫酸と炭酸水素ナトリウムの化合で発生する二酸化炭素の圧力によって消火薬剤を放出するもので、水の冷却効果と同時に出る二酸化炭素によって窒息効果もある。普通火災用であるが、筒先を切り替えて霧状に放射すれば電気火災にも使える。円形標識は白・青。 [岸谷孝一] 強化液消火器強化液消火器は、炭酸カリウムの濃厚な水溶液を消火剤として用いるもので、蓄圧式と加圧式(反応式、ガス加圧式)がある。このうち反応式は、濃硫酸の入ったガラス瓶を砕いて硫酸と強化液とを化学反応させ、発生する二酸化炭素の圧力によって強化液を放出させる。適応は普通火災用であるが、筒先を切り替えて霧状に放射すれば、油・電気火災にも使える。円形標識は青・黄・白。 [岸谷孝一] 泡消火器泡消火器は、2種の薬剤の化合によって泡を発生させ、空気の供給を遮断する。普通火災にも使えるが、とくにガソリンなどの燃えやすい油、化学薬品火災に適当である。電気火災には不適当。円形標識は白・黄。 [岸谷孝一] 二酸化炭素消火器二酸化炭素消火器は、二酸化炭素を高圧で圧縮して液化させ、放射口からガス状で放射させる。1キログラムの液化二酸化炭素は、普通15℃で534リットルのガス体に膨張するので、火災部の空気を追い出して、窒息消火させる。室内での消火効果は大きいが、使用者が窒息しないように注意する必要がある。消火後の水ぬれや汚損がまったくないのが長所。油・電気火災に適当である。円形標識は黄・青。 [岸谷孝一] ハロゲン化物消火器ハロゲン化物消火器は、使用される消火薬剤は、ハロン1011、ハロン2402、ハロン1301の3種類である。放射された薬剤は窒息および抑制作用を有し、油・電気火災に適している。円形標識は黄・青。 [岸谷孝一] 粉末消火器粉末消火器は、消火薬剤の成分により次の4種類に大別される。 (1)粉末(ABC)消火器 リン酸アンモニウムを主成分とし、乾燥させた微粉末をシリコン樹脂などにより防湿処理したもので、淡赤色に着色されている。放射された薬剤は、燃焼面を被覆して窒息、抑制作用により消火させる。普通火災(A)、油火災(B)・電気火災(C)に適する。円形標識は白・黄・青。 (2)粉末(Na)消火器 炭酸水素ナトリウムを主成分とした微粉末で、窒息、抑制作用で消火させる。粉末(ABC)と同様の防湿処理が施してある。普通火災には適応はなく、油・電気火災に適する。円形標識は黄・青。 (3)粉末(K)消火器 炭酸カリウムを主成分とした微粉末で、防湿処理は(1)(2)と同様である。消火作用および適応は(2)と同じである。 (4)粉末(KU)消火器 炭酸水素カリウムと尿素(Urea)の反応物を主成分とするのでKUとよぶ。油、電気火災に適用し、粉末はねずみ色である。円形標識は黄・青。 [岸谷孝一] 消火器に関する一般的注意事項設置場所は、目につきやすく容易に使える場所で、通行のじゃまにならない所で、振動が少なく、湿度・温度とも高くない場所がよい。また、消火器は永久に使えるものではないので、半年に一度ぐらいは検査して、不足した圧力を補充したり、薬剤を取り替えたり、ホースの破損などに注意する必要がある。なお消火器は、総務省(旧自治省)消防庁の規格に合格したものには日本消防検定協会が検定マークをつけることになっているので、それらのマークのついているものを備え付けることが必要である。 [岸谷孝一] [参照項目] |©Shogakukan"> 粉末消火器の構造 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
<<: Gastroenterology - shoukaika
>>: Shang Ke-xi; Shang K`o-hsi
Recommend
WAVE
…However, when World War I broke out, in addition...
Sarumata (monkey thigh) - Sarumata
Short pants-style underpants for men with a genero...
Female Swordplay
Swordplays performed by women. They were differen...
Antep - Antep
...Population: 716,000 (1994). Formerly called Ay...
Chondrus verrucosa (English spelling) Chondrusverrucosa
…[Mitsuo Chihara]. . . *Some of the terminology t...
incest taboo
It usually refers to a rule or custom that prohib...
LTD - LTD
Laser target designator : A device that shines a l...
Meliosma rigida (English spelling) Meliosmarigida
… [Toshio Hamatani]. … *Some of the terminology t...
Mihara [village] - Mihara
A village in Hata district in the southwest of Koc...
Radium - radium (English spelling)
It belongs to Group 2 of the periodic table and i...
Yo - Yo
〘noun〙① Under the ritsuryo system, an item paid to...
Ayatsuko
〘 noun 〙 A charm to ward off evil. Usually, when a...
Wladyslaw II Jagiello
…[Miyajima Naoki]. … From the Jagiellonian Dynast...
Kaku Saiyu
He was a commander of the anti-Japanese volunteer...
Sendai River
A river that flows north through eastern Tottori P...


![Jonan [town] - Jonan](/upload/images/67cbdf15be4d1.webp)