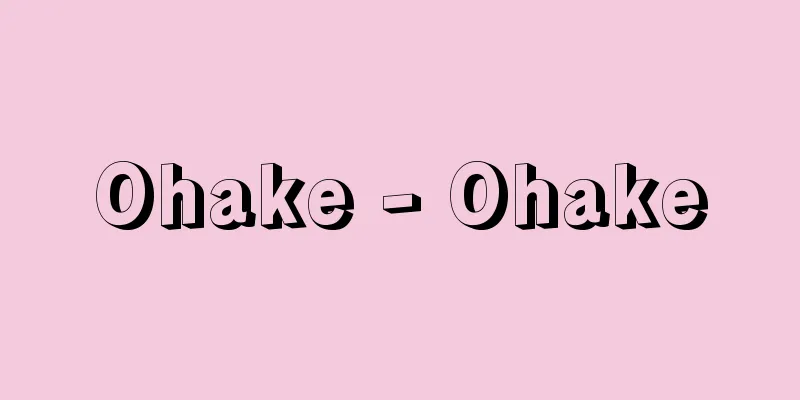Triangle - Sankakukei

|
A figure consisting of three points that are not on the same line and three line segments connecting them. The three points are called the vertices of a triangle, and the three line segments are called the sides of the triangle. The three angles formed by two sides of a triangle are called the angles of the triangle, and the three sides and three angles are called the six elements of a triangle. The sum of the three angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees. The sum of two sides of a triangle is longer than the third side, and the difference between the two sides is shorter than the third side. A circle that passes through the three vertices of a triangle is called the circumscribing circle, and a circle that is tangent to the three sides of a triangle is called the inscribing circle. Every triangle can be drawn with a circumscribing circle and an inscribing circle. Of the six elements of a triangle, namely, three sides and three angles, (1) a triangle is determined by giving two sides and the angles between them. (2) If two angles are given, the remaining angle is determined, and if one more side is determined, the triangle is determined. (3) If three line segments are given and the condition that the sum of the lengths of two line segments is always greater than the length of the third line segment is satisfied, a triangle with three line segments as sides is determined. These three conditions are called the conditions for determining sides and angles, angles and angles, and sides and angles, respectively. When all three angles of a triangle are acute, it is called an acute triangle. When one angle of a triangle is a right angle, it is called a right triangle, and when one angle is an obtuse angle, it is called an obtuse triangle. In right and obtuse triangles, the remaining two angles are all acute. When two sides of a triangle are equal, it is called an isosceles triangle, and the angle between the two equal sides is called the apex angle, and the opposite side is called the base. The angles at both ends of the base of an isosceles triangle are equal in size, and these are called the base angles of the isosceles triangle. When the three sides of a triangle are equal, the three angles are also equal, and their size is 60 degrees. A triangle with three equal sides is called an equilateral triangle. A right-angled isosceles triangle is a right-angled triangle with two equal sides that are equal to each other and the base angle is 45 degrees. Also, the two angles of a right triangle divided by one of the perpendicular lines of an equilateral triangle are 60 degrees and 30 degrees. The side that is opposite the right angle of a right triangle is called the hypotenuse of the right triangle. The center of the circumscribing circle of a triangle is called the circumcenter and the center of the incenter of the triangle. There are other unique features of triangles: the centroid, the orthocenter, and the circumcenter. Together, these are called the five centers of a triangle. [Toshio Shibata] Area of a Triangle There are various formulas to express the area of a triangle. The area S of a triangle with the length of one side a and its height h is S = a h/2. It is also possible to multiply the product of the lengths of the two sides a and b by half the sine of the angle θ between them. In other words, S = ( ab sinθ)/2. Heron's formula is a formula to express the area using the three sides of a triangle. If the lengths of the three sides are a , b , and c , then the area S of the triangle is [Toshio Shibata] [Reference items] | | | | | |©Shogakukan "> Main triangles and how to calculate their area Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
同一直線上にない3点とそれらを結んでできる三つの線分からなる図形。その3点を三角形の頂点といい、三つの線分を三角形の辺という。三角形の二つの辺でできる三つの角を三角形の角といい、3辺、3角を三角形の六要素という。三角形の三つの角の和はどの三角形でも一定で180度である。三角形の2辺の和は第3辺より長く、2辺の差は第3辺より短い。三角形の三つの頂点を通る円を外接円といい、三角形の三つの辺に接する円を内接円という。どの三角形も外接円、内接円がかける。 三角形の六要素、すなわち、3辺3角のうち、(1)2辺とその挟む角を与えれば三角形は定まる。(2)2角を与えれば残りの角も定まり、さらに1辺を定めれば三角形は決定する。(3)線分を三つ与えて、2線分の長さの和がもう一つの線分の長さよりもつねに大きいという条件を満たすなら、3線分を辺とする三角形が決定する。以上の3条件をそれぞれ、辺角辺、角辺角、辺辺辺の決定条件という。 三角形の三つの角がいずれも鋭角のとき鋭角三角形という。三角形の一つの角が直角のとき直角三角形、一つの角が鈍角のとき鈍角三角形という。直角三角形や鈍角三角形では残りの2角はいずれも鋭角である。三角形の2辺が等しいとき二等辺三角形といい、等しい2辺が挟む角を頂角、その対辺を底辺という。二等辺三角形の底辺の両端の角は大きさが等しく、それらを二等辺三角形の底角という。三角形の3辺が等しいとき三つの角も等しくなり、その大きさは60度である。3辺の等しい三角形を正三角形という。直角三角形で直角を挟む2辺が等しい三角形を直角二等辺三角形という。その底角は45度である。また、正三角形の一つの垂線で分けられる直角三角形の二つの角は60度、30度である。直角三角形の直角に対する辺を直角三角形の斜辺という。 三角形の外接円の中心、内接円の中心をそれぞれ三角形の外心、内心という。このほか三角形については特有な点がある。重心、垂心、傍(ぼう)心である。あわせて三角形の五心という。 [柴田敏男] 三角形の面積三角形の面積を表す公式はいろいろある。1辺の長さがaで、これに対する高さがhの三角形の面積Sは、S=ah/2である。また、2辺の長さa、bの積に、その挟む角θの正弦の2分の1を乗じてもよい。つまり、S=(absinθ)/2である。面積を三角形の3辺で表す公式にヘロンの公式がある。3辺の長さをa、b、cとすれば、三角形の面積Sは [柴田敏男] [参照項目] | | | | | |©Shogakukan"> おもな三角形と面積の求め方 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
<<: Suan-xue qi-meng (English: Mathematical Enlightenment)
>>: Triangular bandage - Sankakukin
Recommend
Edodokoro - Edodokoro
...It is found in Japan and central and southern ...
Bridgeport - Bridgeport (English spelling)
Located in the southwestern tip of Connecticut, U...
Hôtel Ritz
…The Japanese translation of Escoffier's book...
Aleksey Mihaylovich Remizov
Russian novelist. Born into a Moscow merchant fam...
Umaasubarmin - Umaasubarmin
…His birth and death years are unknown, but he is...
Gakukan-in
During the Heian period, this was a university sc...
Fanning phenomenon
...This is a pathological sole cutaneous reflex s...
Iida Sekien
...A scholar of Japanese classics and a poet of t...
Tama no Dan - Tama no Dan
The name of a part of the Noh play "Ama (Divi...
Treasury of Atreus
One of the most representative tholos-type tombs, ...
Pound (English spelling)
A unit of mass in the imperial system. Its symbol ...
Arima Naizen Sumiyoshi - Arima Naizen Sumiyoshi
…In 1724 (Kyoho 9), after the transfer of the lor...
Georges Canguilhem
French historian and philosopher of science. Born...
Elgin
...Anti-British movements were growing around Gua...
Beer hall - beer hall
A popular restaurant that serves draft beer and m...