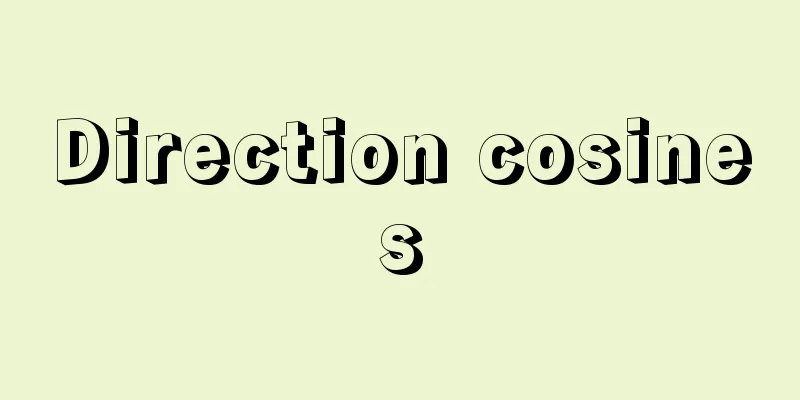Greek alphabet - Girishamoji

|
The Greek alphabet was probably created around the 9th century BC when the Greeks borrowed the Semitic Phoenician alphabet and made their own modifications to it. The names and arrangement of the individual letters are almost the same as those of the Phoenician alphabet, but this writing system is epoch-making in the history of writing in that it included vowel letters that were not present in the Semitic alphabet and established a strictly phonetic principle of one letter per sound. Ancient Greek letters had various variants depending on the region, but can be broadly divided into two types: the "Eastern Greek type" that developed mainly in Ionia in Asia Minor, and the "Western Greek type" that was used mainly in mainland Greece. The former type, which consists of 24 letters, became widespread as the standard Greek alphabet from the 4th century BC onwards. In ancient times, only capital letters were used, and lowercase letters developed from medieval cursive script. On the other hand, it was the Western Greek alphabet that was introduced to Italy and became the basis for the Latin alphabet, and this difference is reflected in the differences between the current Greek and Latin alphabets. This Latin alphabet was inherited by modern Western European languages and became the most powerful writing system in the world, but writing systems directly derived from the Greek alphabet include the ancient Gothic alphabet, the Armenian alphabet, and the Cyrillic alphabet, which was created around the 9th century to write Slavic languages. [Katsumi Matsumoto] ©Shogakukan "> Greek letters and phonetic values Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
ギリシア文字は、おそらく紀元前9世紀のころ、ギリシア人がセム系のフェニキア文字を借用し、これに独自の改変を加えてできあがった。個々の文字の名称と配列はフェニキア文字のそれとほぼ同じであるが、セム文字にはなかった母音文字を備え、1字1音による厳密に音素的な表音原理を確立した点で、この文字体系は文字史上に画期的な意味をもっている。 古い時期のギリシア文字は、地域によっていろいろな変種があったが、大別すると、小アジアのイオニアを中心に発達した「東ギリシア型」と、主としてギリシア本土で行われた「西ギリシア型」の二つに分かれる。前4世紀以降ギリシアの標準アルファベットとして普及したのは前者の型で、これは24字からなる。古くは大文字だけで、小文字は中世の草書体から発達した。 一方、イタリアに移入されてラテン文字の基になったのは西ギリシア型のアルファベットで、その違いが現在のギリシア文字とラテン文字の違いに反映している。このラテン文字は近代の西欧諸言語に継承されて、世界でもっとも有力な文字体系となったが、ギリシア文字から直接派生した文字体系としては、古くはゴート文字、アルメニア文字、そして9世紀ごろスラブ語の表記のためにつくられたキリル文字などがある。 [松本克己] ©Shogakukan"> ギリシア文字と音価 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
Recommend
collector
…These agents are collectively called flotation r...
Trieu Tran
The second long-lasting and stable dynasty that su...
And Soil - And Soil
...The area of black soil in Japan is about 5.5...
Konmei Pond Shoji - Konmei Pond Shoji
A folding screen placed in the Hirobisashi of Seir...
Quilate
...Anyway, the traditional British unit of measur...
Eels Statement - Eels Statement
This was a speech given by W.C. Eells, an advisor ...
Demospongiae
…They are generally large and found in the deep s...
Cashew Resin Enamel - Cashew Resin Enamel
…The coating is strong and chemically resistant, ...
New edition of Utazaimon - Shinpan Utazaimon
Joruri Gidayubushi (a type of Japanese drama with...
Wild Geese - Cancer
A full-length novel by Mori Ogai. It was serializ...
Panthera tigris sondaica (English spelling) Pantheratigrissondaica
…[Maki Sachiko]. . . *Some of the terminology tha...
Sodar (English spelling)
Abbreviation of sonic radar or sound radar, also c...
Cut wheat - Kirimugi
〘Noun〙 ("Mugi" means noodles ) A food ...
pimpernel
...A few species of this genus, including this on...
Darcy
…Permeability is the degree of ease with which a ...