Flow meter - Ryuryokei (English spelling) flowmeter
|
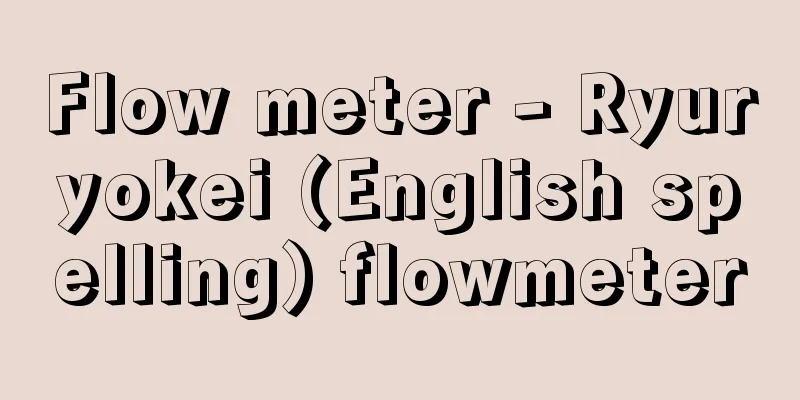
An instrument for measuring the volume or mass per unit time of a fluid (gas, liquid, steam) flowing through a pipe or channel. A flow meter that measures volume is called a volumetric flowmeter, and a flow meter that measures mass is called a mass flowmeter. A volumetric flow meter equipped with a mechanism that displays the total amount of fluid flowing within a certain period of time is also called an integrating volume meter. There are various principles and methods for measuring flow rate, and they are used according to the type of fluid being measured and the purpose of the measurement. Below, the main types of flowmeters according to their principles are listed and their features are described. (1) Restriction flowmeters: A "restriction" such as an orifice, nozzle, or Venturi tube is placed in the middle of a pipe, and the pressure difference that occurs before and after the fluid flows through it is measured, and the flow rate is calculated using Bernoulli's theorem. They can be used for gases, liquids, and steam, and are the most widely used type of instrument in industrial measurement. (2) Area flow meter: This works on the same principle as a restriction flow meter, but in this case, the cross-sectional area of the restriction opening increases or decreases under the condition of a constant differential pressure. The flow rate is calculated from the size of the flow path created by the flow of fluid pushing aside a float or piston that tries to block the pipe with a constant force. (3) Weir flowmeter: When a liquid with a free surface flows over a weir, there is a certain relationship between the flow rate and the height of the liquid surface upstream of the weir. This makes use of the fact that this meter is often used to measure the water flow in a waterway. (4) Flowmeters that use dynamic pressure These meters calculate the flow rate by measuring the force (or pressure difference) generated by dynamic pressure when the fluid changes direction at a bend in a pipeline, etc., and can measure mass flow rate. (5) Coriolis force flowmeters These flowmeters measure the mass flow rate from the magnitude of the Coriolis force that is generated when a fluid passes through a vibrating semicircular arc-shaped pipeline. They are effectively used for measuring the amount of compressed gas being transported. (6) Volumetric flowmeter Also known as a measurement type flowmeter, this type of flowmeter measures the amount of fluid passing through by repeatedly filling and discharging a space of a fixed volume with the fluid. It uses various moving mechanisms such as piston cylinders, rotary pistons, and oval gears, and converts the flow of the fluid into rotational motion and reads it. For liquids, errors due to pressure fluctuations and viscosity are small, making it the type of device that can provide the most accurate measurements. It can also be used to measure gas, and is used in household gas meters. (7) Impeller flowmeter: This is a type of flowmeter that measures the flow rate by the rotation of an impeller that rotates in response to the flow of fluid. It is relatively small and can measure large flow rates, and its characteristics include the fact that an integrated value can be obtained by the total number of rotations. There are various types, such as axial flow and tangential flow types, and domestic water meters are an example of the tangential flow type. (8) Flowmeters that use a flow meter This type of flowmeter measures the average or representative speed of the fluid flowing through a pipe, and calculates the flow rate by multiplying this by the cross-sectional area of the pipe. They are classified according to the principle by which they detect the flow velocity. Representative examples of this type include electromagnetic flowmeters, ultrasonic flowmeters, thermal flowmeters, and Karman vortex flowmeters. They are characterized by low pressure loss and no disturbance to the flow. [Mitsui Kiyoto] [References] | | principle| |©Shogakukan "> Main types and principles of flow meters Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
管路や溝を通って流れる流体(気体、液体、蒸気)の単位時間当りの体積または質量を測定するための計器。体積を測定する方式を体積流量計、質量を測定する方式を質量流量計とよび、一定時間内に流れた流体の総量を表示する機構を備えた体積流量計は積算体積計ともよぶ。 流量を測定するにはいろいろな原理・方法があり、対象とする流体の種類や測定の目的によって使い分けられている。以下に原理別におもな流量計の種類をあげ特徴を述べる。 (1)絞り流量計 管路の途中にオリフィス、ノズル、ベンチュリー管などの「絞り」を設け、ここを流体が流れるときその前後に生じる圧力差を測定し、ベルヌーイの定理によって流量を求める。気体、液体、蒸気のいずれに対しても使用可能で、工業計測においてもっとも広く用いられる器種である。 (2)面積流量計 絞り流量計と同じ原理によるが、この場合は差圧一定という条件のもとで絞りの開口部の断面積が増減する方式を用いる。一定の力で管路をふさごうとするフロートやピストンなどを流体の流れが押しのけてつくる流路の大きさなどから流量を求める。 (3)堰(せき)流量計 自由液面をもった液体が「堰」を越えて流れ落ちるとき、その流量と堰の上流側の液面の高さとが一定の関係をもつことを利用する。多くは水路中の水流の測定に用いられる。 (4)動圧を利用する流量計 管路の屈曲部などで流体が流れの向きを変える際に動圧によって生じる力(または圧力差)を測定して流量を求めるもので、質量流量が測定できる。 (5)コリオリの力を利用する流量計 振動する半円弧状の管路を流体が通過する際に発生するコリオリの力の大きさから質量流量を測定するもので、圧縮ガスを移送する際の計量などに効果的に利用される。 (6)容積流量計 実測式流量計ともいわれ、一定容積をもった空間に流体を充満し排出するという動作を繰り返して通過流体の量を量り取る方式で、ピストンシリンダー、ロータリーピストン、オーバル歯車などさまざまな運動機構が利用され、流体の流れが回転運動に変換されて読み取られる。液体の場合、圧力変動や粘度の影響による誤差が小さく、もっとも高精度の測定ができる器種である。気体の計量にも適用可能であり、家庭用ガスメーターに利用されている。 (7)翼車流量計 流体の流れを受けて回転する羽根車の回転によって流量を求めるもので、比較的小形で大流量の測定ができ、また、回転総数によって積算値が得られる点が特徴である。軸流型、接線流型などいろいろな構造があり、家庭用の水道のメーターは接線流型の一例である。 (8)流速計を利用する流量計 管路中を流れる流体の速さの平均値または代表値を測定して、これと管路の断面積との積の形で流量を求める方式の流量計で、流速を検出する原理によって分類されている。この方式の代表例として、電磁流量計、超音波流量計、熱式流量計、カルマン渦流量計などがあげられる。圧力損失が小さく、流れを乱さないことが特徴である。 [三井清人] [参照項目] | | | |©Shogakukan"> 流量計のおもな種類と原理 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
Recommend
Gutingi
...Population: 128,000 (1995). First appeared in ...
Tannu-Uriangkhai (English spelling)
The Uryankhai people lived in northwestern Mongoli...
Emerald Pearl
Name of stone. Blue-green granite from Norway. Cha...
Oshika Cobalt Line
…Together with Ayukawa in Oshika Town, it was onc...
Kaminaka [town] - Kaminaka
This old town in Onyu District occupies the upper ...
Licchavi (English spelling)
A tribe in ancient North India. Their state was on...
Cardinal vowels
A phonetic vowel is a set of phonemes and the phon...
Stieglitz - Alfred Stieglitz
A photographer known as the father of modern Amer...
Wimpy - Wimpy
...An orphan who lost his father at a young age, ...
Modulor (English spelling)
A system of scale invented and proposed by Le Corb...
Damnacanthus major
…[Mr. Makoto Fukuoka]. … *Some of the terminology...
Different jurisdiction - Cankatsuchigai
1. The court that hears the claim does not have ju...
husaria
…Batoly made Zamoyski his deputy in 1876 and vizi...
Mr. Ta - King
A clan active in ancient Japan. The character Ta c...
Cinématographe (English spelling)
…Inspired by the unveiling of Edison's Kineto...









