Lung capacity

|
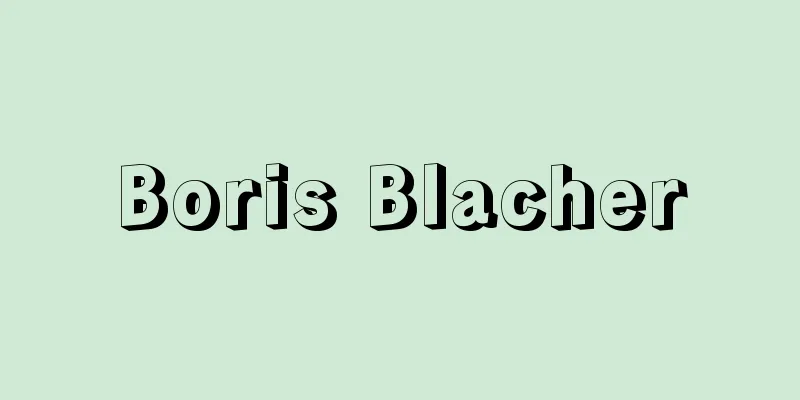
It is the maximum amount of air that the lungs can consciously take in and out. It is an index of lung volume, and vital capacity is affected by muscle function related to respiratory movement (intercostal muscles and diaphragm). The lungs are located inside the thoracic cavity, which is made up of the diaphragm and chest wall, and the lungs passively expand and contract depending on the change in the volume of the thoracic cavity. In this way, the lungs take in and out air. The diaphragm and intercostal muscles change the volume of the thoracic cavity, and these are called respiratory muscles. Vital capacity is the total respiratory volume when you take a deep breath (inspiratory reserve volume) from normal breathing (tidal volume) and then exhale as much air as you can (expiratory reserve volume). Vital capacity varies depending on height, sex, age, posture, etc. As the rib cage expands with growth, vital capacity increases, and it is larger when standing than when lying down. The estimated normal value of vital capacity (for adults aged 18 and over) is calculated using the following formula. Men = {27.63 - (0.112 x age)} x height, Women = {21.78 - (0.101 x age)} x height. The actual vital capacity when the estimated normal value is 100% is called the percent vital capacity, and a percent vital capacity of 100% is normal, and below 80% is abnormal. Vital capacity is used in lung function tests because it indicates the ventilation capacity of the lungs. There are expiratory vital capacity, which is measured by having the subject exhale as much as possible slowly, and forced vital capacity, which is measured by having the subject exhale as much as possible as quickly as possible. The amount of forced vital capacity exhaled in the first second is called the 1-second volume, and the ratio of the 1-second volume to the forced vital capacity expressed as a percentage is called the 1-second rate. Even with the same vital capacity, lung function changes depending on how quickly it can be exhaled. These tests are measured using a spirometer or other device. [Yoda Tamae] "Standard Physiology" edited by Toshinori Hongo, Gravity Hiroshi, and Junichi Toyoda, 6th Edition (2005, Igaku Shoin) Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
意識的に肺が出し入れすることのできる空気の最大量をいう。肺の容積を表す指標で、肺活量は呼吸運動に関する筋機能(肋間筋(ろっかんきん)や横隔膜)に影響される。肺は横隔膜と胸壁からできている胸腔(きょうくう)内にあり、胸腔容積の変化によって肺は他動的に膨らんだりしぼんだりする。このようにして肺は空気の出し入れを行っている。胸腔容積を変えているのが、横隔膜と肋間筋で、これらは呼吸筋とよばれている。普通の呼吸(1回呼吸気量)から思い切り息を吸い込み(予備吸気量)、ついで吐き出せる限りの息(予備呼気量)を吐き出したときの全呼吸気量を肺活量としている。肺活量は身長、性別、年齢、姿勢などによって異なる。成長とともに胸郭が広がるため、肺活量は大きくなり、臥位(がい)よりも立位のほうが大きくなる。肺活量の推測正常値(18歳以上成人)は以下の公式より算出される。男性={27.63-(0.112×年齢)}×身長、女性={21.78-(0.101×年齢)}×身長。 推測正常値を100%としたときの実際の肺活量をパーセント(%)肺活量といい、パーセント肺活量は100%が正常であり、80%以下になると異常である。肺活量は肺の換気能力を示すことから肺の機能検査に用いられている。ゆっくりとできるだけ多く吐き出させて測定する呼気肺活量とできるだけ早く一気に吐き出させて測定する努力肺活量があり、努力肺活量のうちで最初の1秒間に吐き出される量を1秒量といい、1秒量の努力肺活量に対する割合を%で表したものを1秒率とよぶ。同じ肺活量であってもそれを早く吐き出せるかどうかにより肺機能は変化する。これらの検査はスパイロメーターなどによって測定されている。 [依田珠江] 『本郷利憲・廣重力・豊田順一監修『標準生理学』第6版(2005・医学書院)』 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
>>: Vaigach Island (English spelling)
Recommend
Power supply station
…Power supply operations are the nerve system of ...
puppet-theater
…It is also called puppet theater. In English, it...
Munch, PA (English spelling) MunchPA
...National romanticism fostered outstanding arti...
Glide - About
This API was used in the "Voodoo" series...
Kingdom of Loango - Kingdom of Loango
Loango was a kingdom that existed in central Afric...
Kumifu - Kumifu
From the establishment of industrial capitalism i...
Iwakuraji Temple
This area is located in the southeastern part of T...
Beida (English spelling)
A regional capital city in northeastern Libya, No...
singing
...In early modern Joruri, Jiuta, and Sokyoku, it...
Apollo (mythology) - Apollo
…One of the twelve Olympian gods in Greek mytholo...
Alcohol-related problems
...Mental and physical disorders caused by alcoho...
Autobahn - Autobahn (English spelling) German
It is a common German noun meaning a highway for ...
《Old Man's Ramblings》 - My Nephew's Ramblings
...The title of a Joruri manuscript. There are tw...
Needlework - Hariko
A girl employed by a tailor to sew. Ohariko. ※Thre...
History Research Society
A private academic research organization in histor...