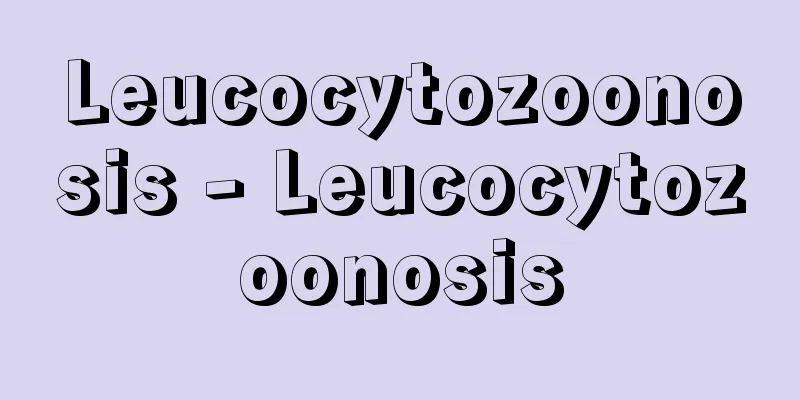Interglacial period - Kanpyoki

|
Between glacial periods, when glaciers expanded and developed, this was a period when the climate was as warm as today. During this period, the climate warmed, and the ice sheets that extended to mid-latitude regions melted rapidly, and the glaciers retreated. This caused the sea level to rise and a rapid transgression, which brought the sea level to its current level or even higher. The temperature also rose significantly, and the degree of warming was more pronounced at higher latitudes, and it is said that the sea level around continental glaciers was about 10 degrees higher than during the glacial period. In areas where glaciers did not develop, one piece of evidence for an interglacial period is the transgression deposits caused by sea level rise. Shallow marine deposits from the last interglacial period (Riss-Würm Interglacial, 70,000 to 80,000 years ago to about 130,000 years ago) are distributed all over the world, and in Japan, marine deposits known as deposits from the Shimosueyoshi Transgression Period can be found in various places. The Shimosueyoshi Formation, found in the northeastern part of Yokohama, unconformably covers the underlying Kazusa Group, and consists of gravel and sand in the lower layer, mud in the middle, and sand in the upper layer, showing a cycle of sedimentary facies. This layer contains many shallow-water shellfish fossils, mammal fossils such as the Naumann's elephant and the Japanese dove (Cervus praenipponicus ), and plant fossils such as the Japanese walnut (Juglans Sieboldiana hosenjiana) . Inferring the climate at that time from these plant and animal fossils, it can be said that the depositional period of the middle mud layer in particular was slightly warmer than today. [Yoshiaki Matsushima] [Reference] |Shikama Cenozoic Quaternary Pleistocene Specimen width: approx. 7.5 cm Produced in Kawasaki City, Kanagawa Prefecture Photo: National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology Geological Survey of Japan (GSJ F3992) Serbus praenipponicus (Japanese… Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
氷河の発達拡大した時期である氷期と氷期との間にあって、現在と同程度に温暖な気候を示した時期。この時期には、気候は温暖化し、中緯度地域まで分布していた氷床が急速に融解し氷河も後退した。そのため海面が上昇して急激な海進がおこり、海面は現在の位置かそれ以上にまであがった。気温の上昇も大きく、暖化の程度は高緯度ほど顕著に現れ、大陸氷河周辺では氷期に比べて約10℃前後は高まったといわれる。氷河の発達しなかった地域では、間氷期を認める証拠の一つに、海面上昇による海進堆積物(たいせきぶつ)がある。最終間氷期(リス‐ビュルム間氷期、7~8万年前から約13万年前)の浅海堆積物は世界各地に分布しており、日本においても、下末吉海進期(しもすえよしかいしんき)の堆積物で知られる海成層が各地にみられる。横浜市北東部に分布する下末吉層は、基盤の上総(かずさ)層群を不整合に覆って、下部層が礫(れき)や砂層、中部が泥層、上部が砂層からなり、1サイクルの堆積相を示す。本層中には浅海生の貝類化石、ナウマンゾウおよびニホンムカシジカCervus praenipponicusなどの哺乳(ほにゅう)動物化石、ホウゼンジグルミJuglans Sieboldiana hosenjianaなどの植物化石が多く含まれる。これらの動植物化石から当時の気候を推定すると、とくに中部泥層の堆積期は現在より若干温暖であったといえる。 [松島義章] [参照項目] |Shikama 新生代第四紀更新世 標本の幅約7.5cm 神奈川県川崎市産写真/産業技術総合研究所地質調査総合センター(GSJ F3992)"> セルブス・プラエニッポニクス(ニホンム… 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
<<: "Kanpei Gyoki" - Kanpyo Gyoki
Recommend
Environmental music - Kankyo Ongaku (English)
Generally speaking, in contrast to music performed...
Cetaceans - Whale body
…A general term for marine fishes belonging to th...
Uritsuke - Uritsuke
…These customers are often fixed for each peddler...
Inventory of property
A list of all assets and liabilities owned by a c...
Toyama [city] - Toyama
A city in central Toyama Prefecture. Established a...
Bevin, Ernest
Born: March 9, 1881, Winsford [Died] April 14, 195...
Java Servant Society - Java Hokoukai
During World War II, the Japanese military invaded...
Takauji Ashikaga
A military commander during the Northern and Sout...
Bakeneko movie - Bakenekoeiga
This is a type of ghost story unique to Japan, and...
Edmund Dulac
1882‐1953 An illustrator born in Toulouse, France....
Guido d'Arezzo
Italian music theorist from about 991 to after 103...
Hepatic lobule
It is a histological unit of the liver that has th...
Photo zenith tube - Shashintenchoto
This is a device for observing the meridian passa...
Balafon
...The ladle-shaped one is split lengthwise in tw...
Informel (English) Informel French
This refers to abstract art with a lyrical and ex...