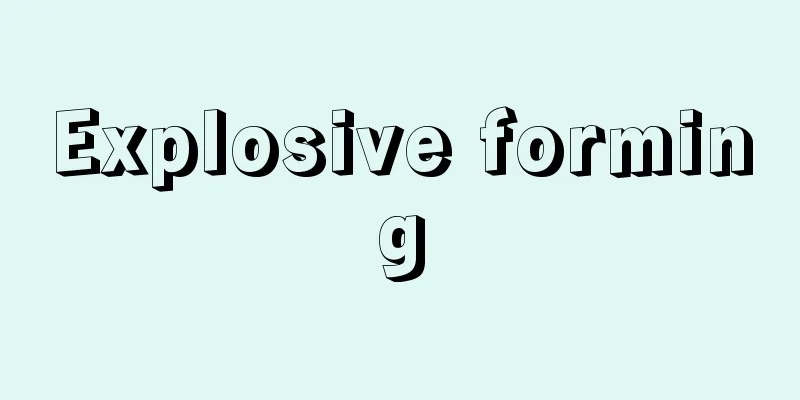Diaphragm process

|
A method for producing chlorine and sodium hydroxide (caustic soda) by electrolysis of salt water. Other methods include the mercury method and the ion exchange membrane method (→ Ion exchange membrane salt production). The mercury method was predominant because it produced high-purity sodium hydroxide, but was discontinued in Japan due to the problem of mercury pollution, and was temporarily replaced by the diaphragm method. An iron net is used as the cathode, and an insoluble metal electrode or graphite is used as the anode, and the two electrode chambers are separated by a diaphragm made of asbestos or other material. When salt water is electrolyzed, sodium hydroxide and hydrogen are produced in the cathode chamber, and chlorine is produced in the anode chamber. The role of the diaphragm is important, as it directly affects the current efficiency and the purity of the products, and prevents the separation of the products at both electrodes and the mixing of the solutions in the two electrode chambers, so various methods are used. The composition of the effluent extracted from the cathode chamber is 10-12% sodium hydroxide and 11-14% sodium chloride. When this is concentrated in a vacuum kettle, sodium chloride precipitates due to the difference in solubility, and sodium hydroxide is concentrated. Since sodium hydroxide produced by the diaphragm process contains sodium chloride and has a low purity, its use has been rapidly reduced with the establishment of ion exchange membrane technology. Source: Encyclopaedia Britannica Concise Encyclopedia About Encyclopaedia Britannica Concise Encyclopedia Information |
|
食塩水の電気分解により塩素と水酸化ナトリウム (カセイソーダ) を製造する方法の一つ。このほかに水銀法とイオン交換膜法 (→イオン交換膜法製塩 ) があり,水銀法は純度の高い水酸化ナトリウムが得られることから優勢であったが,水銀公害の問題から日本では中止され,隔膜法に一時切替えられた。鉄網を陰極,不溶性金属極または黒鉛を陽極とし,両極室は石綿などの隔膜で分離される。食塩水を電解すると陰極室に水酸化ナトリウムと水素が,陽極室には塩素が生じる。隔膜の役割は重要で,電流効率と生成物の純度に直接影響があり,両極生成物の分離と両極室溶液の混合を防ぐ役目をするので,種々の工夫がなされている。陰極室から取出される流出液の組成は水酸化ナトリウム 10~12%,塩化ナトリウム 11~14%。これを真空釜で濃縮すると溶解度の差により塩化ナトリウムは析出し,水酸化ナトリウムは濃縮される。隔膜法水酸化ナトリウム中には塩化ナトリウムを含み純度が低いため,イオン交換膜法の技術が確立されたことに伴い,急速に縮小されている。
出典 ブリタニカ国際大百科事典 小項目事典ブリタニカ国際大百科事典 小項目事典について 情報 |
>>: Keratomalacia - Kakumakukankasho
Recommend
Rückert - Friedrich Rückert
1788‐1866 German poet and orientalist. Belonging t...
Golden Hour
Golden hour is a time when the entertainment progr...
Kashiwara Hachiman Shrine - Kaibara Hachiman Shrine
...Various industries have also been established ...
potential device
...A capacitive voltage divider, which uses capac...
Kaseda Manor
A manor in Ito District, Kii Province (present-day...
Konstitutsiya N. Murav'yova
After studying at Moscow University, he participa...
Ashitaba
Nutrition and Function Angelica tree is a perenni...
Basilica - Basilica (Latin)
The name of a public building in ancient Rome tha...
Notsuhara [town] - Notsuhara
A former town in Oita County, central Oita Prefect...
Croup
Hoarse voice: Mucous membranes in the throat and t...
Lepidurus arcticus
…Japanese horseshoe crabs are said to have been i...
Kamakura Highway - Kamakura Highway
It is a general term for the old roads leading to...
Kurobe River
A river that flows through eastern Toyama Prefect...
Stone Buddha - Senbutsu
Buddhist statues are made by cutting clay into mol...
Merano (English spelling)
Meran in German. A city in the foothills of the Al...