Usuchaki - Usuchaki
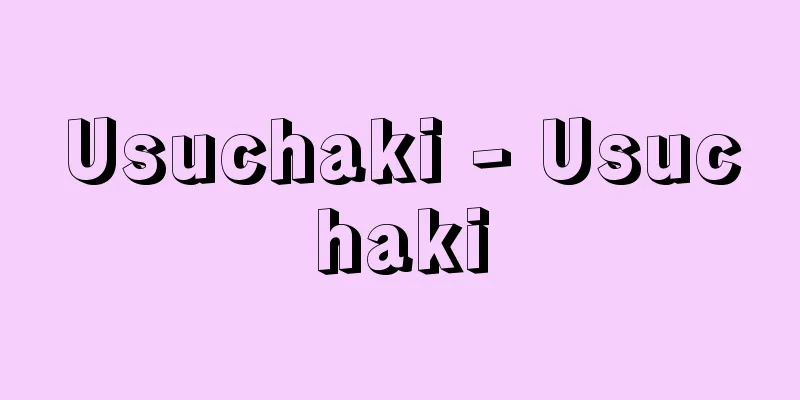
|
A general term for tea utensils for thin tea. It is also called usuuki or usuchaya. In general, the term "natsume" is sometimes used as a general term for usuchaya, but "natsume" is the name for one type of usuchaya. Compared to tea utensils for thick tea, they are made of a variety of materials, including lacquerware such as shinnuri, wood, bamboo, ikkanbari, ceramics, ivory, kagoji, lacquerware, and metal. The basic shapes are broadly divided into four types: natsume, zungiri, nakatsugi, and fubuki. The term usuchaya first appeared in literature in the mid-Edo period in the "Kaiki," and before that it was referred to by individual names such as Kinrinji, natsume, and nakatsugi. [Kouichi Tsutsui] kindsIt is said that natsume tea caddies were originally adapted from the hikiya tea caddies used in bunrin and nasu tea caddies, and that the name comes from their resemblance to the fruit of the jujube plant. They are mainly black lacquered, but some are decorated with lacquer or are made of wood. They are said to have been created by Haneda Goro during the time of Murata Juko, and include seven types of thin natsume tea caddies: Shirihari natsume, large natsume, medium natsume, small natsume, flat natsume, tsubotsubo natsume, and goboshi natsume, as well as Joou natsume, Seiami natsume, Dobari natsume, Naga natsume, Washi natsume, Ippuku natsume, Kawataro natsume, and Machi natsume. Atama-kiri can also be written as sun-kiri. It refers to a shape where the top is cut off in a single line. A representative example is Kinrin-ji Temple. Legend has it that Emperor Godaigo, during his stay at his residence, Yoshino Kinpusen-ji Temple (Kinrin-ji Temple), gave tea to the monks, and made this from a stump of ivy from the mountaintop at that time. Kinrin-ji Temple, which Sen no Rikyu favored and built in later years, was ordered to be made by the first Sakai Shunkei, and is black lacquered on the inside and shunkei-lacquered on the outside, with the ivy grain showing through. Tea kettle, known as "mukashigata," is also a type of atama-kiri. Nakatsugi is a type of thin tea ware that is literally cylindrical with a joint in the center and a separate body and lid. Depending on the shape of the joint and lid, they can be divided into the following types: Nakatsugi, Mennakatsugi, Yukibuki, Mentori, Chaoke, Atamagiri, Kinrinji, Yakuki, Ryugo, Akoda, Anglerfish, Hyo Nakatsugi, and Koaka. Yukibuki belongs to the Nakatsugi category and is a type of thin tea utensil with a surfaced shoulder and hem. It is generally written as "Fubuki," but in the world of tea it is written as "Yukibuki." It is called this because of its shape, as if you were walking through a blizzard and could not see your feet or what is above you. The six types of utensils other than Natsume - Yukibuki, Men-Nakatsugi, Atamagiri, Yakuki, Oshiroitoki, and Chaoke - are called Usuuki Rokki. As for lacquer artists, there are famous craftsmen such as Goro Haneda in the Juko era (Muromachi period), Yozo and Kizo in the Joo era (Sengoku period), Moriami, Hidetsugu, and Fujishige in the Rikyu, Oribe, and Enshu eras (Azuchi-Momoyama period). In the Edo period, the generations of Socho and Sotetsu, as well as Dokei, Doshi, and Ikkan, were well-known. [Kouichi Tsutsui] ©Shogakukan "> Names of the parts of a thin tea utensil © Yoshiyasu Tanaka Main types of usuchachi ware Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
薄茶を入れる茶器の総称。薄器とも薄茶入れとも別称する。一般に「棗(なつめ)」の称を薄茶器の総称とする場合があるが、「棗」は薄茶器の一種の呼称である。材質は真塗りをはじめとした塗り物、木地、竹材、一閑張(いっかんばり)、陶磁器、象牙(ぞうげ)、籠地(かごじ)、堆朱(ついしゅ)、金属など、濃茶(こいちゃ)の茶入れに比して多様である。基本の形状は、棗、頭切(ずんぎり)、中次(なかつぎ)、雪吹(ふぶき)の4種に大別される。薄茶器の称が文献に表れたのは江戸中期の『槐記(かいき)』を初見とし、それ以前は金輪寺(きんりんじ)、棗、中次など個々の名で登場する。 [筒井紘一] 種類棗は元来、文琳(ぶんりん)や茄子(なす)茶入れの挽家(ひきや)を応用したものといわれ、植物のナツメの実に形姿が似ているところからの名称といわれる。黒塗りを主体とし、蒔絵(まきえ)もの、木地のものもある。村田珠光(じゅこう)の時代の羽田(はねだ)五郎が創始したといわれ、尻張(しりはり)棗、大棗、中棗、小棗、平棗、つぼつぼ棗、碁笥(ごけ)棗の薄器七種をはじめ、紹鴎(じょうおう)棗、盛阿弥(せいあみ)棗、胴張棗、長棗、鷲(わし)棗、一服棗、河太郎棗、町棗などがある。 頭切は寸切とも書く。頭部を一文字に断ち切った形をいう。代表は金輪寺。後醍醐(ごだいご)天皇が御座所の吉野金峰山寺(きんぷせんじ)(金輪寺)に滞在中、衆僧に茶を賜ったが、そのとき山頂のツタの木株をもってつくったものと伝説される。後年、千利休(せんのりきゅう)が好んでつくった金輪寺は、初代堺春慶(さかいしゅんけい)に命じてつくらせたもので、内面は黒漆、外面は春慶塗、ツタの木目が透けている。「昔型(むかしがた)」の名で呼称される茶桶(ちゃおけ)も頭切の一種である。 中次は文字どおり円筒形の中央部に合口があって、身、蓋(ふた)が分かれた薄茶器の一種。合口や蓋の形の変化から次のような種類に分けられる。中次、面中次(めんなかつぎ)、雪吹、面取(めんとり)、茶桶、頭切、金輪寺、薬器(やくき)、立鼓(りゅうご)、阿古陀(あこだ)、鮟鱇(あんこう)、瓢(ひょう)中次、甲赤(こうあか)などがある。 雪吹は中次に属し、肩と裾(すそ)に面がとってある薄茶器の一種。一般には「吹雪」と書くが、茶の世界だけは「雪吹」と書く。吹雪のなかを歩くと、足元も上方もわからないほどであるとの意から、その形姿を見立ててこのように呼称している。そして棗以外の雪吹、面中次、頭切、薬器、白粉解(おしろいとき)、茶桶の6種を薄器六器という。 また塗師(ぬし)としては、珠光時代(室町時代)の羽田五郎以来、紹鴎時代(戦国時代)の余三(よぞう)、紀三、利休・織部・遠州時代(安土(あづち)桃山時代)の盛阿弥、秀次(ひでつぐ)、藤重(ふじしげ)などが名工としてあげられる。江戸時代に入ると、宗長、宗哲の各代や道恵、道志、一閑などが著名。 [筒井紘一] ©Shogakukan"> 薄茶器の各部名称 ©田中淑安"> 薄茶器のおもな種類 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
<<: Worsted - Worsted (English spelling)
Recommend
Degree of monopoly
When setting the price of their own products, com...
Sminthillus limbatus (English spelling) Sminthilluslimbatus
... The genus Atelopus , which is a toad but has ...
Tomariura
Currently Toba City, Mie Prefecture. Located at th...
Ruzaevka
... Although some industry was established in thi...
Congress of Vienna
An international conference to settle the afterma...
Proletarian Party - Proletarian Party
A general term for social democratic political pa...
Isui
The largest tributary of the Yellow River in China...
signal coloration
… The body color of animals is by no means meanin...
Angelo
Years of birth: unknown. The first Japanese Christ...
Mount Putuo - Mount Fuda
An island in the southeastern part of the Zhousha...
Andachtsbild
...Unlike the Latin people's tendency to seek...
Apus (the Bird of Prey)
Its abbreviation is Aps. It is a small constellati...
Indentation hardness test
...Therefore, in practice, the hardness test meth...
Pax Britannica
…On the other hand, economically, a preferential ...
Gymnopleurus
…A group of beetles belonging to the family Scara...