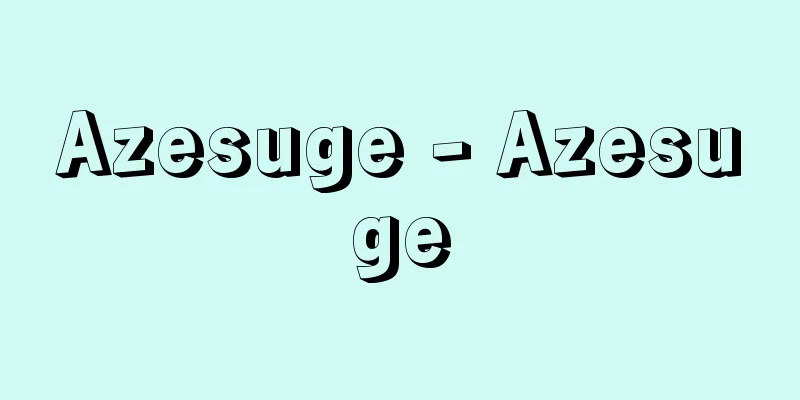Intussusception - Intussusception

|
◎ Intestines overlap, which can be dangerous if left untreated [What kind of disease is it?] Part of the intestine penetrates into the intestine on the anal side, like shortening the tube of a telescope, causing it to become double-layered. The digestive tract is connected from the mouth to the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus. Ileocolic intussusception (figure "Intussusception"), in which the end of the small intestine (ileum) enters the beginning of the large intestine (cecum), is often seen. When intestines are packed into a small space, blood flow becomes difficult and over time they will suffer necrosis (death of tissue cells), so it is dangerous to leave them as they are. It is most commonly seen in infants around 6 months of age, and is rare in those under 3 months of age and over 3 years of age. It is also more common in boys, with about four times as many cases as girls. Why the intestine penetrates into the intestine is unknown in about 95% of cases, but it is thought that it may be related to infection with a virus called adenovirus. Indeed, since intussusception is often accompanied by colds and diarrhea, it cannot be denied that it may be triggered by the swelling of the intestinal lymph nodes due to viral infection. In addition, in approximately 5% of cases, there is a disease that is thought to be the cause of intussusception, such as intestinal polyps or Meckel's diverticulum, and this is more common in children over the age of 2. It starts suddenly with severe abdominal pain [Symptoms] The three main symptoms are abdominal pain, vomiting, and bloody stools. Due to intestinal obstruction caused by intussusception, a child who had been healthy until then suddenly becomes irritable, turns pale, and begins to cry violently. Infants who cannot express their pain in words writhe in agony. The intense pain will disappear after a while, but will return. At first, the baby will be in a relatively good mood between the pains, but as the pain repeats and time passes, the baby will lose energy and become listless. The baby's crying will be intense and loud at first, but will gradually become weaker. In many cases, vomiting occurs. This is due to intestinal obstruction, and the frequency of vomiting increases over time. At first, the vomit is stomach contents, but gradually it becomes a yellow liquid containing bile. In about 60% of cases, mucus and blood in the stool appears. In most cases, this occurs within 12 hours of the onset of the illness, but sometimes it does not occur until 1-2 days later. The stool looks like strawberry jam or tomato juice. If a previously happy infant suddenly begins crying intermittently and intensely, this could be a sign of intussusception and should be referred to a paediatrician or surgeon immediately. Although an enema often produces bloody and mucus-filled stools, it can also worsen symptoms, so it is only performed when a doctor deems it necessary. [Testing and diagnosis] When intussusception is suspected, X-ray fluoroscopy and ultrasound examinations are performed. When an aqueous solution containing barium, which does not transmit X-rays, is injected into the anus and X-ray fluoroscopy is performed (barium enema method), the overlapping part of the intestine appears shaped like a crab's pincers or coiled. This allows the diagnosis of intussusception to be made. Recently, the air enema method, which uses air instead of a barium solution, has been developed and is becoming more commonly used because it is safer than the barium method. ◎ Immediate treatment with enema or surgery [Treatment] Once a diagnosis of intussusception is confirmed, treatment must be administered immediately, because the longer the time passes, the more intestinal necrosis will progress, increasing the risk of the intestinal wall rupturing and causing peritonitis. Treatment options include conservative treatment with enema or surgery. The choice of treatment is determined based on the course of the disease, symptoms, examination findings, and test results. Usually, if the disease is diagnosed within 24 hours of onset, it can be cured with enema, but even if it is discovered early, surgery may be necessary. ● Enema method In the case of ileocolic intussusception occurring within 24 hours after onset, a barium solution or air is injected into the anus under general anesthesia, and pressure is applied little by little to loosen and reposition the overlapped intestines. Using X-ray fluoroscopy, the barium or air is used to reposition the overlapped intestines, and treatment is completed when it is confirmed that the intestines have been sufficiently inserted further up. Recurrence after reduction enema occurs in approximately 10% of cases, so the patient will need to be hospitalized for a few days to be monitored. ●Since surgical enema reduces the intestine using pressure, there is a risk of rupturing the intestinal wall if blood circulation is impaired. Also, in places where it is difficult to reduce the intestine or if the intestine is doubled up, reduction using enema may not be possible. Furthermore, at the time of diagnosis, the intestine may have already ruptured and leaked its contents into the abdominal cavity, causing peritonitis. Such cases are candidates for surgery. The abdomen is opened to observe the intestines, and if the changes due to impaired blood flow to the intestinal wall are mild, the overlapping intestines are pulled out and returned to their original position. If the intestines have become necrotic or perforated, surgery to remove part of the intestines and reconnect them (anastomosis surgery) is required. Prognosis It depends on the time to treatment. If it is within 24 hours after onset, most cases can be cured without surgery. It is important to pay attention to the age at which it is most likely to occur and the symptoms. Intussusception caused by polyps, Meckel's diverticulum, etc. often requires surgery, even if the onset of symptoms is short. Source: Shogakukan Home Medical Library Information |
|
◎腸が重なり、放置すると危険 [どんな病気か] 腸の一部が、肛門(こうもん)側の腸の中に、ちょうど望遠鏡の筒(つつ)を短くするように入り込んで、二重に重なった状態になってしまうものです。 消化管は口から食道、胃、小腸、大腸、そして肛門へとつながっています。小腸の終わりの部分(回腸(かいちょう))が、大腸の始まりの部分(盲腸(もうちょう))に入り込む回腸結腸型腸重積症(かいちょうけっちょうがたちょうじゅうせきしょう)(図「腸重積症」)が多くみられます。 狭いところにつめ込まれた腸は血液が流れにくくなり、時間が経つと壊死(えし)(組織細胞の死滅)をおこすため、放置するのは危険です。 生後6か月前後の乳児にもっとも多くみられ、生後3か月未満、3歳以上ではまれになります。また、男児に多く、女児例の約4倍といわれています。 なぜ腸が腸の中に入り込むのかは、発生例の約95%で不明ですが、アデノウイルスというウイルスの感染と関係があるのではないかと考えられています。確かに腸重積症はかぜや下痢(げり)をしばしば合併するので、ウイルス感染によって腸のリンパ節が肥大(ひだい)することが誘因となる可能性は否定できません。 なお、腸管のポリープ、メッケル憩室(けいしつ)など、腸重積の原因と考えられる疾患がある例が約5%ほどあり、2歳以上の子どもに多くみられます。 ◎突然、激しい腹痛で始まる [症状] 三大症状は腹痛、嘔吐(おうと)、血便(けつべん)です。腸重積症による腸閉塞(ちょうへいそく)のため激しい腹痛が始まり、それまで元気であった子どもが、突然不機嫌になり、顔色が真っ青になり激しく泣きだします。ことばで痛みを訴えられない乳児はからだをよじって苦しみます。 激しい痛みはしばらくすると一時消えますが、またぶり返します。最初のうちは痛みと痛みの間は比較的機嫌がよくけろりとしていますが、痛みがくり返され、時間がたつとともに元気がなくなり、ぐったりしてきます。泣き声も、初めは激しく強いのですが、しだいに弱々しくなります。 多くの場合、嘔吐がみられます。これは腸管の通過障害のためで、時間がたつにつれ回数が増します。吐物(とぶつ)は、最初のうちは胃の内容物ですが、しだいに胆汁(たんじゅう)を含んだ黄色い液になります。 また、粘液(ねんえき)と血液の混ざった粘血便(ねんけつべん)が約60%の例でみられます。多くの場合、病気が始まってから12時間以内に生じますが、ときには1~2日たっても生じないことがあります。便はイチゴジャム、あるいはトマトジュースのようにみえます。 いままで機嫌がよかった乳幼児が突然、間欠的(かんけつてき)に激しく泣くときは腸重積症の可能性があります。小児科医あるいは外科医をすぐに受診しましょう。 なお、浣腸(かんちょう)をすると粘血便が出ることが多いのですが、症状が悪化することもあるため、医師が必要と判断したときのみ行ないます。 [検査と診断] 腸重積症が疑われるときにはX線透視、超音波検査が行なわれます。X線を透過しないバリウムを含む水溶液を肛門(こうもん)から注入してX線透視すると(バリウム注腸法(ちゅうちょうほう))、腸が重なった部分がカニのハサミのような形あるいはコイル状にみえます。これで腸重積症の診断がつきます。 最近、バリウム水溶液の代わりに空気を用いる空気注腸法が開発されました。バリウム法より安全性が高いため、よく使われるようになりつつあります。 ◎注腸法(ちゅうちょうほう)か手術でただちに治療 [治療] 腸重積症の診断が確定すれば、ただちに治療が行なわれなければなりません。時間がたつほど腸の壊死が進み、腸壁が破れて腹膜炎(ふくまくえん)をおこす危険性が高まるからです。 治療法は注腸法による保存的方法と手術とがあります。どちらの方法で治療するかは病気の経過、症状、診察所見、検査成績で判断されます。ふつう、発症24時間以内ならば、ほとんど注腸法で治りますが、早期に見つかっても手術が必要なこともあります。 ●注腸法(ちゅうちょうほう) 発症してから24時間以内の回腸結腸型腸重積症の場合、全身麻酔下にバリウム水溶液あるいは空気を肛門から注入し、少しずつ圧力をかけて、肛門側から押し戻すようにして重なった腸を解きほぐし、整復する方法です。X線で透視しながら、バリウムあるいは空気が重なった腸を整復(せいふく)し、さらに上の方まで十分入り込むことを確認して治療が終わります。 注腸整復後の再発が約10%の例にみられるため、数日入院して様子をみなければなりません。 ●手術 注腸法は圧力で整復するため、血行障害が進んでいると腸壁が破れてしまう危険性があります。また、整復しにくい場所や、入り込んだ腸が二重になっていたりすると、注腸法では整復できないこともあります。さらに、診断時にすでに壊死した腸が破れ、腸の内容物が腹腔(ふくくう)に漏(も)れ出し、腹膜炎をおこしていることもあります。このような例が手術対象となります。 開腹して腸を観察し、腸壁の血行障害による変化が軽い場合は、重なった腸を引き出してもとに戻します。腸が壊死や穿孔(せんこう)をおこしているときは、腸の一部を切除してつなぎ合わせる手術(吻合(ふんごう)手術)が必要になります。 ●予後(よご) 治療までの時間で決まります。発症後24時間以内ならば、多くは手術をしないでも治ります。おこりやすい年齢、症状に注意が必要です。 ポリープやメッケル憩室などが原因の腸重積は、発症後の時間が短くとも、しばしば手術が必要になります。 出典 小学館家庭医学館について 情報 |
Recommend
Giffen, R.
...The phenomenon whereby a price increase increa...
Venus-shaped shield clam
It is a bivalve mollusca of the family Veneridae ...
Ghost stories - Kaidanbanashi
〘Noun〙 A story about monsters and ghosts. Also, es...
Mohamedanism
… What is Islam? Islam is a monotheistic religion...
Input/Output Unit
A general term for a device that inputs data into...
Cattleya - Cattleya
A genus in the orchid family (APG classification:...
Mystery - Puzzle
A type of word game. Depending on the region, it ...
Morus rubra (English spelling) Morusrubra
… [Okamoto Motoji]. … *Some of the terminology th...
Kannoji Temple
[1] Former name of Tennoji Temple in Yanaka, Taito...
double-hung
…The French window was developed in the 16th cent...
Castle, WE - Castle
...But he became critical when he could not obtai...
Constitutional law - Seitaisho
The Act on the Organization of the Government was ...
Electric detonator
Among detonators, a type of pyrotechnic device in...
Heavenly King - Tenno
Tenno-machi was formerly a town in Minamiakita Co...
New Harmony (English)
...Party utopias are both theoretical demands and...