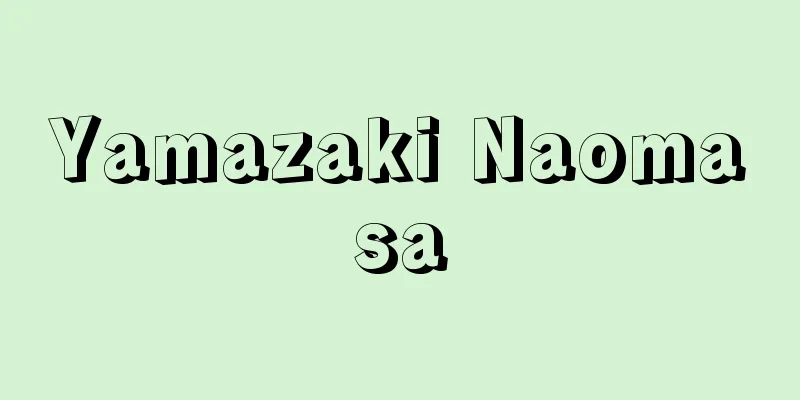Food self-sufficiency rate

|
An index showing the degree to which a country's total food supply is supplied by domestic production. In statistics from the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, it is written as "food self-sufficiency rate." Usually, it is expressed by the percentage of domestic production to the amount of food consumed by each item (self-sufficiency rate by item). Looking at the self-sufficiency rate by item, it can be seen that in Japan, only rice (99%) and chicken eggs (96%) are almost self-sufficient. Soybeans (4%) and wheat (11%) have remained remarkably low. Also, since the mid-1980s, the self-sufficiency rate of major items has dropped significantly. Vegetables, which were once high, dropped from 95% to 86%, fish and shellfish from 96% to 72%, and meat from 81% to 56%. The self-sufficiency rate of feed required for meat production is only 26%, with little change (figures are a comparison between 1985 and 1997). Self-sufficiency rates are influenced by two aspects: consumer-side factors such as changes in eating habits, and supply-side factors such as the state of trade and domestic production. In the case of beef, there have been changes in the trade system (import liberalization) and a large increase in consumption, and changes in conditions other than domestic production have been the cause of the decline in self-sufficiency rates. However, for other items, there have been no major changes in the trade system or consumption, and the decline is largely due to a decrease in domestic agricultural producers. The background to this is the influx of cheap agricultural products from Asian countries, which has caused a large drop in domestic prices, leading to concerns about the future of agriculture. In the past, the calculation of the overall self-sufficiency rate, which indicates the self-sufficiency rate of food as a whole, used a method of calculating the supply amount using price as a common scale, but nowadays, the supply calorie self-sufficiency rate, which is calculated mainly by the supply calorie content (calories), is mainly used. In this method, livestock products are counted at the calorie content of the feed required for their production. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages, and the supply calorie self-sufficiency rate has the problem that it does not reflect the domestic production of livestock products or the supply of vegetables, which have low calorie content. Japan's overall self-sufficiency rate fell from 52% in 1985 (Showa 60) to 41% in 1997 (Heisei 9). In comparison with other countries, the self-sufficiency rate of grains is 109% in the United States, 106% in the former West Germany, and 28% in Japan (figures for other countries are for 1988, and for Japan for 1997). The further decline in the food self-sufficiency rate, which is extremely low even among developed capitalist countries, has sparked much discussion about the nature of food supply and consumption. Then, against the backdrop of public anxiety over the decline in food self-sufficiency, the Food, Agriculture, and Rural Areas Basic Law was enacted and put into effect in July 1999, which, for the first time, set targets for improving food self-sufficiency. [Yoko Niyama] Subsequent developmentsEven in the 21st century, Japan's food self-sufficiency rate continues to decline gradually due to the increase in imported agricultural products and the decline in demand for rice. The supply calorie self-sufficiency rate in 2018 was 37%, the lowest ever recorded, matching the record low of 1993, when there was a serious rice crop failure. The Japanese government has taken measures to improve self-sufficiency, such as encouraging local production and consumption and increasing demand for rice flour, but the situation has not improved. In 2015, the government's target of raising the supply calorie self-sufficiency rate to 50% by 2025 was revised downward to 45%. The supply calorie self-sufficiency rates of other countries (as of 2013) are 223% for Australia, 130% for the United States, 127% for France, 95% for Germany, and 63% for the United Kingdom, making Japan the lowest among developed countries. Japan's self-sufficiency rate based on production value as of 2018 (the government's target is 73%) is 66%. [Editorial Department, January 21, 2020] [Reference items] |©Shogakukan "> Formula for food self-sufficiency rate Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
一国の食糧総供給量のうち、国内生産で供給される度合いを示す指標。農林水産省の統計資料では「食料自給率」と表記されている。通常、品目別には、国内消費仕向量に対する国内生産量の百分率で表される(品目別自給率)。品目別自給率をみてわかることは、日本では、ほぼ自給しているのは米(99%)と鶏卵(96%)のみである。大豆(4%)、小麦(11%)は著しく低いまま推移している。また、1980年代なかばごろを境に、主要品目の自給率が大幅に低下している。かつて高かった野菜は95%から86%へ、魚貝類は96%から72%へ、肉類も81%から56%へと下がった。肉類の生産に要する飼料の自給率は26%にすぎず、変化はほとんどない(数値は1985年度と1997年度の比較)。 自給率は、食生活の変化という消費側の要因と、貿易や国内生産の状態という供給側の要因との二つの側面に左右される。牛肉では、貿易制度の変化(輸入自由化)と消費量の大幅な増大があり、国内生産以外の条件変化が自給率低下の原因となった。しかし、他の品目では、貿易制度や消費量に大きな変化はなく、国内の農業生産者の減少によるところが大きい。その背景には、アジア諸国から安価な農産物が流入し国内相場が大きく低下したため、農業の先行きに不安がもたれるようになったことがある。 食糧全体の自給率を示す総合自給率の算定には、かつては価額を共通尺度として供給量を算出する方式なども用いられていたが、現在はおもに供給熱量(カロリー)によって算出する供給熱量自給率が使用される。この方式では、畜産物はその生産に要した飼料の熱量の段階でとらえられる。いずれの方式も一長一短があり、供給熱量自給率には、畜産物の国内生産部分や、熱量の低い野菜の供給の状態が反映されないという問題がある。日本の総合自給率は、1985年度(昭和60)の52%から1997年度(平成9)には41%へと下がった。諸外国と比較すると、穀物自給率はアメリカ109%、旧西ドイツ106%、日本28%となっている(外国の数値は1988年度、日本は1997年度)。先進資本主義国のなかでも著しく低い食糧自給率のなおいっそうの低下は、食糧供給と消費のあり方をめぐって多くの論議をよんでいる。そして、食糧自給率の低下に対する国民の不安が背景となり、1999年(平成11)7月に成立・施行された「食料・農業・農村基本法」では、はじめて目標を設定して食糧自給率の向上を図ることが定められた。 [新山陽子] その後の動き21世紀に入っても、輸入農産物の増加や米の需要減退で、日本の食糧自給率は徐々に低下を続けている。2018年(平成30)の供給熱量自給率は37%と、米の深刻な凶作だった1993年(平成5)と並び、過去最低を記録した。日本政府は地産地消の推奨や米粉の需要拡大などの自給率向上策をとっているが改善していない。2015年には、供給熱量自給率を2025年までに50%へ引き上げるとした政府目標を45%へ下方修正した。諸外国の供給熱量自給率(2013年時点)はオーストラリアが223%、アメリカは130%、フランスは127%、ドイツは95%、イギリスは63%で、日本は先進国のなかで最低水準にある。なお日本の2018年時点の生産額ベースの自給率(政府目標は73%)は66%である。 [編集部 2020年1月21日] [参照項目] |©Shogakukan"> 食糧自給率の算式 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
<<: Food securities - Shokuryo Shoken
>>: Food Control Special Account
Recommend
Leh
...It is a mountainous region in which the four m...
Berger mixture
… Smoke is used as a concealment screen and as a ...
dung-pusher
…Its English name is also sacred beetle. It is al...
José Batlle y Ordóñez
1856‐1929 President of Uruguay. Served 1903-07, 19...
Pinocytosis
…Endocytosis is a general term for the action of ...
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
…Abbreviation for Food and Agriculture Organizati...
Catharsis (Greek)
The original meaning of the word in ancient Greek...
Barros
...is a general term for dark clayey soils found ...
Dwight David Eisenhower
A US Army marshal, a hero of World War II, and th...
Durban - Durban (English spelling)
A port city in the southern part of KwaZulu-Natal...
Procurement Implementation Headquarters - Chotatsujisshihonbu
It is one of the affiliated organizations of the D...
Attack - Attack
… [Yukio Hattori] [Kabuki Glossary] With a few ex...
Iinuma Sukemune
Year of death: Eijin 1.4.22 (1293.5.29) Year of bi...
Jenny - François Gény
French legal scholar. He taught civil law at the ...
Barrister
A semiconductor element whose resistance value cha...