Eustachian tube - Time

|
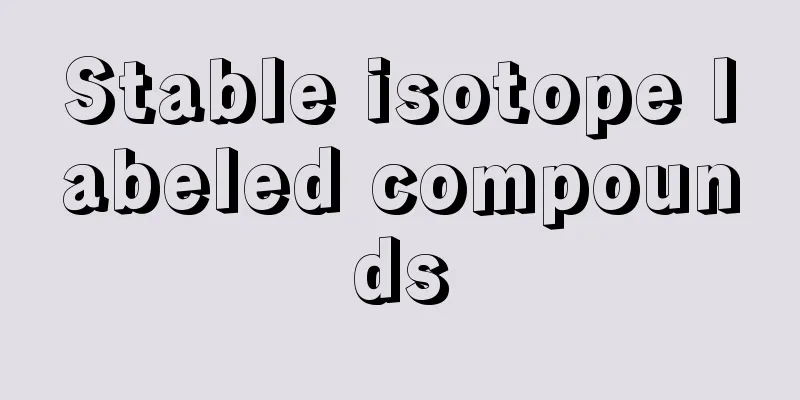
It is a 36 mm long tube that starts from the tympanic opening in the anterior wall of the tympanic cavity of the middle ear and opens into the pharyngeal opening of the Eustachian tube in the lateral wall of the nasal part of the pharynx (posterior to the nasal cavity). The wall of the Eustachian tube is made of bone for about 12 mm near the tympanic cavity (bony part), and 24 mm near the pharynx is made of cartilage and fibrous connective tissue. The Eustachian tube cartilage surrounds the inner, upper and outer walls of the Eustachian tube (cartilaginous part), and the lower wall is made of connective tissue (membranous plate). The Eustachian tube runs anteriorly and inferiorly, but in infants it runs almost horizontally. Furthermore, infants have a short Eustachian tube, which makes them prone to otitis media. The thickness of the Eustachian tube is not uniform throughout, being the widest at the pharyngeal opening of the Eustachian tube, followed by the tympanic opening. The narrowest part is the border between the bony and cartilaginous parts (the isthmus of the Eustachian tube). However, because the tympanic cavity and pharynx are connected by the Eustachian tube, the internal pressure of the tympanic cavity is the same as the external pressure. Normally, the Eustachian tube is closed, but when swallowing, the levator veli palatini and tensor veli palatini muscles contract, pulling the lower wall of the Eustachian tube cartilage downward and opening the Eustachian tube. The Eustachian tube is also called the Eustachian tube because it was discovered by Eustachian B. Eustachii, a 16th century Italian anatomist and personal physician to the Pope. [Kazuyo Shimai] [Reference item] | |©Shogakukan "> Ear structure Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
中耳の鼓室の前壁にある鼓室口から始まり、咽頭(いんとう)鼻部(鼻腔(びくう)後方)の外側壁にある耳管咽頭口に開く長さ36ミリメートルの管をいう。耳管の壁は、鼓室寄りの長さ12ミリメートルほどが骨からなり(骨性部)、咽頭寄りの24ミリメートルが軟骨と線維性結合組織からなっている。耳管軟骨は耳管壁の内側、上壁、外側壁を囲み(軟骨部)、下壁には結合組織がある(膜性板)。耳管の走る方向は前内下方であるが、乳幼児ではほぼ水平に走っている。さらに乳幼児では耳管が短いため、中耳炎がおこりやすい。耳管の太さは全体に一様でなく、耳管咽頭口でもっとも太く、鼓室口が次に太い。もっとも狭いのは骨性部と軟骨部との境(耳管峡)である。しかし、鼓室と咽頭とは耳管でつながれているため、鼓室の内圧は外圧と同じになっている。通常、耳管は閉鎖しているが、嚥下(えんげ)の際には口蓋帆挙筋(こうがいはんきょきん)と口蓋帆張筋が収縮し、耳管軟骨部の下壁が下方に引かれるので耳管が開く。耳管は、16世紀のイタリアの解剖学者で、ローマ法王の侍医でもあったユースタキーB. Eustachiiによってみいだされたため、ユースタキー管(エウスタキオ管、エウスターキョ管、欧氏管)ともよぶ。 [嶋井和世] [参照項目] | |©Shogakukan"> 耳の構造 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
Recommend
Controlled price system
...The methods of price policy vary depending on ...
Spirited Away - Kamikakushi
It refers to a child or other person suddenly dis...
field mustard
...The latter three species are plants that arose...
Sharp Turn - Kyusenkai
[noun] (suru) When an aircraft, ship, etc. changes...
Kikenkobogun Ancient Tombs
A group of ancient tombs from the Shang to Han dyn...
Agriculture and Calendar - Erga kai Hēmerai
A work by Greek poet Hesiod around 700 BCE. It is ...
Athabascan people
...There have been anti-government movements by t...
Kinnaird, M.
…It corresponds to the YMCA. It was formed in 187...
Joyo
A famous celadon kiln from the Song Dynasty in Ch...
Sorghum vulgare; great millet
An annual grass of the grass family. It is also ca...
Katsuobushimushi (English name) skin beetles
A general term for insects belonging to the famil...
Ferrite - ferrite (English spelling)
(1) A composite oxide of trivalent iron oxide ( F...
Nepomucky, J.
…He was also called John of Nepomuk. In Czech, he...
Diets
…(c) The consonant group hs becomes ss through as...
Infinite Embrace
A full-length novel by Takii Kosaku. Published by ...