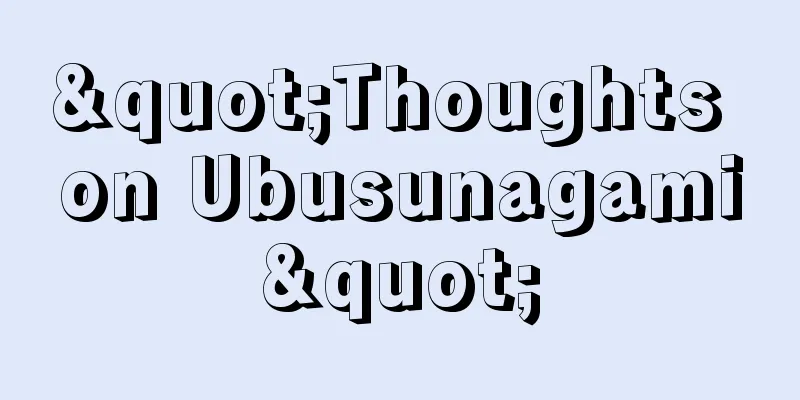Acetic acid fermentation - Sakusan fermentation

|
This is a type of oxidative fermentation, and refers to the process in which alcohol is aerobically oxidized to acetaldehyde and then to acetic acid. The reaction can be expressed as follows:
Brewed vinegar that has been fermented and aged in this way contains, in addition to the main component, acetic acid, various organic acids, amino acids, sugars, etc., and is used in various food processing applications. [Ito Seiga] Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
酸化発酵の一種で、アルコールを好気的に酸化し、アセトアルデヒドを経て酢酸にする過程をいう。その反応は次のように表すことができる。
このようにして発酵生産され熟成させた醸造酢は、主成分である酢酸のほかに、各種の有機酸、アミノ酸、糖などを含み、各種の食品加工に用いられる。 [伊藤菁莪] 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
<<: Vinyl Acetate Resin - Vinyl Acetate Resin
>>: Lead acetate paper - Sakusannamarishi
Recommend
Tobis-Klangfilm
...However, Germany had a well-developed system o...
Canary, MJ - Quite
…A female hero of the American West. Her real nam...
Psychotria rubra
An evergreen shrub or small tree of the Rubiaceae ...
Rank Sugoroku - Kan'i Sugoroku
… Picture sugoroku is believed to have originated...
dienophile
...In both industrial and laboratory use, it is u...
Vater's papilla (English spelling)
…The common bile duct merges with the main pancre...
Shohachi Ishii
1926-1980 A wrestler from the Showa era. Born on ...
Flat glass - Itagarasu (English spelling) Flat glass
A general term for glass products made into plate...
Lifeboat - Lifeboat
A small wooden or steel boat that is carried on a ...
Luigi Russolo
Italian painter and composer. He was initially in...
Shortwave broadcasting - tampahoso (English spelling) short-wave broadcasting
Audio broadcasting using shortwave radio waves in...
Ogishima Island
…In the waterfront, reclaimed land was developed ...
Oxya japonica japonica (English spelling) Oxyajaponicajaponica
…[Tokuji Chiba]. … *Some of the terminology that ...
Keats - John Keats
A British poet. Along with Byron and Shelley, he ...
Preliminary prospectus - karimokuromisho
…The obligation to deliver a prospectus arises wh...