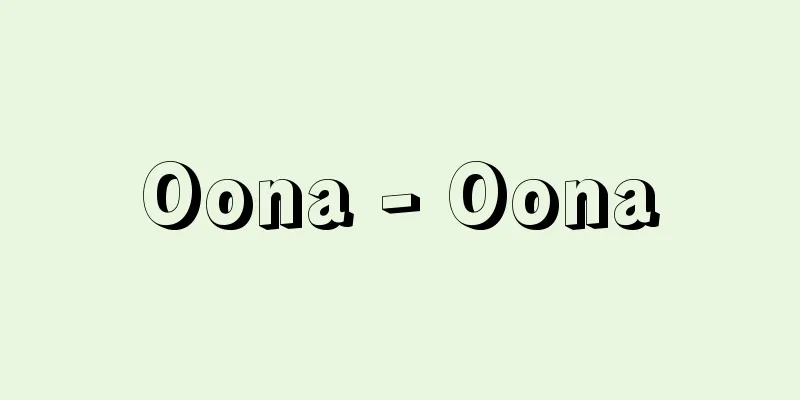Functional group

|
A group of atoms that characterizes an organic compound, also called a functional group or functional group. Organic compounds with the same functional group have similar properties and reactivity, so organic compounds are classified by their functional groups. The main functional groups are shown in . As can be seen from this, most functional groups contain heteroatoms such as oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), sulfur (S), phosphorus (P), and halogens (fluorine F, chlorine Cl, bromine Br, and iodine I). However, carbon groups such as the vinyl group, which contains a carbon-carbon double bond (C=C), and the ethynyl group, which contains a triple bond (C≡C), are also functional groups that represent unique properties. A group of compounds that have the same functional group but differ only in the number of carbon atoms is called a homologue, or homologous series. For example, methanol (methyl alcohol) CH 3 OH and decanol CH 3 (CH 2 ) 9 OH are homologues with the hydroxyl group -OH as the functional group. A compound may have two or more of the same functional groups in the same molecule. For example, succinic acid (HOOCCH 2 CH 2 COOH) has two carboxyl groups in the molecule. Some compounds have two or more different functional groups in the same molecule. For example, p (para)-nitrophenol ( p -NO 2 C 6 H 4 OH) has a nitro group and a phenolic hydroxyl group in the same molecule, so it has the properties of both a nitro compound and a phenol. Compounds with multiple functional groups in the molecule are called multifunctional compounds. Amino acids such as glycine (H 2 NCH 2 COOH) are also bifunctional compounds with an amino group and a carboxy group in the molecule, and show the properties of both amines and carboxylic acids, but when there are two or more substituents in a molecule, the substituents may interact with each other within the molecule and change the properties. In the case of amino acids, the basic amino group and the acidic carboxy group react within the molecule to form a salt, H 3 N + CH 2 COO - , which weakens the acidity. In general, organic compounds consist of a carbon skeleton and functional groups. The saturated carbon skeleton, also called a residue, is less reactive and less susceptible to chemical changes. Residues often consist of alkyl moieties, aromatic hydrocarbon moieties, or both. The same functional group has different properties depending on whether it is attached to an alkyl moiety or an aromatic nucleus. For example, a hydroxyl group becomes an alcohol when bonded to an alkyl group, and a phenol when bonded to an aromatic ring. [Takeo Sato and Masaru Hirota] "Tutorial Chemistry Series 3: Chemistry of Functional Groups" by James R. Hanson, translated by Toyoda Masahiro (2003, Kagaku Dojin) [Reference] | | | |* is a divalent group that is bonded to two hydrocarbon groups . Main functional groups (table) Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
有機化合物を特性づける原子団で、機能原子団あるいは作用基ともいう。同じ官能基をもつ有機化合物は性質や反応性が類似しているので、有機化合物は官能基によって分類される。おもな官能基をに示す。これをみるとわかるように、ほとんどの官能基は酸素(O)、窒素(N)、硫黄(いおう)(S)、リン(P)、ハロゲン(フッ素F、塩素Cl、臭素Br、ヨウ素I)などのヘテロ原子を含んでいる。しかし、炭素‐炭素二重結合(C=C)を含むビニル基や三重結合(C≡C)を含むエチニル基のような炭素基もその特有な性質を代表する官能基である。 同じ官能基をもち炭素数のみを異にする一群の化合物を同族体、あるいは同族列化合物という。たとえば、メタノール(メチルアルコール)CH3OHとデカノールCH3(CH2)9OHは、ヒドロキシ基-OHを官能基とする同族体である。 一つの化合物が同じ分子内に同じ種類の官能基を二つ以上もつことがある。たとえば、コハク酸(HOOCCH2CH2COOH)は分子内に二つのカルボキシ基(カルボキシル基)をもっている。同じ分子内に2種類以上の異なる官能基をもつ化合物もある。たとえば、p(パラ)-ニトロフェノール(p-NO2C6H4OH)は同じ分子内にニトロ基とフェノール性のヒドロキシ基をもっているので、ニトロ化合物とフェノールの両方の性質をもっている。このように分子内に複数の官能基をもつ化合物を多官能基化合物とよんでいる。グリシン(H2NCH2COOH)などのアミノ酸も分子内にアミノ基とカルボキシ基をもっている二官能基化合物であり、アミンとカルボン酸の両方の性質を示すが、一つの分子内に二つ以上の置換基があると分子内で置換基どうしが相互作用をして性質が変わることもある。アミノ酸の場合には分子内で塩基性のアミノ基と酸性のカルボキシ基が反応して塩をつくってH3N+CH2COO-になっているので、酸性が弱まっている。 一般に有機化合物は炭素骨格と官能基からなる。飽和炭素骨格は残基ともよばれ、反応性が乏しく化学変化を受けにくい。残基としてはアルキル部分、芳香族炭化水素部分、あるいはその両者からなる場合が多い。同じ官能基でもアルキル部分につくか、あるいは芳香核につくかによって性質は異なる。たとえばヒドロキシ基はアルキル基に結合するとアルコールになり、芳香環につくとフェノールとなる。 [佐藤武雄・廣田 穰] 『James R. Hanson著、豊田真弘訳『チュートリアル化学シリーズ3 官能基の化学』(2003・化学同人)』 [参照項目] | | | |*は2価の基で二つの炭化水素基と結合している©Shogakukan"> おもな官能基〔表〕 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
>>: Encouragement of Agriculture - Kannou
Recommend
Honma Yusei
Year of death: August 16, 1850 (September 21, 1850...
Mausoleum of Qait Bai
…capital of the Arab Republic of Egypt. Populatio...
Hamagiku (Chrysanthemum nipponicum) - Hamagiku (English spelling)
A perennial plant of the Asteraceae family that gr...
Witwatersrand (English spelling)
A gold-producing region in the northern part of So...
Grand Rapids (English spelling)
A city in southwest Michigan, USA. Population 190,...
Debye-Hückel theory
This theory of strong electrolyte solutions was de...
Azuma Kagami - Azuma Kagami
Also written as "Toukagami." A history b...
Nagoya Railroad - Nagoya Railroad
A private railway company. Founded in 1894 as Aich...
Yukiyoshi Aoyama
1855 * -1930 Daimyo and aristocrats from the end ...
Gág, W. (English spelling) GagW
...In recent years, noteworthy painters have also...
Olfactory gland
→Bowman's gland Source: Asakura Publishing Nut...
Festus (English spelling) Sextus Pompeius Festus
Roman grammarian from the late 2nd century. Date o...
Literary Revolution
A cultural and ideological innovation movement th...
Panic - Panic (English spelling)
In economic terms, it means a panic. In social ps...
Masao Kume
Novelist and playwright. Born on November 23, 189...