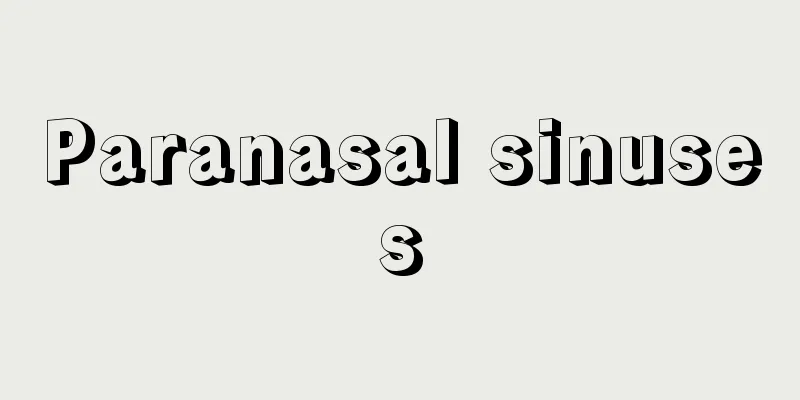Shock absorber - Shock absorber

|
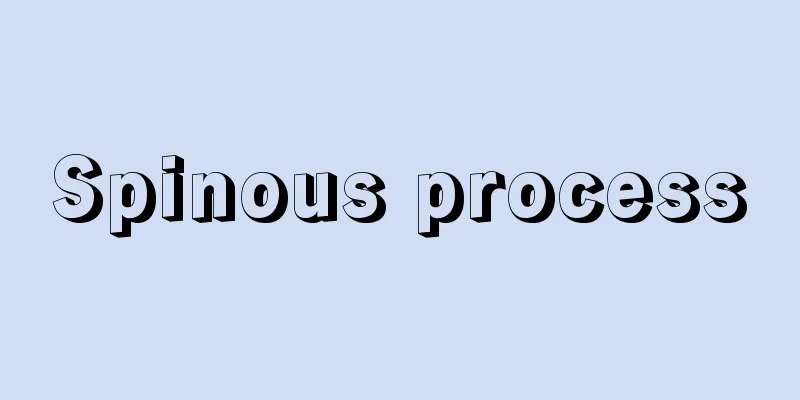
This refers to springs, anti-vibration rubber, hydraulic devices, etc. that absorb kinetic energy between a moving body and another object or a fixed wall, and reduce vibrations and shocks applied to the object. There are several causes of vibration, such as vibration being transmitted from a reciprocating object, vibration occurring when there is an imbalance in the rotating part, or vibration becoming severe when resonance occurs. Therefore, to prevent vibration, it is sufficient to remove the cause. For example, to reduce the vibration of an automobile engine, the number of cylinders is increased and the direction of the piston movement is adjusted to minimize the cause of vibration. In the case of a rotating body, the amount of imbalance is measured with a balancing tester, and the amount of imbalance is reduced as much as possible by grinding it off or attaching an extra weight to the opposite side of the center of rotation. To avoid resonance, the frequency of vibration can be changed in some way, or a method can be used to dampen the vibration so that the amplitude does not become too large when resonance occurs. However, in the case of automobiles, the speed varies over a wide range, and the vibrations imposed on the vehicle body by unevenness on the road cannot be eliminated, so various shock absorbers are used to reduce the vibrations of the vehicle body. (1) Leaf springs Springs are most commonly used to absorb vibrations and shocks. Springs come in various types, including coil springs and plate springs. A leaf spring is made up of several stacked plate springs. They are attached between the axle and the body of automobiles, freight cars, and passenger cars to prevent the transmission of strong vibrations from the road or rails to the body of the car. (2) Coil springs are steel wire wound into a coil, with the diameter of the wire varying from large to small. Coil springs also come in a variety of diameters, and are used for different purposes. When installing an engine or motor, a coil spring is placed between the mounting base to prevent the transmission of engine vibrations and to prevent the engine itself from vibrating violently. (3) Torsion springs: If one end of a rod is fixed and the other end is twisted, and the torsional angle is not too large, the torsional deformation of the rod will return to its original state when the twisting force is removed. Because it stores strain energy due to the torsional force when twisted, it can be used to cushion shocks caused by external forces. This type of spring is called a torsion spring, and is used as a buffer between the axle and the body of an automobile. (4) Anti-vibration rubber Rubber deforms when an external force is applied, but unlike metals, it has the property of returning to its original shape when the external force is removed, even if the deformation is quite large. In other words, it does not lose its elasticity even if the deformation is large. Rubber also has viscous properties inside, so it absorbs the energy of external forces well. Therefore, it is convenient as a material to prevent vibration and soften shocks. Anti-vibration rubber is usually made by bonding rubber to a metal plate, and there are various shapes. For example, rubber is sandwiched between two metal plates, or rubber is sandwiched between two cylinders of different sizes. Since rubber is good at absorbing shocks and vibrations even when tensile force, compressive force, shear force, or a combination of these forces is applied, anti-vibration rubber is used to attach automobile engines to the body. Anti-vibration rubber is used in various fields, such as installing it on the floor to prevent vibrations or shocks generated by motors and machine tools from being transmitted to the floor, and supporting measuring instruments with anti-vibration rubber to prevent them from being subjected to vibrations from other sources. (5) Air springs Rubber balls, tires, and other rubber containers with air sealed inside can be used as shock absorbers because they absorb the energy of vibrations and shocks. The tires used in automobile and bicycle wheels are also a type of air spring. Air springs are used in buses and subway cars to support the body of the car. They have the effect of reducing vibrations and shocks caused by unevenness in roads or rails, improving the ride comfort. (6) Dashpot It consists of a cylinder and a piston, with oil inside the cylinder. There is a small hole in part of the piston, and the oil inside the cylinder can flow out in front of and behind the piston through this hole. When an impact force is applied to the piston, the oil flows through the small hole, but because the hole is small, the oil flows slowly. Therefore, the piston does not move suddenly, but slowly. In other words, it is possible to soften the impact applied to the piston. This is called a dashpot, and is widely used as a shock absorber. For example, when an airplane lands and the wheels of the landing gear touch the runway, dashpots are attached to the landing gear to absorb the impact so that the aircraft is not subjected to an impact force. Dashpots are also attached between the axles and the body of the car to prevent the impact from unevenness in the road from being transmitted to the body of the car. (7) Foam rubber Plastic that contains many small holes, like expanded plastic, is called foam rubber and is used for cushioning purposes. When transporting goods, wrapping the product in foam rubber and placing it in a wooden or paper container can cushion the shocks and vibrations that occur during transport and prevent damage to the product. [Hidetaro Nakayama] ©Shogakukan "> Main types of shock absorbers Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
運動体と他の物体または固定壁との間で運動エネルギーを吸収し、物体に加わる振動や衝撃を和らげるばね、防振ゴム、油圧装置などをいう。往復運動をするものがあると、そこから振動が伝わってくる、回転部分に不つり合いがあると振動がおこる、あるいは共振状態になると振動が激しくなるというように、振動の原因はいくつかある。したがって、振動を防ぐのにはその原因を取り除けばよい。たとえば自動車のエンジンの振動を少なくするのには、シリンダーの数を増やし、ピストンの運動する方向を調整して振動の原因を極力小さくする。回転体の場合には、つり合い試験機などで不つり合い量を測定し、それを削り取ったり、また回転中心の反対側に余分のおもりをつけるなどしてなるべく不つり合いの量を小さくする。共振を避けるのには、振動数をなんらかの方法で変えるとか、あるいは共振した場合にその振幅があまり大きくならないように振動を減衰させるくふうをする。しかし、自動車のように、速度が広い範囲に変動し、道路の凹凸により車体に加わる振動はその原因を取り除くことができないので、車体の振動を少なくするために各種の緩衝装置が用いられる。 (1)リーフスプリング(板ばね) 振動や衝撃を吸収するのにもっとも普通に用いられているのはスプリング(ばね)である。ばねはコイルばね、板状のものなどがある。板状のものを何枚か重ねたものをリーフスプリングといい、自動車、貨車、客車などに車軸と車体との間に取り付けられて、道路やレールからの激しい振動が車体に伝わるのを防いでいる。 (2)コイルばね 鋼鉄の針金をコイル状に巻いたもので、針金の径は大小さまざまである。コイルばねの径もいろいろあり、目的によって使い分ける。エンジンやモーターなどを取り付けるときに、取付け台との間にコイルばねを入れて、エンジンなどの振動が伝わるのを防いだり、またエンジン自身が激しく振動するのを防いだりする。 (3)トーションばね(ねじりばね) 棒の一端を固定し、他端をねじると、そのねじり角があまり大きくないときには、ねじる力を取り除くと棒のねじり変形はもとに戻る。ねじられたときにねじり力によるひずみエネルギーを蓄えるので、外力による衝撃などを和らげるのに使用できる。これをトーションばねといい、自動車の車軸と車体との間で緩衝用に使用されている。 (4)防振ゴム ゴムは外力を加えると変形するが、金属などと違って変形がかなり大きくても、外力を取り除いたときにもとに戻る性質をもっている。すなわち変形量が大きくても弾性的性質を失わない。またゴムはその内部に粘性的性質をもち、外力のエネルギーをよく吸収する。したがって振動の防止、衝撃を和らげる部材として都合がいい。防振ゴムは普通、金属の板にゴムを接着したものが用いられ、その形はいろいろある。2枚の金属の板の間にゴムを挟んだもの、あるいは大小二つの円筒の間にゴムを挟んだものなどである。引張り力、圧縮力、剪断(せんだん)力、あるいはそれらの力が組み合わせられて加わった場合でも衝撃や振動をよく吸収するので、自動車のエンジンを車体に取り付けるのに防振ゴムを介して行っている。モーター、工作機械などから発生する振動、あるいは衝撃を床に伝えないために防振ゴムの上に設置したり、また他からの振動が加わらないように測定器を防振ゴムで支えるなど、各方面で使用されている。 (5)空気ばね ゴムまり、タイヤのようにゴム製の容器の中に空気を密閉したものは、振動や衝撃のエネルギーを吸収するので緩衝用として使用できる。自動車や自転車の車輪に使用しているタイヤも空気ばねの一種である。バスあるいは地下鉄の車両で車体を支えるために空気ばねが使用されている。道路あるいはレールなどの凹凸による振動や衝撃を和らげ、乗り心地をよくする効果がある。 (6)ダッシュポット シリンダーとピストンからなり、シリンダーの中に油が入っている。ピストンの一部に小さな穴があいていて、シリンダー内の油はこの穴を通してピストンの前後に流れ出ることができる。ピストンに衝撃力が加わった場合、油は小さな穴を通って流れるが、穴が小さいので油の流れはゆっくりしている。したがって、ピストンは急激には動かないでゆっくりと動く。すなわちピストンに加わった衝撃を緩和することができる。これをダッシュポットといい、緩衝装置として広く用いられている。たとえば飛行機が着陸するときに脚の車輪が滑走路に接するとき機体に衝撃力が加わらないように、脚の部分にダッシュポットがついていて、衝撃を吸収する。また自動車の車軸と車体との間にもダッシュポットをつけ、道路の凹凸による衝撃が車体に伝わらないようになっている。 (7)フォームラバー 発泡プラスチックのように、小さな穴をたくさん含んでいるプラスチックをフォームラバーといい、緩衝用に使用する。荷物を輸送するときなど、製品をフォームラバーで包み、木あるいは原紙の容器に入れれば輸送途中に加わる衝撃や振動を和らげ、製品の破損を防止することができる。 [中山秀太郎] ©Shogakukan"> 緩衝装置のおもな種類 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
Recommend
Hara
…He is the chief deity of Hinduism, along with Vi...
X-ray computed tomography
… [Medical Use] X-ray photography is the most fam...
Edition of the Nouvelle Ruby Française - Edition of the Nouvelle Ruby Française
…Founder of a major French publishing house. In 1...
Snow patch
Snow that does not melt and remains in mountain v...
Noguchi House
A manor located in Funai-gun, Tanba Province (curr...
Flashover
A state in which electrodes in a gas are bridged b...
Political Economy Club
…He retired from the front line of the business w...
Men's makeup - Otoko no Kesho
...Creams and lotions contain medicinal plants or...
Tradescantia navicularis (English spelling)
… [Takabayashi Masatoshi]. … *Some of the termino...
Lindley, W.
In addition to draining sewage, they also serve a...
Pisonia alba (English spelling)
…[Kazuo Furusato]. … *Some of the terminology tha...
《Der blutige und sterbende Jesus》 (English notation) Derblutige und sterbende Jesus
...In fact, in the 18th century, the style of rel...
Scutellaria laeteviolacea (English spelling)
…[Murata Gen]. … *Some of the terminology that me...
Limonium tetragonum (English spelling) Limoniumtetragonum
… [Ken Inoue]. … *Some of the terminology that me...
Wart gong - Ibodora
...The gongs come in various sizes, with diameter...