Eye socket - Ganka
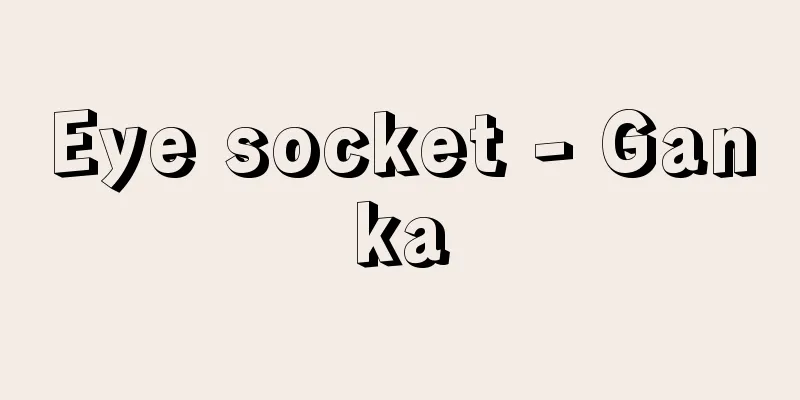
|
The orbital cavity is a pair of depressions formed by the skull (facial skull) that form the face to accommodate the eyeball and its associated tissues (eye muscles, blood vessels, nerves, lacrimal gland and its appendages, and orbital fat tissue around the eyeball). Its overall shape is a four-sided cone. Its base is the orbital entrance, and its tip faces posterior-medially. Therefore, if the long axes of the left and right orbits are extended, they intersect at the internal occipital protuberance at the posterior end of the inner surface of the occipital bone. The optic canal is formed at the posterior end of the orbit. The bone walls that form the orbit include the ethmoid bone, sphenoid bone, maxilla, and lacrimal bone on the medial wall (nasal side), and the frontal bone and parts of the sphenoid bone on the upper wall. The maxilla, frontal bone, and palatine bone are involved in the lower wall, while the sphenoid and zygomatic bones are involved in the lateral wall (temporal side). Of the four sides, the medial wall is the thinnest. Above and below the orbital wall are bony gaps called the superior orbital fissure and the inferior orbital fissure, through which the nerves and arteries and veins related to the eye enter and exit. The optic nerve and ophthalmic artery pass through the optic canal. Most of the eye muscles that control eye movement (oculomotor muscles) arise from the common tendon ring that surrounds the inside of the optic canal and superior orbital fissure, and are attached to the eyeball. In the anterior part of the medial orbital wall is a depression called the lacrimal sac fossa, which contains the lacrimal sac. Tears that accumulate in the lacrimal sac flow through the nasolacrimal duct into the inferior nasal meatus. The volume of the eye socket is approximately 26.0 cubic centimeters in men and 23.0 cubic centimeters in women. [Kazuyo Shimai] [Reference] |©Shogakukan "> Names of parts of the skull Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
顔面を形づくっている頭蓋骨(とうがいこつ)(顔面頭蓋)が、眼球およびその付属組織(眼筋、脈管、神経、涙腺(るいせん)とその付属器、眼球周囲の眼窩脂肪組織)を収容するために形成した1対の陥凹部のことで、全体の形態は四面錐体(すいたい)形をしている。その底面は眼窩入口にあたり、先端部は後内側方向を向いている。したがって、左右両眼窩の長軸を延長すると、後頭骨内面後端の内後頭隆起の部分で交差する。眼窩後端部には視神経管がつくられている。眼窩を形成している骨壁は内側壁(鼻側)では篩骨(しこつ)、蝶形骨(ちょうけいこつ)、上顎骨(じょうがくこつ)、涙骨が関与し、上壁では前頭骨と蝶形骨の一部が関与する。下壁では上顎骨、前頭骨、口蓋骨(こうがいこつ)が関与し、外側壁(側頭側)では蝶形骨と頬骨(きょうこつ)が関与する。四面のうち、内側壁がもっとも壁が薄い。眼窩壁の上と下には、上眼窩裂および下眼窩裂という骨間隙(こつかんげき)があり、眼球に関係する神経や動静脈が出入りする。視神経管には、視神経、眼動脈が通っている。眼球の運動をつかさどる眼筋(動眼筋)の大部分は、視神経管と上眼窩裂の内側を囲む総腱輪(そうけんりん)からおこり、眼球に付着している。眼窩内側壁の前部には涙嚢窩(るいのうか)というくぼみがあり、涙嚢を入れる。涙嚢にたまった涙液は鼻涙管を通って下鼻道に出る。眼窩の容積は男子で約26.0立方センチメートル、女子で約23.0立方センチメートルとされている。 [嶋井和世] [参照項目] |©Shogakukan"> 頭蓋の各部名称 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
Recommend
Accessories - akusesarii (English spelling)
A general term for accessories and attachments. O...
Organization Internationale de Radiodiffusion et Télévision
…[Kazuhiko Goto]. … *Some of the terms mentioned ...
Foot print
…In the broadest sense, it is the trajectory of a...
Rhododendron quinquefolium (English name) Rhododendronquinquefolium
…[Yoshiharu Iijima]. … *Some of the terminology t...
Agatsuma Line
A railway line operated by JR East, which connects...
Ulugh Muhammed - Urugumuhammed
…One of the successor states to the Kipchak Khana...
Evgeniy Aleksandrovich Mravinskiy
Russian conductor. He studied composition and con...
NEA - New Energy Agency
The abbreviation for the National Education Associ...
Ring toss - Ring toss
A type of game. Players throw rings made of metal...
Hill, J.
...The IWW was a precursor to the Congress of Ind...
gueux
…At this time, his aide, Berlémond, whispered in ...
Iimori Copper Mine
…Agriculture, centered on the cultivation of mand...
Pine root oil; wood turpentine oil
An oil made by low-temperature (below 400°C) dry d...
Himalayan cedar
An evergreen coniferous tall tree of the Pinaceae...
Pyatachok
… [Monetary system] The metric system has been us...