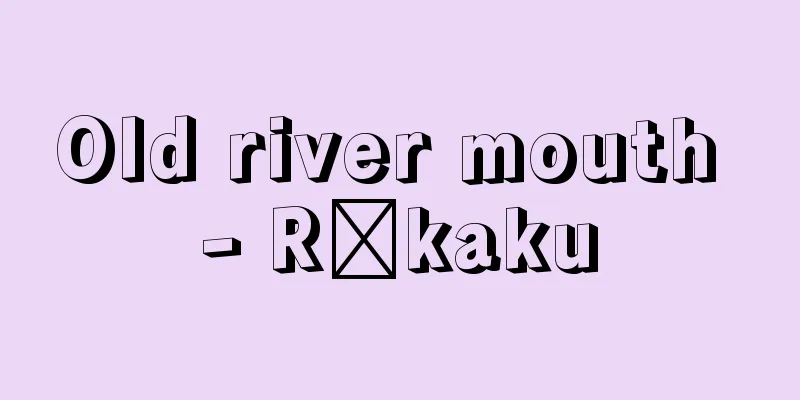Carolingian dynasty (English spelling) Carolingiens French

|
A dynasty that ruled the latter half of the Frankish Kingdom, replacing the Merovingian dynasty. Its name is derived from the most prominent member of the family, Charlemagne, but it is also called the House of Arnulf or House of Pepin, as its royal lineage can be traced back to Arnulf, Bishop of Metz, and Pepin the Elder, a powerful ruler in Austrasia. Pepin the Elder's son Ansegisel and Pepin the Elder's daughter Begga were the sons of Arnulf and Begga, and he became mayor of the palace of Austrasia, laying the foundation for the rise of the Carolingian dynasty. Pepin the Elder defeated Neustria at the Battle of Tertry in 687 and became mayor of the palace of the entire Frankish kingdom, and his illegitimate son Charles Martel defeated Muslims who had invaded from Spain at the Battle of Tours and Poitiers in 732, establishing the authority of the Carolingian dynasty. With this power as a backdrop, he deposed the nominal king of the Merovingian dynasty in 751 and took the throne himself, founding the Carolingian dynasty. Pepin's kingship was given legitimacy by the approval of Pope Zacharias, and this marked the beginning of an alliance between the Carolingian monarchy and the papacy. The Carolingian Kingdom reached its height under Pepin the Short's son, Charlemagne, who achieved political unification of most of Western Europe, stretching from the Pyrenees in the west to the Elbe River in the east, and from the North Sea in the north to central Italy in the south. In 800, Charlemagne was crowned Roman Emperor by Pope Leo III. Charlemagne also devoted himself to the revival of classical culture, and thanks to the efforts of many scholars, including Alcuin, the results were what would later be known as the Carolingian Renaissance. After the death of Charlemagne's son Louis I (Louis the Pious), the empire was divided among his three sons (Treaty of Verdun). His eldest son Lothar inherited the throne of Lorraine, Burgundy, and Italy, his second son Louis inherited East Francia, and his youngest son Charles (Charles I) inherited West Francia. Furthermore, due to the extinction of Lothar's bloodline, Lorraine was also divided between the East and West Frankish kingdoms (Treaty of Merssen), and the Carolingian dynasty in East Francia was extinguished with the death of the infant king Louis in 911, and the Carolingian dynasty in West Francia with the death of Louis V in 987. As a result, the Kingdom of Germany (Duke of Saxony) was established in the East Frankish Kingdom through Conrad I, and the Kingdom of France (Duke of Capetian) was established in the West Frankish Kingdom. [Shosuke Hirajo] [References] | |©Shogakukan "> Carolingian dynasty/brief family tree Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
メロビング朝にかわって、フランク王国の後半を支配した王朝。この名称は家門中もっとも傑出した人物、カール大帝にちなんだものであるが、王家の系譜がメッツ司教アルヌルフおよびアウストラシア地域の大豪族大ピピンにさかのぼるため、アルヌルフ家またはピピン家ともよばれる。アルヌルフの息子アンセギゼルと大ピピンの娘ベッガとの間に生まれたのが中ピピンで、アウストラシアの宮宰となり、カロリング家興隆の基礎を置いた。中ピピンは687年テルトリーの戦いでノイストリアを破り、全フランク王国の宮宰となり、その庶子カール・マルテルは732年トゥール・ポアチエの戦いでスペインから侵入したイスラム教徒を敗走させ、カロリング家の権威を確立した。その子小ピピンはこの力を背景に、751年メロビング家の名目的国王を廃して自ら王位につき、カロリング朝を開いた。ピピンの王位は教皇ザカリアスの承認によって正当性を与えられ、ここからカロリング王権と教皇権との提携が始まった。カロリング王国は小ピピンの子カール大帝(シャルルマーニュ)のとき最盛期を迎え、西はピレネー山脈から東はエルベ川に、北は北海から南は中部イタリアに至る西ヨーロッパの大部分の政治的統一が達成され、800年、カールは教皇レオ3世の手でローマ皇帝として戴冠(たいかん)された。カールはまた古典文化の復興にも力を注ぎ、アルクインをはじめ多くの学者たちの努力により、後世カロリング朝ルネサンスとよばれる成果が実現された。 カール大帝の子ルートウィヒ1世(ルイ1世、敬虔(けいけん)帝)の死後、帝国は3人の息子に分割された(ベルダン条約)。長子ロタールはロートリンゲン、ブルグンド、イタリアと皇帝位を、次子ルートウィヒは東フランクを、末子カール(シャルル1世)は西フランクを相続。さらにロタールの血統の断絶により、ロートリンゲンも東西フランク王国によって分割され(メルセン条約)、東フランクのカロリング家は911年のルートウィヒ幼児王の死により、西フランクのカロリング家は987年のルイ5世の死により断絶した。その結果、東フランク王国では、コンラート1世を経てザクセン朝のドイツ王国が、西フランク王国では、カペー朝のフランス王国が成立した。 [平城照介] [参照項目] | |©Shogakukan"> カロリング朝/略系図 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
>>: Caroline Islands - Caroline
Recommend
Toshio Irie
…It was discussed whether Heavener's back cra...
Shida Rinzaburou - Shida Rinzaburou
Electrical engineer. Born in Hizen Province (Saga...
How to identify -
This method of public notice has been recognized ...
linear energy transfer
…It is an abbreviation for linear energy transfer...
Hanshin Expressway - Hanshin Expressway
This is a toll expressway built in Osaka City, Ko...
Tokyo Winter Hazel - Tokyo Winter Hazel
An evergreen shrub or small tree of the Hamamelid...
Kanhotai - Intermediate
…There are plates with rows of small holes and pl...
Gunboat - Houkan (English spelling) Gunboat
A relatively small, slow warship used for patrolli...
Acupuncture - Acupuncture
A metallic needle or needle-like instrument used f...
Pearse, W.
…Irish educator and man of letters. Leader of the...
Borderline schizophrenia
These are cases that are positioned on the border ...
Bipalium trilineatum (English spelling)
… [Minoru Imajima]. … *Some of the terminology th...
Blood Center
A facility that acts as an intermediary between p...
Asian giant hornet - giant hornet
…Many species of hornets are found mainly in temp...
Giant Panda
...The recorded lifespan in captivity was 13 year...