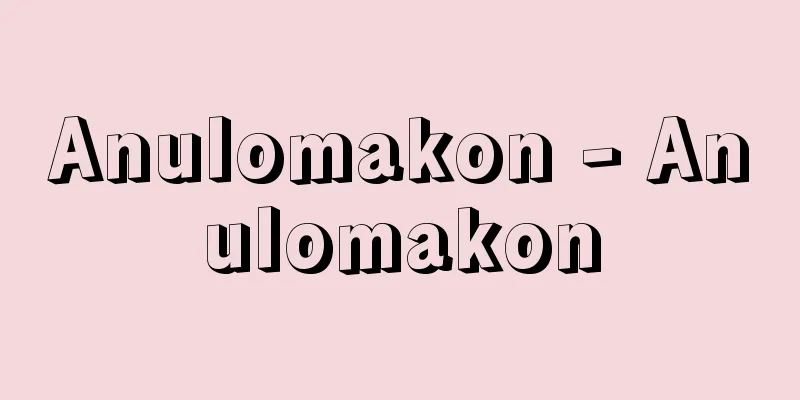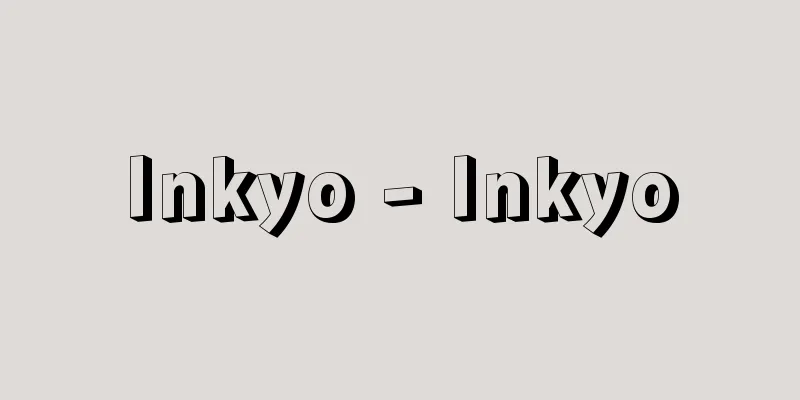Chrome Yellow

|
A pigment whose main component is lead chromate (II) PbCrO4 , also known as chrome yellow. It is the third most produced colored pigment after carbon black and red iron oxide. The color ranges from pale yellow to orange-red, depending on the manufacturing method and composition. The manufacturing process involves dissolving lead monoxide in nitric acid to make lead nitrate, and then adding aqueous solutions of sodium dichromate and sodium sulfate to this in the case of yellow chrome 10G and yellow chrome chrome 5G to produce a solid solution of Pb(SCr) O4 . Yellow chrome G is made of lead chromate (II). The crystal structure is also orthorhombic in yellow chrome 10G on the lead sulfate (II) side, while yellow chrome chrome 5G and yellow chrome G on the lead chromate (II) side are monoclinic. Yellow chrome R is obtained by adding an alkaline aqueous solution to lead chromate (II) and heating it, and is thought to have a composition of PbO・PbCrO4 , but in X-ray analysis, some samples show diffraction peaks that match PbO・PbCrO4 , while others show different diffraction patterns, and it is presumed that the composition changes to some extent depending on the conditions of the alkaline treatment. Yellow Chromium 5R has the same composition as Yellow Chromium R, but the particle size is different. The spectral reflectance curve also changes in the order of Yellow Chromium 10G → 5G → G → Yellow Chromium R, with the absorption from the ultraviolet region gradually becoming stronger and penetrating into the visible region, from yellow due to the green of 10G to yellow for 5G and Yellow Chromium G, and then yellow-orange to orange for Yellow Chromium R and Yellow Chromium 5R, which have absorption penetrating into the green region at about 520 millimicrons. It is used to color paints, printing inks, and plastics. [Jun Otsuka] The curve has sharp undulations and the color tone is clear. As the curve moves to the right (longer wavelengths), the color changes from yellow to orange. ©Shogakukan "> Spectral reflectance curve of yellow lead Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
クロム酸鉛(Ⅱ)PbCrO4を主成分とする顔料で、クロムエローともいう。生産量は有色顔料中カーボンブラック、べんがらに次ぎ、主要な顔料である。色調は製法、組成により淡黄から橙赤(とうせき)まである。 製法は、一酸化鉛を硝酸に溶かして硝酸鉛とし、これに黄鉛10Gおよび黄鉛5Gの場合は二クロム酸ナトリウムと硫酸ナトリウムの水溶液を加えPb(SCr)O4の固溶体を生成させる。黄鉛Gはクロム酸鉛(Ⅱ)からできている。結晶構造も、硫酸鉛(Ⅱ)側の黄鉛10Gでは斜方晶、クロム酸鉛(Ⅱ)側の黄鉛5Gおよび黄鉛Gでは単斜晶となる。黄鉛Rはクロム酸鉛(Ⅱ)にアルカリ水溶液を加えて加熱すると得られ、PbO・PbCrO4の組成と考えられているが、X線分析では試料によりPbO・PbCrO4と一致する回折ピークを示すものや、異なった回折パターンを示すものもあり、アルカリ処理の条件により、ある程度組成に変化があると推定される。 黄鉛5Rの組成は黄鉛Rと同じで、粒子の大きさが違う。分光反射率曲線も黄鉛10G→5G→G→黄鉛Rの順に、紫外部からの吸収がしだいに強く可視部に食い込み、10Gの緑によった黄から5G、黄鉛Gの黄、さらに吸収が約520ミリミクロンの緑の部分まで食い込んでいる黄鉛R、黄鉛5Rでは黄橙色から橙色になる。塗料、印刷インキ、プラスチックの着色に用いられる。 [大塚 淳] 曲線の起伏がシャープで、色調は鮮明。曲線が右(長波長側)に移動するにつれ、黄→橙となる©Shogakukan"> 黄鉛の分光反射率曲線 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
Recommend
Angora rabbit fur - Angora rabbit fur
…Sheep wool is the hair cut from sheep, also call...
Anne of Green Gables
…Canadian author. Her eight-volume Anne series, w...
Khūzistān (English spelling)
A region in southwestern Iran, downstream of the Q...
Kikunori - Kikunori
… In addition, there are varieties of chrysanthem...
Yabase Oil Field - Yabase Yuden
This oil field is located in the western part of ...
Weighted equivalent continuous perceived sound level
...When judging compliance with environmental sta...
Mario Castelnuovo‐Tedesco
1895‐1968 A Jewish composer born in Italy. His tal...
Apotheke - Apotheke
… Pharmaceuticals [Takashi Tatsuno] [Western] Alr...
Kandoh
...Located in the upper reaches of the Shirakawa ...
Diligence - Shojin
To make an effort wholeheartedly. To eliminate ev...
Kenji Kawata
1900-1995 Labor activist and politician from the ...
Miyama [town] - Miyama
An old town in Kitamuro District facing the Kumano...
Santa Fe
The capital of northern New Mexico in the United S...
VC - VC
Abbreviation for Vibration Compensation. Name of T...
Meng Jiangnu - Moukyou
A woman who appears in ancient Chinese tales. Whe...