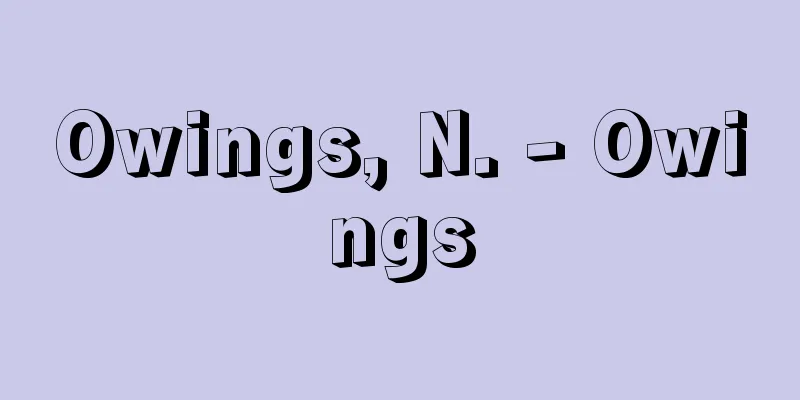Calyx

|
A calyx is the outer ring of the perianth (heteroperanth flower), which is one of the components of a flower and has two clearly distinguishable rings, the inner and outer rings. It is usually smaller and thicker than the inner ring (corolla), is green due to the presence of chlorophyll, and is often hairy on the outer surface, protecting the internal organs of the flower when it is in bud. However, in plants such as the Ranunculaceae, the calyx often turns colored and becomes petal-like, and serves to attract insects. The flower leaves that are made up of the calyx are called sepals and are considered to be homologous to leaves. In plants such as the Magnoliaceae, the sepals are separate and fall off after the flower has finished blooming. In plants such as the poppy, the calyx falls off earlier than the corolla, accompanying flowering. In many families, the calyx is persistent, but the persistent calyx attached to the fruit is called the calyx. In plants such as the Chinese lantern plant, the calyx grows after flowering and covers the fruit. Like the corolla, in advanced flowers the sepals are fused together to form a gamopetalous calyx. The upper part of the gamopetalous calyx is usually divided into lobes and the lower part is tubular, but when the tubular part extends to encase the ovary, it is called the calyx tube. Usually, the corolla and stamens are attached around the base of the calyx lobes, so the ovary is generally inferior in flowers that form a calyx tube. In the Asteraceae family, the calyx lobes are often degenerate and are transformed into scales or pappus. [Michio Tamura] ©Shogakukan "> Names of the parts of angiosperm flowers Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
花の構成要素の一つで、内外2輪がはっきり区別できる花被(かひ)(異花被花)の外輪を萼という。普通は内輪(花冠)よりも小さくて厚く、クロロフィルを含み緑色を呈し、外面には毛があるものが多く、つぼみの状態で花の内部の諸器官を保護する。しかし、キンポウゲ科などでは萼は色づいて花弁状になるものが多く、昆虫誘引の役目をもつ。萼で構成している花葉(かよう)は萼片とよばれ、葉と相同と考えられる。モクレン科などのようにそれぞれの萼片は離生し、花が終わると落ちるものが原始的とみなされる。ケシなどでは萼は花冠よりも早く、開花に伴って落ちる。多くの科では萼は宿存するが、果実についている宿存萼はへたとよばれる。ホオズキなどでは萼は花期後に成長して果実を包むようになる。花冠と同様に、進化した花では各萼片は合着して合弁萼となる。 合弁萼の上部は普通は裂片に分かれ、下部は筒状となるが、筒状部が伸長して子房を包むようになったものを萼筒(がくとう)という。普通、萼裂片の基部のあたりに花冠や雄しべがつくので、萼筒を形成する花は一般に子房は下位となる。キク科では萼裂片は退化しているものが多く、また変形して鱗片(りんぺん)や冠毛になる。 [田村道夫] ©Shogakukan"> 被子植物の花の各部名称 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
>>: Kagu - Kagu (English spelling) kagu
Recommend
Stable azoic dyes - Antiazoic dyes
…Printing paste consists of paste, dye, chemicals...
Hinokumadera Temple
This temple was located in Asuka Village, Takaichi...
Tsunezumi - Tsunezumi
An area in the eastern part of Mito City, Ibaraki...
Adrenergic nerve blocking drugs
... Clinically, they are used to treat arrhythmia...
Court tennis
...It was only with the accumulation of long pole...
Waiver of inheritance rights - Iryubun no broom
...In addition, the right to claim for reduction ...
Preretinal bleeding
...Pathological bleeding occurs when blood is rel...
Dopamine - dopamin (English spelling) dopamine
4-(2-aminoethyl)-1,2-benzenediol. Its chemical fo...
Investiturstreit
Conflicts between the Pope and secular monarchs, e...
Harvestman - Harvestman (English spelling)
A general term for arthropods belonging to the ord...
Shintaro Ishihara
Novelist. Born in Hyogo Prefecture. Graduated from...
Surplus - joyokin (English spelling) surplus
In accounting, it refers to the amount of shareho...
Ilahabad (English spelling)
...It is also one of the most important holy plac...
Japanese literature
The Japanese people, surrounded by the sea, have ...
Matsukawa [village] - Matsukawa
A village in Kitaazumi County in northwest Nagano ...