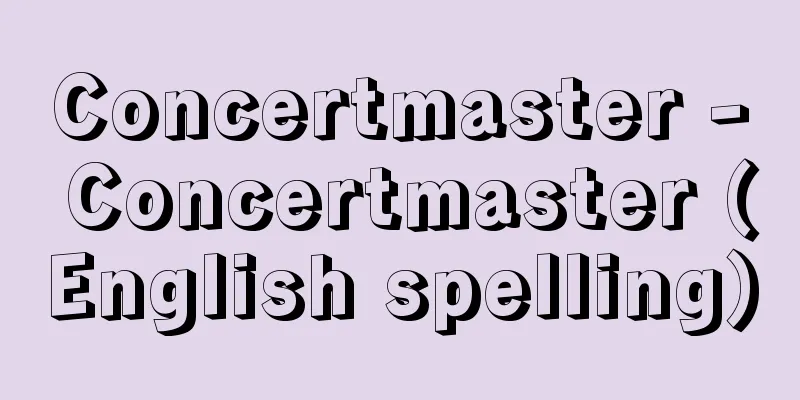Eight Laws of the Eiji Character

|
The character 永 (eight strokes) has been used since ancient times as a method for the transmission and learning of calligraphy, under the name of the "eight methods of the character 永" (eight strokes), because each stroke of the character 永 (eight) is interpreted as embracing all the fundamentals of calligraphy (brush strokes). The names of each part are given according to the stroke order: (1) soku (side) (first stroke dot), (2) roku (second stroke horizontal stroke), (3) do (third stroke vertical stroke), (4) teki (fourth stroke plectrum), (5) saku (strategy) (fifth stroke, a stroke drawn from the left to the upper right), (6) ryaku (sixth stroke, a stroke drawn from the left to the lower left), (7) taku (seventh stroke, a stroke drawn from the right to the lower left), and (8) taku (eighth stroke, a stroke drawn from the left to the lower right). The names are very apt for the strokes that radiate up, down, left, and right. According to the theory of Han Fanming of the Tang Dynasty, its origins lie in the time when clerical script was born, and it was passed down from Cui Yan of the Later Han Dynasty to Zhong Yao, Wang Xizhi, and Zhi Yong, who then passed it on to Zhang Xu in the Tang Dynasty. It is also said to have been invented by Cai Yong (133-192) of the Han Dynasty, as stated in the Wakan Sansai Zue, Volume 27, that "The eight methods of ancient calligraphy written by Cai Yong are many and eternal, and the eight methods have the power to communicate everything" (Wakan Sansai Zue, Volume 27). It is said to have been invented by Cai Yong of the Han Dynasty, but the exact creator is unknown. It was imported to Japan during the Edo period, and became popular as a convenient way to teach beginners how to write. [Mitsuharu Kanzaki] ©Shogakukan "> Eight Laws of Eternity Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
「永」の字の各点画が、書法(用筆法)上のすべての基本を包含している、という解釈から、古くから「永字八法」の名で、書法伝授や手習いの初歩的段階の一方法として用いられてきた。各部の名称は筆順に従って、(1)側(そく)(第一筆の点)、(2)勒(ろく)(第二筆の横画)、(3)努(ど)(第三筆の縦画)、(4)趯(てき)(第四筆の撥)、(5)策(さく)(第五筆、左から右上に引く画)、(6)掠(りゃく)(第六筆、続いて左下へ引く画)、(7)啄(たく)(第七筆、右から左下に引く画)、(8)磔(たく)(第八筆、左から右下に向かって引く画)の8法。上下左右に放射する筆画に、実に的確な名称を冠している。唐時代の韓方明(かんほうめい)の説によれば、その起源はすでに隷書(れいしょ)体の生まれたころにあり、後漢(ごかん)時代の崔瑗(さいえん)より鐘繇(しょうよう)、王羲之(おうぎし)、智永(ちえい)に伝えられ、さらに唐に入り張旭(ちょうきょく)に相伝されたという。また「八法乃蔡邕(さいよう)所書古人用筆之術多於永字取法以其八法之勢能通一切勢也」(『和漢三才図会』巻27)とあり、漢時代の蔡邕(133―192)の考案ともいうが、確かな創案者は不明である。わが国には江戸時代に輸入され、手習いの初学者へ指導の便法として流行した。 [神崎充晴] ©Shogakukan"> 永字八法 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
>>: Wi-ssi Chosǒn (English spelling)
Recommend
LRCS - LRCS
League of Red Cross Societies . Founded in 1919 as...
Kinyo Wakashu - Kinyo Wakashu
This was the fifth imperially commissioned anthol...
Crocus chrysanthus (English spelling) Crocuschrysanthus
…[Hiroshi Aramata]. … *Some of the terminology th...
Doliolum denticulatum (English spelling) Doliolum denticulatum
…It is found in the warm waters of the world'...
Rice Year - Inadashi
…The Bontoc Igorot people of the Philippines, who...
Ultramarine
…After wandering around the world, he moved to Ca...
Shinagawa
This area is located in the northeastern part of ...
Family: Angelfish
...Until recently, the scientific name of this sp...
Necklace - Neck ornament
Also known as necklaces. Necklaces have been used ...
devilfish
...The name comes from the fact that there are ba...
Kuichou County - Kuichou County
...Population: 390,000 (1994). Qiuzi County was e...
National Stadium - National Stadium
A special corporation and the stadium under its j...
Phasianidae
...This is thought to be due to the Helvestre bod...
Divine Song - Kamiuta
〘Noun〙① Songs sung by gods. Songs said to have bee...
Paradise Nuts (English spelling)
The seeds of several species of the genus Lecythis...


![Yunokoya [Hot Spring] - Yunokoya](/upload/images/67cd14bed2bf8.webp)