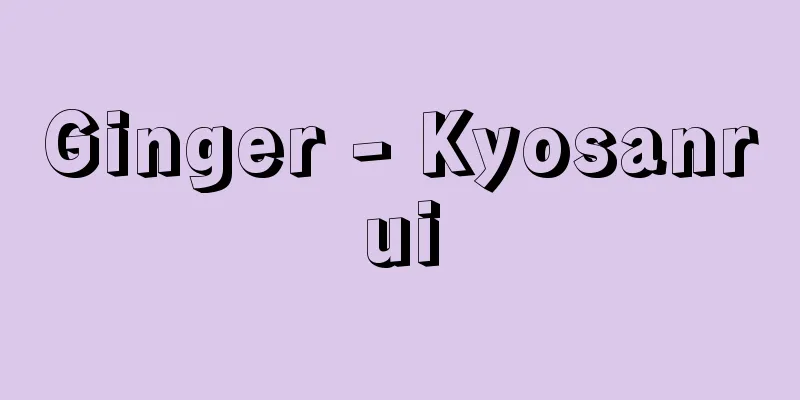Safety lamp - Anzento (English spelling)

|
A lighting device used in coal mines where explosive methane gas exists. Cap lamp-type safety lights, which are equipped with a battery carried on the waist and a lamp attached to a safety hat, are designed to electrically and physically prevent methane gas from igniting. They were imported and popularized in the late Meiji period, and began to be produced domestically around 1933 (Showa 8). Prior to that, volatile oil safety lights were used. In the early 19th century, coal mines in England were plagued by frequent gas explosions caused by ignition sources from lighting fixtures inside the mines. British chemist Davy observed that when a fine wire mesh is held over a gas flame, even if flammable gas is present above the mesh, it does not ignite through the mesh. Based on this, in 1815 he invented a safety lamp in which a volatile oil flame was enclosed in a wire mesh tube. Around the same time, WR Clanny and G. Stephenson, independently of Davy, invented safety lights based on a similar principle. Davy lights were dim and insufficient as lighting devices because they only used wire mesh, but Cluny lights were made of waist glass and wire mesh and were excellent as lighting devices. Later, Wolf of Germany improved on them and introduced them to Japan, and Wolf lights became synonymous with safety lights. When methane gas enters a safety light, the flame extends in proportion to the gas concentration, so the gas concentration can be determined by measuring the length of the flame. Safety lights are no longer used as lighting devices, but are recognized as simple flammable gas detectors. [Nobuo Fusamura] Usually, a mantle is attached to the outside of the wire mesh (shrouded door type or bonnet type) . Safety lamp structure Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
爆発性のメタンガスが存在する炭鉱の坑内で使用する照明具。蓄電池を腰に携帯し、安全帽に灯部を装着するキャップランプ形安全電灯は電気的、物理的にメタンガスに着火しないように作られていて、明治後期に輸入されて普及、1933年(昭和8)ごろから国産化された。それ以前は揮発油安全灯が使用された。19世紀の初期、イギリスの炭鉱では坑内照明具が着火源となってガス爆発が多発して困っていた。イギリスの化学者デービーはガスの炎の上に目の細かい金網をかざすと、たとえ金網より上に燃焼性のガスが存在していても、網を通してこれに着火することはないという現象を観察し、これに基づいて1815年に、揮発油の炎を金網の筒で包んだ安全灯を発明した。同じころデービーとは独立にクラニーW. R. ClannyやスティーブンソンG. Stephensonらも同様な原理の安全灯を発明した。デービー灯は金網だけを用いていたので照明具としては暗く不十分であったが、クラニー灯は腰ガラスと金網からなり照明具として優れていた。のちにこれをドイツのウルフ社が改良し日本にも導入され、ウルフ灯は安全灯の代名詞のようになった。メタンガスが安全灯の灯内に入ると、ガスの濃度に比例して炎が伸びるので、炎の長さを測ってガス濃度を知ることができる。安全灯は現在照明具としては使用されていないが、簡易可燃性ガス検知器として認められている。 [房村信雄] 普通、金網の外側に外套をつける(よろい戸型またはボンネット型)©Shogakukan"> 安全灯の構造 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
Recommend
Emperor Shunzhi
The third emperor of the Qing Dynasty of China (r...
talc
...A type of magnesium clay mineral. Also called ...
scirocco
… Santa AnaA northerly, dry, hot wind accompanied...
Africa Expedition - Africa Exploration
[Ancient and Middle Ages] The earliest African ex...
Mathew B. Brady
1823‐96 American photographer. Born near Lake Geor...
Keesh - Keesh
...After the Abbasid Caliphate declined in the 10...
Nemeth (English spelling)
Born: April 18, 1901 in Nagybanya [Died] March 3, ...
XYZ Incident
…During his presidency, he faced fierce oppositio...
Tobias George Smollett
A British novelist born in Scotland. He was popul...
Shame - haji (English spelling)
When people experience feelings of shame, they ar...
Yangon - Yangon (English spelling)
The largest city in the Union of Myanmar (Burma)....
Coordinated water - Haisui (English spelling)
In the narrow sense, it refers to the water of cry...
Fujimori Seikichi
Novelist and playwright. Born on August 28, 1892,...
Kaiyo (English spelling) Joseph Caillaux
1863‐1944 A French radical politician. Originally ...
Sweet bamboo - Kanchiku
…The wood is hard and easy to split into small pi...
![Airbus Industry [company] - Airbus Industrie](/upload/images/67cf95e143a19.webp)