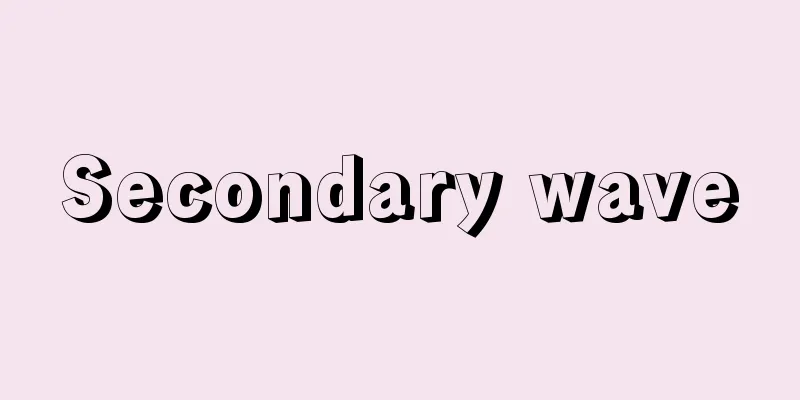Input-output table - Sangyōrenkanhyō (English name) input-output table

|
A statistical table showing the transactions of goods and services between industries over a certain period of time in a single matrix. It clarifies the economic structure of a country and is important basic data for many economic statistical surveys, including the System of National Accounts (SNA). It is also often used in economic spillover analysis, showing how production spreads to other industries when new demand arises in one industry. In Japan, in addition to the input-output table (national table) which is compiled every five years through the joint work of 10 government ministries and agencies, the following input-output tables are also compiled: regional input-output tables (compiled every five years by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry), prefectural and city input-output tables (compiled roughly every five years by prefectures and cities), extended input-output tables (which estimate the most recent industrial structure using the national table as a benchmark and are compiled annually by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry), international input-output tables (compiled by the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry and the Institute of Developing Economies), and various analytical input-output tables (compiled by various institutions depending on the purpose of analysis). Here, we will explain the structure of the input-output table and the main statistical tables using the national table as an example. [Nobuo Iizuka September 17, 2020] Structure of the Input-Output TableThe vertical direction (columns) of an input-output table shows how much raw material (intermediate input) an industry (called a sector) purchases from which sector, and how much of the goods and services it produces domestically. The value obtained by subtracting intermediate inputs from domestic production is called gross value added, and it shows how much was distributed to total wages (employee income), corporate profits (operating surplus), etc. In an input-output table, the breakdown (cost structure) of payments for raw materials, labor, etc. is called input. Meanwhile, the horizontal direction (rows) shows which sectors purchase the goods and services produced by a certain sector as raw materials (intermediate demand) and whether these are allocated to consumption, investment, exports, etc. (final demand). As some of these goods and services are covered by imports, the domestic production amount on the right-hand side of the row is calculated by adding up intermediate demand and final demand minus imports. The domestic production amount on the right-hand side of each sector's row is equal to the domestic production amount at the bottom of the column. In an input-output table, the breakdown of sales destinations (sales channel composition) of the goods and services produced in each sector, shown in each row, is called output. Because it shows the structure of inputs and outputs in this way, the input-output table is also called an input-output table (I/O table). The input-output table is provided as a basic transaction table. In the "2015 Input-Output Table" published in June 2019 (Reiwa 1), the basic classification was set as the most detailed sector classification, with 509 sectors (rows) x 391 sectors (columns). Based on this basic classification, basic transaction tables are also provided for the integrated minor classification (187 classifications), integrated medium classification (107 classifications), and integrated major classification (37 classifications), which integrate classifications with similar activities. In addition to the Basic Transaction Table, the Input-Output Table provides various other tables for the purpose of contributing to economic analysis. The input coefficient table shows the units of raw materials, etc. required to produce one unit in a certain sector. The inverse matrix coefficient table shows how much production will occur in each sector through the demand for goods and services (intermediate inputs) required for production in that sector when one unit of new final demand occurs in that sector. According to the 2015 (Heisei 27) input-output table, domestic production exceeded 1,000 trillion yen (approximately 1,018 trillion yen) for the first time since the table began to be compiled in 1955 (Showa 30). [Nobuo Iizuka September 17, 2020] Historical developmentsThe French physiocratic economist Francis Quesnay attempted to integrate various economic activities in society into sectors with common content and to grasp the interrelationships between these sectors in the mid-18th century, and published the results in his Tables de l'Economica. However, Quesnay only used this table as a tool for theoretically analyzing the social reproduction process of the economy, and only provided hypothetical numerical examples for the table. The first person to create an input-output table using actual data was the American economist William Leontief. He created input-output tables for the American economy in 1919 and 1929, and used them to achieve remarkable results in analyzing and forecasting the American economy. As a result, the usefulness of this method attracted the attention of government agencies in the United States and other countries. Especially after World War II, input-output tables were created by government agencies in European and American countries, and have been widely used in analyzing national economies and formulating policies. In Japan, the Ministry of International Trade and Industry (currently the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry) and the Economic Planning Agency (currently the Cabinet Office) prepared the "1951 Input-Output Table" for the first time in 1955. Since the 1955 Table, it has been prepared every five years by the Administrative Management Agency (later the Management and Coordination Agency, currently the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications) and other related ministries and agencies in collaboration. After the reorganization of ministries and agencies in January 2001, it has become the joint work of 10 ministries and agencies (Cabinet Office, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, Ministry of Finance, Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare, Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, Financial Services Agency, and Ministry of the Environment), and it has continued to be prepared to this day. In August 1978, when Japan's national income statistics were fully shifted to the new SNA standard set by the United Nations (UN), the Input-Output Table was incorporated into the calculation system as the Table of Output of Goods and Services by Economic Activity (V Table) and the Table of Input of Goods and Services by Economic Activity (U Table), linked to national income accounts, etc. However, because the SNA must be compiled annually, it is not possible to include sufficiently detailed input-output tables in it. Therefore, detailed input-output tables are currently compiled and published every five years separately from the SNA, while paying close attention to their relationship with the annual figures. [Tadashi Takashima and Nobuo Iizuka, September 17, 2020] [References] | | | | | | | |Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
産業間において一定期間に行われた財やサービス取引を一つの行列表(マトリックス)に示した統計表。一国の経済構造を明らかにし、国民経済計算(SNA)を始めとして多くの経済統計調査にとって重要となる基本データになっている。また、ある産業で新たな需要が発生した場合に、他の産業にどのように生産が波及しているかという経済波及分析に用いられることも多い。 日本では、10府省庁の共同作業による産業連関表(全国表)を5年ごとに作成しているほか、以下の産業連関表が作成されている。地域産業連関表(経済産業省が5年ごとに作成)、都道府県・市産業連関表(都道府県・市がおおむね5年ごとに作成)、延長産業連関表(全国表をベンチマークとして直近の産業構造を推計したもので、経済産業省が毎年作成)、国際産業連関表(経済産業省やアジア経済研究所が作成)、各種分析用産業連関表(分析目的に応じて各機関が作成)などである。 ここでは全国表を例に産業連関表の構造とおもな統計表について説明する。 [飯塚信夫 2020年9月17日] 産業連関表の構造産業連関表の縦方向(列)には、ある産業(部門とよばれる)がどの部門からどれだけ原材料を購入(中間投入)し、どれだけ財やサービスを国内生産しているかが記述されている。国内生産額から中間投入を差し引いたものは粗付加価値とよばれ、賃金総額(雇用者所得)、企業の利益(営業余剰)などにそれぞれどれだけ分配されたかが示されている。この原材料や労働力などへの支払いの内訳(費用構成)を、産業連関表では投入inputとよんでいる。 一方、横方向(行)には、ある部門が生産した財やサービスを、どの部門が原材料として購入(中間需要)し、消費、投資、輸出などに振り向けられているか(最終需要)を記述している。こうした財やサービスは、輸入でまかなわれているものもあるので、行の右端の国内生産額は、中間需要と最終需要を合計して、輸入を差し引いたものとして算出される。部門ごとの行の右端の国内生産額と、列の下端の国内生産額は等しくなっている。各行で示されている、それぞれの部門で生産された財・サービスの販売先の内訳(販路構成)を、産業連関表では産出outputとよんでいる。 このように、投入と産出の構造を示していることから、産業連関表は投入産出表input-output table(I/O表)ともよばれる。 産業連関表は、取引基本表として提供されている。2019年(令和1)6月に公表された「2015年産業連関表」では、もっとも詳細な部門の分類として基本分類は(行)509部門×(列)391部門とした。この基本分類に基づき、活動内容が類似した分類を統合した、統合小分類(187分類)、統合中分類(107分類)および統合大分類(37分類)の取引基本表も提供している。 産業連関表は、取引基本表以外にも、経済分析に資することなどを目的に、さまざまな表を提供している。投入係数表は、ある部門において1単位の生産を行う際に必要とされる原材料等の単位を示したものである。逆行列係数表は、ある部門に対して新たな最終需要が1単位発生した場合に、当該部門の生産のために必要とされる(中間投入される)財・サービスの需要を通して、各部門の生産がどれだけ発生するかを示している。 2015年(平成27)産業連関表では、1955年(昭和30)の産業連関表の作成開始以来、初めて国内生産額が1000兆円を超えた(約1018兆円)。 [飯塚信夫 2020年9月17日] 歴史的経過社会で行われるさまざまな経済活動を、内容の共通する部門ごとに統合し、それらの部門間の相互関連として把握する試みは、18世紀の中ごろにフランスの重農主義経済学者F・ケネーによって行われ、その成果は『経済表』として発表された。しかしケネーは、この表を経済の社会的再生産過程を理論的に分析するための用具として用いるにとどまり、表について仮説的な数字例を置いたにすぎなかった。実際のデータによる産業連関表を初めて作成したのはアメリカの経済学者W・レオンチェフである。彼は、1919年と1929年のアメリカ経済について、その産業連関表を作成し、それらを用いてアメリカ経済の分析と予測に目覚ましい成果をあげた。そのため、この方法の有用性はアメリカをはじめ各国政府諸機関の注目するところとなった。とくに第二次世界大戦後は、欧米各国の政府機関によって産業連関表が作成され、国民経済の分析や政策策定に広く利用されてきた。 日本においても、1955年に初めて通商産業省(現、経済産業省)と経済企画庁(現、内閣府)の手で「昭和26年産業連関表」が作成され、昭和30年表以降は行政管理庁(後の総務庁、現、総務省)を中心に関係省庁の共同作業によって5年ごとに作成され、2001年1月の省庁再編を経て10府省庁(内閣府、総務省、経済産業省、財務省、農林水産省、厚生労働省、文部科学省、国土交通省、金融庁、環境省)の共同作業となり、今日に至っている。1978年8月に、日本の国民所得統計が国際連合(国連)による新しいSNAの基準に全面移行したのに伴い、産業連関表はその計算体系のなかに、経済活動別財貨・サービス産出表(V表)および経済活動別財貨・サービス投入表(U表)として国民所得勘定等と関連づけて組み込まれることになった。しかし、SNAは毎年作成されねばならないため、そのなかに十分詳細な産業連関表を盛ることはできず、したがって、その年次計数との関連に注意を払いつつ、現在も同計算体系とは別に、5年ごとの詳細な産業連関表が作成・公表されている。 [高島 忠・飯塚信夫 2020年9月17日] [参照項目] | | | | | | | |出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
<<: Round Table Conference on Industry and Labour
Recommend
Melanoplus mexicanus (English spelling) Melanoplus mexicanus
...Lachoppers that fly in swarms are called flyin...
Oosugi
A mistranslation of "too many." It is us...
Antarctic Treaty
The Basic Treaty on Antarctica was signed in Wash...
Phasianus soemmerringii intermedius (English spelling) Phasianus soemmerringii intermedius
…[Ryozo Kakizawa]. … *Some of the terminology tha...
National Treasury Revenues and Balances - Kokko Shushi
From the government's perspective, the Treasur...
Johannes Anglicus (English spelling)
…She was mentioned and popularized by 13th-centur...
Disc Gauge - Enban Gauge
...the end surface is either flat, cylindrical, o...
Avanti!
…In 1915, together with Mussolini, he supported I...
Aberdeen (English spelling)
A city in the northeast of Scotland, United Kingdo...
Yellow flax
A shrub of the Linaceae family cultivated for orna...
Cadastre - Chiseki
This is the equivalent of a land register. Origin...
Pinus sylvestris (English spelling)
… [Makoto Nishida]. … *Some of the terminology th...
khāqān (English spelling) khaqan
...This means a person who was entrusted with sec...
Lean burn method
…At this time, the combustion is improved so as n...
Aimores [Mountains] - Aimores
…The coastal mountain range Serra do Mar, which s...