Moment of inertia
|
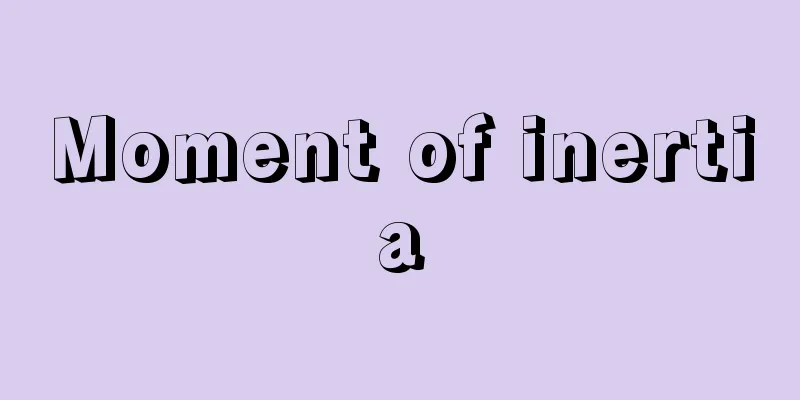
The mass m of each mass in the mass system is multiplied by the square of the distance r to a certain line, and the sum of these is called the moment of inertia of the mass system with respect to that line. In the case of a rigid body, it is divided into infinitesimal parts, and the mass dm of each part is multiplied by the square of the distance r, and integrated over the whole. The moment of inertia I of a rigid body with respect to a constant line (direction cosines λ, μ, ν) passing through the origin of a rectangular coordinate system is I=λ 2 I xx +μ 2 I yy +ν 2 I zz -2λμI xy The radius of gyration is k, determined by dividing the moment of inertia I of an object relative to a certain line by its total mass M, k 2 = I/M. In other words, an object will have the same moment of inertia as a single mass point of mass M that is a distance k from the axis of rotation. If the moment of inertia I of an object relative to an axis passing through its center of gravity is Ig , then the moment of inertia I relative to a parallel axis d away from that axis is given by I = Ig + Md 2 , which is called the parallel axis theorem. [Mitsuo Muraoka] Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
質点系の各質点の質量mに、ある一定直線までのそれぞれの距離rの2乗を掛けて全部について加えた量Σmiri2を、その直線に関する質点系の慣性モーメントという。剛体の場合は微小部分に分け、各部分の質量dmに距離rの2乗を掛け、全体に対して積分することによって 直角座標系の原点を通る一定直線(方向余弦λ、μ、ν)に関する剛体の慣性モーメントIは ある直線に関する物体の慣性モーメントIをその全質量Mで割ったk2=I/Mより定められるkを回転半径という。すなわち、物体は質量Mの一つの質点が回転軸からkの距離にあると同じ慣性モーメントをもつことになる。また物体の重心を通る軸に関する慣性モーメントをIgとすると、その軸からdだけ離れた平行軸に関する慣性モーメントIはI=Ig+Md2で与えられ、これを平行軸の定理という。 [村岡光男] 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
<<: Tariff issue - kanzei mondai (English spelling)
Recommend
Ekei
A monk from the Azuchi-Momoyama period. Founder of...
Battle of Ostia - Battle of Ostia
…In the early 4th century, a bishopric was establ...
Kingdom of Arada
...It flourished from the beginning of the 17th c...
"Igansai Sakura-hin" - Igansai Ouhin
…Although double-flowered cherry trees, which had...
Joseon white porcelain
A type of porcelain from the Joseon Dynasty in Kor...
Treaty of peace with Japan
…The official name of the Treaty is the Treaty of...
Okura Tanenao
...Since Okura Haruzane went to Kyushu as a punit...
Space motion sickness
...The effects of radiation, which was an initial...
Current collector - collector
A device that is placed between the stationary and...
Kansai Railway - Kansai Railway
A private railway with a major line network betwe...
The beginning of Kabuki
A commentary on Kabuki. Written by Tamenaga Itcho....
Owari Clay - Owari Clay
…After that, Western-style blast furnaces began o...
Areca palm (English spelling) Chrysalidocarpus lutescens; areca palm; butterfly palm
It is a palm plant native to Madagascar. It was on...
Ochanomizu - Ochanomizu
This district stretches from Kanda Surugadai in C...
Brachycera
…In brachyceran and cyclorha adult insects, the a...







![William [I] - William](/upload/images/67caf8bf63c43.webp)