Coastal dike

|
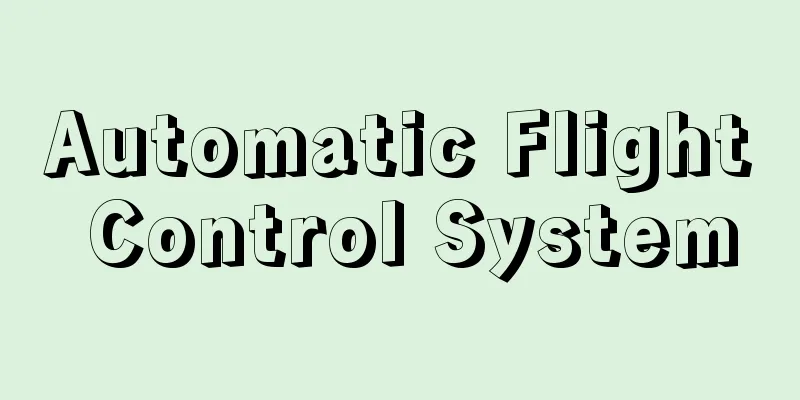
A coastal protection facility that prevents seawater from invading land due to high tides, tsunamis, and waves, and is constructed near the coastline and parallel to it. It is sometimes used to prevent the loss of sandy beaches due to erosion. Generally, the existing ground is raised with piled soil or concrete, and the front slope, top surface, and back slope are completely covered with concrete or asphalt. The base of the front slope is subject to scouring by the action of waves, so the footing is adequately reinforced with stone, and since there is a risk of collapse due to the residual water flowing into the rear and connecting with the water vein, sheet piles are driven in to prevent water leakage. In many cases, a wave return is provided, and since this part can be subjected to shocking wave forces, it is reinforced with steel bars. Structural styles include upright types with nearly vertical slopes, inclined types with inclined slopes, and hybrid types that combine the two. Upright types are often built as a single unit out of concrete without using soil and are chosen when the site for the levee is small and the foundation ground is good. Inclined types are widely used when a relatively large site is available and a large amount of soil for the levee body is available, as they can be constructed even if the ground is not very good. Hybrid types are used when it is possible to combine the two appropriately and have the advantages of both types. [Takao Horiguchi] [Reference] |©Shogakukan "> Example of coastal embankment (inclined type) Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
高潮、津波、波浪などにより海水が陸地に浸入するのを防ぐ海岸保全施設の一つで、海岸線付近でこれに平行に築造される。ときには侵食によって砂浜が喪失するのを防ぐために用いられることもある。一般に現地盤を盛り土またはコンクリートなどによって嵩(かさ)上げし、表法面(のりめん)、天端(てんば)面、裏法面をコンクリートまたはアスファルトで完全に被覆する。表法面の基部は波の作用によって洗掘されるので、石材による根固めを十分に行い、また背後の残留水と水脈がつながると、堤防基盤の土砂が流出して崩壊のおそれが生ずるので、矢板などを打ち込んで止水工を施す。多くの場合、波返しを設けており、この部分に衝撃的な波力が作用することもあるので、鉄筋で補強しておく。 構造様式は、法面が鉛直に近い直立型のものと、法面が傾斜している傾斜型、あるいはこれらを組み合わせた複合型などがある。直立型は、土砂を用いず、コンクリートで一体としてつくることが多く、堤防敷地が狭いとき、基礎地盤が良好なときに選択される。傾斜型は、比較的広い敷地が確保され、大量の堤体土砂が得られるときには、地盤がそれほど良好でなくても築造できるので広く用いられている。また複合型は、両者を適当に組み合わせ、両型式の長所をあわせもつことが可能なとき利用されている。 [堀口孝男] [参照項目] |©Shogakukan"> 海岸堤防の例(傾斜型) 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
<<: Coastal forces and coastline development - Coastal forces and coastline development
>>: Coastal Chukchi - Coastal Chukchi
Recommend
Angilbert - Angilbert
…It is also worth noting that England had two poe...
Oscillator strength -
Also called the f- value. A quantity used in spect...
Birth - Shussan (English spelling) Parturition
Childbirth is the act of giving birth, and medica...
Ricci, O. (English spelling) RicciO
Galileo initially aspired to be a doctor and ente...
International Military Tribunal for the Far East
…After World War I, the Permanent Court of Intern...
Cabo Tormentoso (English spelling)
…A small protrusion at the southern tip of the Ca...
Absorption edge
…In general, the absorption coefficient μ decreas...
Internetwork - Internetwork
…An internetwork, or the Internet, is a network o...
Koibuchi Gakuen
Located in Uchihara-cho, Higashiibaraki-gun, Ibara...
Smith, G. (English spelling) SmithG
…After 1855, excavation activities slowed down, a...
Elm
〘Noun〙 (elm) English name of the genus Ulmus of th...
Okinawa lizard - Okinawa lizard
...In a broad sense, it refers to reptiles belong...
Anfissa - Anfissa
…It was also a major player in the Second and Thi...
Antonio, G. (English spelling) AntonioG
...The costumes of men and women, the facial expr...
back of the hand
…The carpus and metacarpus are clearly distinct i...