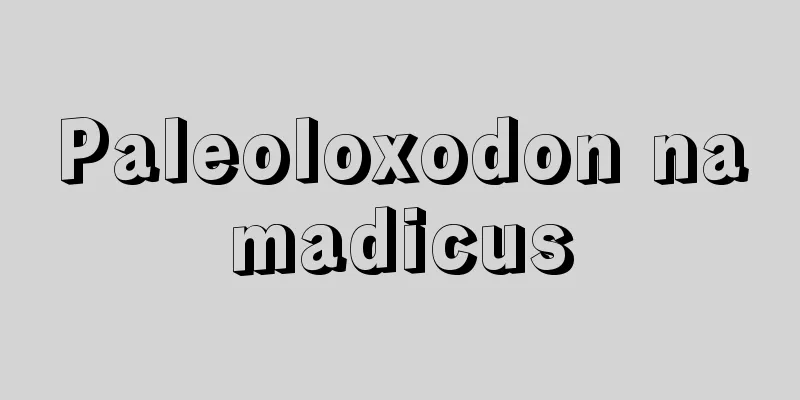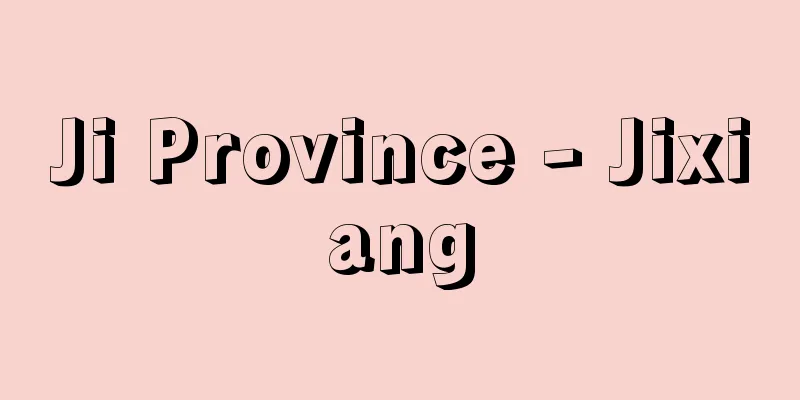Acropolis - Greek
|
In ancient Greek polis (city-states), a small hill formed the main part of the city center along with the agora. A strategic location overlooking the city was chosen, and temples to the polis's guardian deity and other gods were built there. The acropolis also served as a shelter and fortress in emergencies, and the interior of the temple was used as the treasury of the polis. Famous examples include the Acropolis of Athens, the Acrocorinth in Corinth, and the Cadmeia in Thebes. The Acropolis of Athens was registered as a World Heritage Site in 1987 (World Cultural Heritage). [Nobuyuki Maezawa] Acropolis of AthensThe Acropolis of Athens, representative of ancient Greece, is a long and narrow hill measuring approximately 300 meters from east to west and 150 meters from north to south. During the Mycenaean period (13th century BC), a wall of stacked megaliths had already been constructed around the site, and a royal palace was built. Construction of a large-scale temple on the Acropolis began after the time of the tyrant Peisistratos in the second half of the 6th century BC. However, these temples, including those under construction, were thoroughly destroyed by the Persian army that invaded Attica in 480 BC. In the 450s BC, a huge bronze statue of the goddess Athena was made and installed by Phidias to commemorate the victory in the Persian War. After this, full-scale reconstruction of the temple began based on the policy of Pericles, using tribute from the Delian League. Construction continued during the Peloponnesian War, with the Parthenon, Propylaea, Erechtheion, and Temple of Athena Nike being completed between the late 5th and early 4th centuries BC. There has been little building activity since then. Famous buildings around the Acropolis include the Theatre of Dionysus (c. 500 BC, rebuilt in the 320s BC), the Odeon of Pericles (c. 443 BC), and the Odeon of Herodes Atticus (c. 160 AD) on the southern foot of the Acropolis. Under Roman rule, with the establishment of Christianity as the state religion in the late Empire, the temple on the Acropolis was used as a Christian church from the 6th century onwards. [Nobuyuki Maezawa] [References] | | | |©Hayao Nogami "> Reconstruction of the Acropolis of Athens A temple built in the center of the Athenian Acropolis. Designed by the ancient Greek architect Ictinos, it was completed around 438 BC. It is about 30m wide and 70m deep, and has 46 Doric marble columns. Part of the World Heritage Site "Acropolis of Athens" (Greece, registered in 1987) Greece Athens ©Shogakukan "> Parthenon One of the oldest existing theaters in Greece. Built around 500 BC, it was rebuilt from wood to marble in the 320s BC. It is located at the southern foot of the Acropolis. Part of the World Heritage Site "Acropolis of Athens" (Greece, registered in 1987) Greece Athens ©Shogakukan "> Theatre of Dionysus Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
古代ギリシアのポリス(都市国家)において、アゴラとともに中心市の主要部を構成した小高い丘。市街を見下ろす要害の地が選ばれ、ポリスの守護神をはじめとする神々の神殿が建てられていた。アクロポリスは緊急の際の避難所や要塞(ようさい)としての役割も有しており、またその神殿の内部はポリスの国庫として利用された。アテネのアクロポリス、コリントのアクロコリント、テーベのカドメイアなどが有名である。なお、アテネのアクロポリスは1987年に世界遺産の文化遺産として登録されている(世界文化遺産)。 [前沢伸行] アテネのアクロポリス古代ギリシアを代表するアテネのアクロポリスは、東西約300メートル、南北約150メートルの細長い丘である。すでにミケーネ時代(紀元前13世紀)には巨石を積み重ねた城壁が周囲に構築され、王宮が建造されていた。アクロポリスとして大規模な神殿建設が開始されたのは、紀元前6世紀後半の僭主(せんしゅ)ペイシストラトスの時代以後のことである。しかし、建設中のものも含めて、これらの神殿は前480年にアッティカに侵入したペルシア軍によって徹底的に破壊された。前450年代には、ペルシア戦争の勝利を記念して、フェイディアスの手になる女神アテナの巨大な青銅製の像が制作、設置された。この後ペリクレスの政策に基づいて、デロス同盟の貢租を流用した神殿の本格的な再建が開始される。ペロポネソス戦争中も建設は続けられ、前5世紀後半から前4世紀初頭にかけてパルテノン、プロピライア(前門)、エレクテイオン、アテナ・ニケ神殿などが完成した。これ以後の建築活動はわずかである。アクロポリスの周辺地域では、南麓(なんろく)のディオニソス劇場(前500年ごろ。前320年代に改築)、ペリクレス音楽堂(前443年ごろ)、ヘロデス・アッティクス音楽堂(後160年ごろ)などが名高い。 ローマの支配下では、帝政後期のキリスト教国教化とともに後6世紀以降、アクロポリスの神殿はキリスト教会として用いられた。 [前沢伸行] [参照項目] | | | |©野上隼夫"> アテネのアクロポリス復原図 アテネのアクロポリスの中心部に建つ神殿。古代ギリシアの建築家イクティノスの設計で、紀元前438年ごろに完成した。幅約30m、奥行き約70mで、ドーリス式の大理石列柱は46本を数える。世界文化遺産「アテネのアクロポリス」の一部(ギリシア・1987年登録) ギリシア アテネ©Shogakukan"> パルテノン神殿 現存するギリシア最古の劇場の一つ。紀元前500年ごろにつくられ、紀元前320年代に木造から大理石造に改築された。アクロポリスの南麓にある。世界文化遺産「アテネのアクロポリス」の一部(ギリシア・1987年登録) ギリシア アテネ©Shogakukan"> ディオニソス劇場 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
<<: Acropolis Museum - Acropolis Museum (English name)
Recommend
Vacant land - Kuukanchi
Under the ancient Ritsuryo system, uncultivated l...
Shiragegaya (white hair grass) - Shiragegaya (English spelling) velvet grass
A naturalized plant of the grass family native to ...
Socotra [island] - Socotra
An island in the Indian Ocean, about 240 km northe...
Benjamin [of Tudela] (English spelling)
?-1173 A Jewish rabbi and traveller born in Navarr...
Maruyama Park
This park is located at the foot of Mount Higashi...
Dark adaptation
…When we move from a bright place to a dark place...
Omogo Tennansho - Omogo Tennansho
... A . negishii Makino, which is distributed in ...
Yayoi Yoshioka
She established modern medical education for wome...
Widia
...In particular, WC-Mo-Ni alloys are used when n...
Matsuura Seizan
Year of death: June 29, 1841 (August 15, 1841) Yea...
Gran Chaco (English spelling)
…The Gran Chaco is a vast plain in the center of ...
Friendship - Yuai
〘 noun 〙 (adjective verb) The closeness between br...
Art Tatum - Art Treatment
Check out the "Tatum" page. Source: Enc...
Kawaji Dam
...The Sanuki headworks in the middle reaches of ...
Virginia creeper
...It is also used as a material for greening con...


![Ellesmere [island] - Ellesmere](/upload/images/67cb0bafbdd7c.webp)



![Okawa [village] - Okawa](/upload/images/67cb145bd90bf.webp)