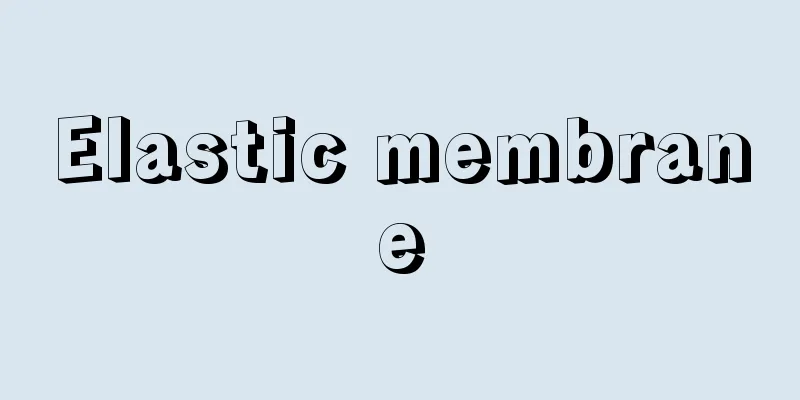Hokyointo - Pagoda

|
They can be made of wood or copper, but are generally stone towers erected in cemeteries. They are characterized by the horse-ear-shaped protrusions (compassages) on the four corners of the lid. Originally they were towers for storing the Hokkyoin Dharani (a sacred book of sacred scrolls), but later the name was given to towers with this characteristic. They are said to have begun in Japan when rice towers about 5 cm in size were made, in which each grain of rice was wrapped in paper with the Hokkyoin Dharani written in ink and stored in it, following the example of the 84,000-to tower made of gilt bronze created by Qian Hongchu, King of Wuyue in China. This rice tower was discovered at Muroji Temple in Nara Prefecture. An older copper tower was excavated from Mount Koya and bears an inscription from the 10th year of Koan (1287), while an older stone tower was excavated from a cave in Kamakura and bears an inscription from the 2nd year of Hoji (1248). From the mid-Kamakura period onwards, stone towers became more common. Ancient towers had a square tower body placed on a base with a flat lid on top and five sorin (spirals) standing on top of it, while those from the Middle Ages onwards had a square tower body placed on a base with a lid and sorin placed on top of that, the lid having several steps and horse-ear-shaped protrusions at the four corners. The earlier the protrusions, the more linear they are. [Yoshihiro Hirose] [Reference] |©Shogakukan "> Names of the various parts of a pagoda Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
木造・銅造もあるが、一般には墓地に造立された石塔。蓋(かさ)(笠)の部分の四隅に馬耳形の突起(方位)をもつのが特徴である。本来は宝篋印陀羅尼(だらに)を納めるための塔であったが、のちにはこの特徴をもつ塔の名称となった。中国の呉越(ごえつ)王の銭弘俶(せんこうしゅく)が作成した金銅製の八万四千塔に倣って、日本でも宝篋印陀羅尼を墨書した紙で籾(もみ)を一粒ずつ包んで納めた5センチメートルほどの籾塔(もみとう)が作成されたのに始まるとされる。この籾塔は奈良県室生(むろう)寺から発見された。銅造では高野山(こうやさん)から発掘された弘安(こうあん)10年(1287)の銘文をもつものがあり、石造では鎌倉の岩窟(がんくつ)から出土した宝治(ほうじ)2年(1248)銘のものなどが古い。鎌倉中期以降は石造のものが多くなる。古代のものは基座の上に方形の塔身を置き、上面の平らな蓋の上に5本の相輪(そうりん)を立てたものであり、中世以降のものは基礎の上に方形の塔身、その上に蓋、相輪が置かれ、蓋には数段の階段があり、四隅に馬耳形の突起が設けられている。突起は早期のものほど直線的である。 [廣瀬良弘] [参照項目] |©Shogakukan"> 宝篋印塔の各部名称 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
Recommend
Northern beetle - Northern beetle
A marine animal belonging to the Chaetognatha phy...
Tetraspora cylindrica (English spelling) Tetraspora cylindrica
…[Mitsuo Chihara]. . . *Some of the terminology t...
Natterer's piranha (English spelling)
...It is hardy and easy to keep, and even though ...
Kutev, F.
...These instruments show Turkish influence, and ...
Takitei Koijyo - Ryuuteirijyo
A comic writer from the late Edo period. Born in ...
Akh
…One of the three ancient Egyptian spiritual conc...
Clusius, C.de (English spelling) ClusiusCde
...This is why the Turkish tulip, which is said t...
Tafelspitz
...Fish dishes include smoked or pickled herring,...
Carfour - Carfour
… Muhammad put an end to the political turmoil in...
Tombstone of Ishikawa Toshitari - Tombstone of Ishikawa
...An official in the Nara period. A descendant o...
Valsalva, AM
…An Italian physician. After graduating from the ...
Mount Rokko
A mountain made of granite rocks that rises to the...
Arabian coffee (English spelling)
...The character "coffee" is used. [Cof...
Okroshka - Okuroshka
...In any case, the recipe is relatively simple, ...
Corruption crime
A crime that violates official duties and damages ...