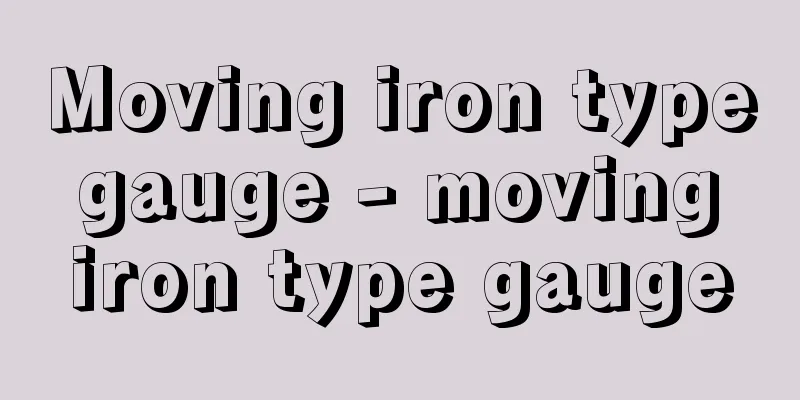Algebraic equations
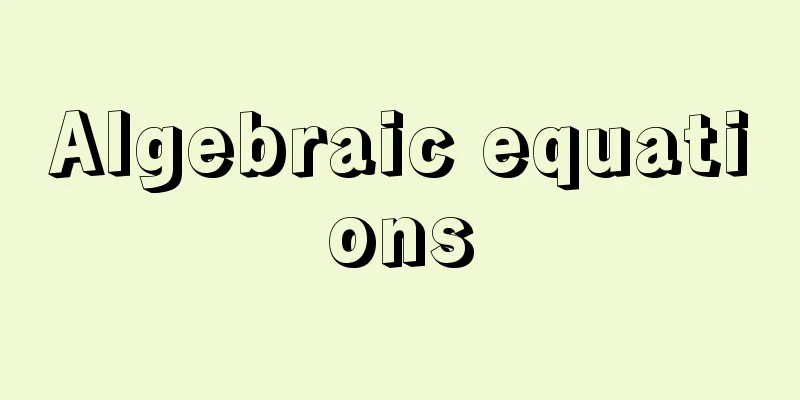
|
An equation with unknowns x, y, z, etc. is f(x,y,z,……)=0 [Tsuneo Adachi] Binomial EquationsAn equation of the form X m -a=0 is called a binomial equation. One of its solutions is expressed as m or a 1/m . When a is a positive real number, m is usually a positive real number. [Tsuneo Adachi] Cubic Equation Cubic equation a 0 X 3 +a 1 X 2 +a 2 X+a 3 =0 [Tsuneo Adachi] Fundamental Theorem of Algebra An n-th degree algebraic equation over the field of complex numbers (complex numbers include the case where they are real numbers. The same applies below) is f(x)=a 0 X n +a 1 X n-1 +…… [Tsuneo Adachi] Equations of degree 5 or higherAlgebraic equations up to degree four can be solved by using power roots, that is, by repeatedly solving binomial equations. This property means that algebraic equations of degree four or less can be solved algebraically. In the early 19th century, Abel proved that algebraic equations of degree five or higher could not in general be solved algebraically. Galois then introduced the concept of groups and sought necessary and sufficient conditions for algebraic equations to be solvable algebraically. This was the beginning of group theory. [Tsuneo Adachi] Multivariate Algebraic Equations When there is more than one unknown, an algebraic equation can have a meaning in plane figures, space figures, or even higher dimensional figures. For example, x 2 +y 2 -1=0 [Tsuneo Adachi] [Reference item] | |Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
未知数x、y、z、……を含む方程式を [足立恒雄] 二項方程式Xm-a=0の形の方程式を二項方程式という。その解の一つをmまたはa1/mで表す。aが正実数のときにはmは正実数とするのが普通である。 [足立恒雄] 三次方程式三次方程式 [足立恒雄] 代数学の基本定理複素数体上のn次代数方程式(複素数は実数である場合を含めていう。以下同様)とは [足立恒雄] 五次以上の方程式四次までの代数方程式はべき根を用いて、つまり、二項方程式を繰り返し解いて解を求めることができた。この性質を、四次以下の代数方程式は代数的に解けるという。 19世紀初頭、アーベルは、五次以上の代数方程式は一般には代数的に解けないことを証明した。続いてガロアは、群の概念を導入して代数方程式が代数的に解ける必要十分条件を求めた。これが群論の始まりである。 [足立恒雄] 多元代数方程式未知数の個数が一より多い場合は、代数方程式は平面図形や空間図形、さらには高次元図形としての意味をもつ。たとえば [足立恒雄] [参照項目] | |出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
<<: Soybean oil - Daizuyu (English spelling) soybean oil
Recommend
Olsen, J.
...The modern group of painters who have escaped ...
Moso
…It is distributed mainly in Lijiang Naxi Autonom...
Schumann, P.
…The other trend, which originated in the early 2...
cocoa
Nutrition and Function Both cocoa and chocolate a...
Bird's nest - performance
Also called "Swallow's nest" or &quo...
masque
...Representative composers include W. Byrd (1543...
Niger (English spelling) Republic of Niger
A typical landlocked country in the interior of W...
Nunobikimaru Incident
An incident in July 1899 in which an attempt was m...
Swallow Exercise - Enkoushi
A state envoy sent by Korea to Beijing in the Qing...
End gold chisel - Makkinru
〘Noun〙 A technique of lacquer crafts in the Nara p...
landskap
...It is a case of regional communities led by no...
Satake Incident
This incident occurred around 1755-57 (5-7th year ...
Individual - Individual
...Most of them are thrillers and melodramas. (4)...
American President Lines
An American liner company. APL is an American abbr...
Nicolas Boileau-Despréaux
French poet and critic. Born in Paris. Studied th...