Ossicles - ossicles

|
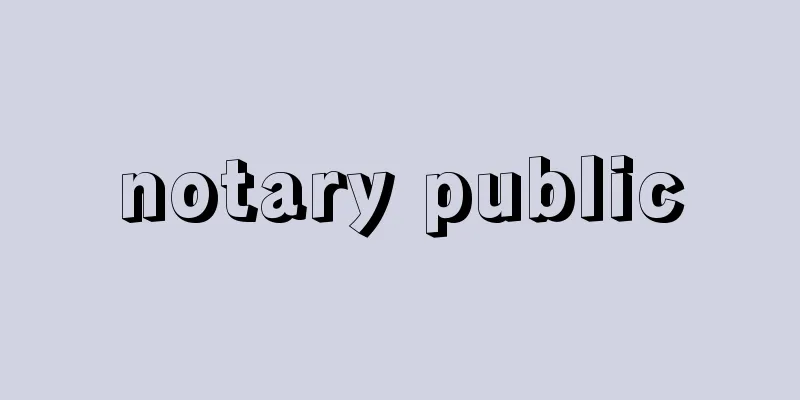
A small bone that transmits sound to the inner ear, also called the auditory or tympanic ossicle. It is located in the middle ear of vertebrates above the age of amphibians, and connects the eardrum to the inner ear. In fish, the hyoglossal cartilage, which is part of the bone that supports the jaw, is modified into a rod-like ossicle in amphibians, reptiles, and birds, called the collicular bone. In mammals, unlike the other three classes, the collicular bone is made up of three bones: the malleus, which is attached to the eardrum, the incus, and finally the stapes, which is attached to the vestibular window of the inner ear. Of these, the stapes is homologous to the collicular bone, but is shorter in length. The other two are thought to have been modified from the articular bone and quadrate bone that support the jaw of lower vertebrates. Some fish (e.g. carp, eels, catfish) have small bones that transmit sound to the inner ear. These bones are called Weberian ossicles. The Weberian organ is made up of modified processes on the front three vertebrae. [Seiichiro Kawashima] Human auditory ossiclesA set of three small bones in the middle ear that spans between the tympanic membrane and the vestibular fenestra. From the tympanic membrane side, the malleus, incus, and stapes (written in katakana in human anatomy) are arranged in this order, and are connected to each other by forming joints. Sound waves received by the tympanic membrane are transmitted to the inner ear via the ossicles. The malleus is the largest of the ossicles and is hammer-shaped. That is, it has a spherical malleus head followed by a thin malleus neck, from which extends a long and thin malleus manubrium. The malleus manubrium is fixed to the tympanic membrane over its entire length, and the blunt round part of the lower end of the manubrium is attached to the umbilicus of the tympanic membrane. Two processes emerge from the malleus neck near the base of the manubrium, and the thick and short outer process of the process faces the tympanic membrane and forms the malleus eminence. The posterior surface of the malleus head has a saddle-shaped articular surface that articulates with the body of the incus. The incus is molar-shaped and consists of the body of the incus and two legs that protrude downward. The body of the incus has a saddle-shaped depression that holds the head of the malleus. The two legs are long and short. The long leg extends parallel to the manubrium of the malleus and has a spherical bulge (pisiform process) at its tip, which articulates with the head of the stapes. The short leg is thick and short, and points almost horizontally toward the mastoid sinus. The stapes is the smallest of the ossicles, and as a whole it has the shape of a stirrup used for horse riding. The base of the stapes, which corresponds to the footplate of the stirrup, is oval in shape and fits the shape of the fenestra vestibularis, blocking it. The front and rear legs that extend from both ends of the footplate are connected to the stapes head. The malleus and stapes are fixed to the surrounding bony walls by ligaments. [Kazuyo Shimai] [Reference] |©Shogakukan "> Location and structure of the ossicles Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
音を内耳に伝える小形の骨で、聴小骨または鼓室小骨ともいう。両生類以上の脊椎(せきつい)動物の中耳にあり、鼓膜と内耳を結ぶ。魚類ではあごを支える骨の一部である舌顎(ぜつがく)軟骨が、両生類、爬虫(はちゅう)類、鳥類では変化して棒状になった一小骨で、耳小柱という。哺乳(ほにゅう)類では他の3綱と異なり、耳小骨は3個の骨からなっている。すなわち、鼓膜に付着する槌骨(つちこつ)、ついで砧骨(きぬたこつ)、最後に内耳の前庭窓につく鐙骨(あぶみこつ)である。これらのうち鐙骨は耳小柱と相同で、長さが短くなったものである。他の二つは、下等脊椎動物のあごを支える関節骨と方形骨から変じたものと考えられている。魚類でも内耳に音を伝える小骨をもっているものがあり(たとえばコイ、ウナギ、ナマズ)、その骨をウェーバー小骨という。ウェーバー小骨は前端3個の椎骨(ついこつ)の突起が変化したもので、ウェーバー器官をつくる。 [川島誠一郎] ヒトの耳小骨中耳の内部にある3個の連鎖した小骨で、鼓膜と前庭窓との間にわたっている。鼓膜側からツチ骨、キヌタ骨、アブミ骨(人体解剖学では片仮名表記)の順に配列し、互いに関節をつくってつながっている。鼓膜が受けた音波は耳小骨を介して内耳に伝えられる。ツチ骨は耳小骨のなかでは最大で、ハンマー状をしている。すなわち、球形のツチ骨頭とそれに続く細いツチ骨頸(けい)があり、ツチ骨頸から細長いツチ骨柄(へい)が伸びている。ツチ骨柄はその全長にわたって鼓膜に固着しており、骨柄の下端の鈍円な部分が鼓膜臍(さい)についている。骨柄の基部あたりでツチ骨頸から2本の突起が出ていて、そのうち太くて短い外側突起が鼓膜のほうに向いていてツチ骨隆起を形成している。ツチ骨頭の後面には鞍(くら)状の関節面があり、キヌタ骨体と関節をつくっている。キヌタ骨は臼歯(きゅうし)状をしており、キヌタ骨体と下方に突出する2本の脚からなっている。キヌタ骨体にはツチ骨頭を入れる鞍状の凹(くぼ)みがある。2本の脚は長脚と短脚で、長脚はツチ骨柄と平行方向に伸びて、その先端が球状に膨らみ(豆状突起)、アブミ骨頭と関節をつくっている。短脚は太くて短く、ほとんど水平に乳突洞方向に向いている。アブミ骨は耳小骨では最小で、全体として乗馬に使う鐙の形をしている。鐙の足板に相当するアブミ骨底は楕円(だえん)形で、前庭窓の形に適応して前庭窓をふさいでいる。足板の両端から出た前脚と後脚はアブミ骨頭で結合する。ツチ骨、アブミ骨はそれぞれ靭帯(じんたい)によって周囲の骨壁に固定されている。 [嶋井和世] [参照項目] |©Shogakukan"> 耳小骨の位置と構造 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
Recommend
Echidnophaga gallinacea (English spelling)
...The Himalayan rat flea, Peromyscopsylla himala...
Barbary Sheep
Like the bharal, this mammal (illustration) is an ...
Amuda Seyon - Amuda Seyon
… From this time until the mid-19th century, Ethi...
Hikarigoke
A medium-length novel by Takeda Taijun (the latte...
Kitagawa [town] - Kitagawa
A former town in Higashiusuki County, Miyazaki Pre...
Terpnosia nigricosta (English spelling) Terpnosianigricosta
…Cicada [Masami Hayashi]. . … *Some of the termin...
Rangeln
… [Europe] Europe tends to have the impression th...
Forestry - Ikurin
Creating and cultivating forests by planting seed...
hat
...hat with a crown and brim, hood, brimless cap,...
Hypobromous acid (English spelling)
One of the oxoacids of bromine. It exists only as...
Kasai-Osaki Uprising
An uprising of local samurai and farmers occurred ...
drugstore beetle
...Drugstore beetles, cigarette beetles, and othe...
Alliance Strategy
→ Alliance Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nippon...
Spanish bayonet (English spelling)
...Most species are shrubs, but some species do n...
ICU Psychiatry - ICU Psychiatry
...In many cases, subjects are aware that these h...