Grimm's Law

|
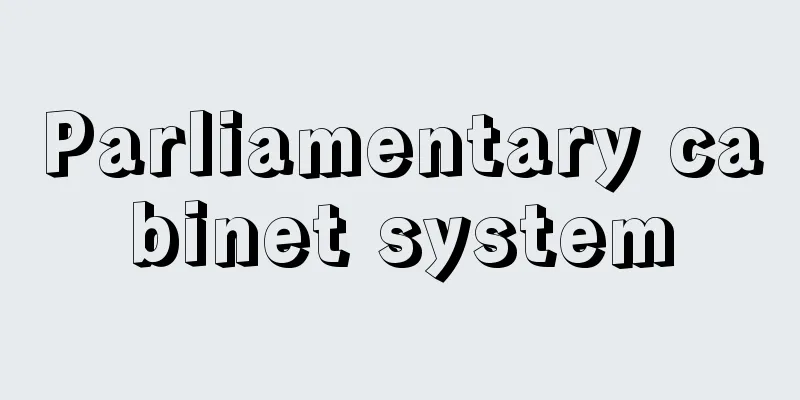
The German linguist and narrator Jacob Grimm established rules for the consonant correspondences between Classical and Germanic languages. In the stops and fricatives of Indo-European and Germanic languages, the following consonant shifts can be seen between voiceless, voiced, and aspirated consonants: (1) The voiceless stops [p, t, k] of the Indo-European root languages became voiceless fricatives [f,θ, x→h] in the Germanic root languages. The initial sounds of Latin p iskis ‘fish’, t enuis ‘thin’, and k aput ‘head’ correspond to the initial sounds of English fish [ f iʃ], thin [ θ in], and head [ h ed]. (2) The voiced stops [b, d, g] of the Indo-European root changed into voiceless stops [p, t, k] of the Germanic root. The Greek kanna b is ‘hemp’, the Latin duo ‘two’ and g enus ‘genus’ correspond to the English hem p , t wo, k in ‘kinship’. (3) The aspirated consonants [bh, dh, gh] of the Indo-European root changed to the unaspirated consonants [b, d, g] of the Germanic root. Sanskrit bh arāmi ‘I carry’, ma dh u ‘honey’, and sti gh noti ‘he climbs’ correspond to English I b ear, mea d ‘mead’, and German stei g en [ʃtaigen] ‘climb’. Grimm classified voiceless fricatives [f,θ,x] and aspirated consonants [bh,dh,gh] into aspirated group A, voiceless stops into hard group T, and voiced sounds into soft group M, and proposed that the law of the transition can be expressed by the following diagram.
[Koizumi Tamotsu] Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
ドイツの言語学・説話学者ヤーコプ・グリムJacob Grimmがたてた、古典語とゲルマン語の間にみられる子音対応に関する規則。印欧基語とゲルマン基語の閉鎖音と摩擦音において、無声・有声・帯気音の間に次のような子音の推移がみられる。 (1)印欧基語の無声閉鎖音[p, t, k]がゲルマン基語では無声摩擦音[f,θ, x→h]となった。ラテン語の piskis「魚」、tenuis「薄い」、kaput「頭」の語頭音が英語の fish[fiʃ], thin[θin], head[hed]の語頭音に対応する。 (2)印欧基語の有声閉鎖音[b, d, g]はゲルマン基語では無声閉鎖音[p, t, k]に変化した。ギリシア語のkannabis「麻」、ラテン語の duo「二」、genus「種属」は、英語のhemp, two, kin「親族」にあたる。 (3)印欧基語の帯気音[bh, dh, gh]はゲルマン基語では無帯気音[b, d, g]に推移した。サンスクリット語の bharāmi「私は運ぶ」、madhu「蜜(みつ)」、stighnoti「彼は登る」は、英語のI bear、mead「蜜酒」、ドイツ語のsteigen[ʃtaigen]「登る」に対応する。グリムは、無声摩擦音[f,θ, x]と帯気音[bh, dh, gh]を気音群Aに、無声閉鎖音を硬音群Tに、有声音を軟音群Mに分類したうえで、下記の図式により推移の法則を表すことができるとした。
[小泉 保] 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
<<: Qrīm Khān (English spelling)
>>: Grimm's Fairy Tales - Grimm's Fairy Tales
Recommend
Solution - Solution
…(3) Meaning: An official is dismissed from his/h...
Sei whale (sardine whale)
A mammal of the family Baleen whale (illustration)...
Astilbe thunbergii (English spelling) Astilbethunbergii
… [Munemin Yanagi]. … From [Awamori Shouma (Awamo...
Japanese Steel - Wako
Also called "wahagane". Steel made using...
Rock bath - Iwaburo
〘 noun 〙 A bath at a hot spring or the like that i...
Active element
A circuit element that acts as an energy source fo...
delusion of jealousy
...This is called the Cain complex, and comes fro...
Fireman - Kasha
Eunuch. See the entry for 'fire'. Source :...
idola
…In this sense, it is the same as a statue of a g...
Hirokawa [town] - Hirokawa
A town in Yame County in the southern part of Fuku...
Sergio Corazzini
Italian poet. Born in Rome. A representative figu...
Stethojulis trossula (English spelling) Stethojulistrossula
… [Makoto Shimizu]. . … *Some of the terminology ...
Gold export ban
Prohibiting the free export of gold meant suspendi...
Sea slug - Sea slug
…A marine fish of the family Scyllidae (illustrat...
Aftername - aftername
…The so-called “Snow Mountain Verse” from the Nir...