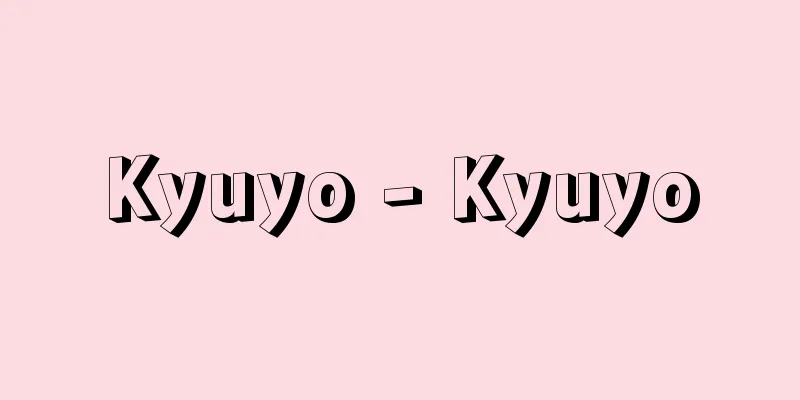Drying - Kansou (English spelling)

|
This is an operation to remove water from a solid by evaporation (or sublimation) to obtain an anhydrous or low-water product. In the chemical industry, there are many operations to remove and recover solvents from solid materials treated with organic solvents, and even if the substance to be removed is not water, the evaporation (sublimation) operation is also included in the category of drying. The term drying is also used for the operation of removing water from liquids or gases, such as "drying insulating oil" and "drying air," but in terms of unit operations, the former is closer to evaporation (or distillation), and the latter is treated as humidity control. Although it is an operation to remove water from solid materials, pressing and centrifugation, which directly separate the liquid, are distinguished from drying as dehydration (solid-liquid separation) operations (hereinafter, for convenience of description, unless otherwise specified, will be explained as removing water from solids, but in most cases it also applies to organic solvents, etc.). The state of water contained in a solid varies greatly depending on the structure of the solid and the amount of water. In nonhydrophilic materials, which do not contain water themselves, water fills the gaps in the material as liquid water, and behaves similarly to water in a capillary tube. As the structure becomes finer, it is naturally subject to capillary forces. When the water content decreases, the water becomes scattered in recesses such as the contact points of the solid structure, and in other parts it exists in an adsorbed state on the internal surface of the solid. When it is dried further, only adsorbed water remains. In hydrophilic materials, the material and water have various bonds in terms of molecular structure, and are homogeneous. In living organisms, it forms cellular structures as cell fluid, or often takes on states such as gel, sol, and colloid. [Yuji Kawamura] Mechanistic elements of drying(1) Movement of moisture within a material to the evaporation surface. The evaporation surface is often the outer surface of the material, but it can also be located inside. (2) Supply of latent heat of vaporization: By convection heat transfer from the outside of the material, radiation heat transfer, or conduction heat transfer inside the material, or a combination of these. Dielectric heating is also used. (3) Removal of evaporated vapor: Remove it from the system by ventilation, evacuation, etc. This concerns the movement of vapor from the material surface to the airflow, but if the evaporation surface is inside the material, the movement of vapor inside the material also becomes an issue. In order to accomplish drying, all of these factors must be quantitatively balanced, which is why it is called a simultaneous heat and mass transfer operation. [Yuji Kawamura] Drying methodDepending on the characteristics of the material, various methods have been devised and put into practical use to satisfy the above drying mechanism and dry efficiently. In general, it is desirable to increase the drying speed, but care must be taken when exceeding a certain limit, as some materials may develop distortions or cracks, or surface hardening (a dense drying layer forms on the surface, which reduces water permeability and has a negative effect on drying). For example, when drying wood, a method of increasing the humidity of the outside air to suppress the drying speed (humidity-controlled drying method) is often used to prevent deformation. On the other hand, drying methods that involve boiling inside the material (such as superheated steam drying method) are generally not normal, but they can be used to dry food and other items because they can dry quickly and produce porous products. Many medicines and foods deteriorate at high temperatures, so they need to be dried at room temperature or below, and in some cases below freezing point. [Yuji Kawamura] “Drying Device” by Ryozo Kiribayashi (1966, Nikkan Kogyo Shimbun)” ©Shogakukan "> Drying Equipment Type Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
固体中に含まれる水分を蒸発(または昇華)によって除去させ、無水または低水分の製品を得るための操作である。化学工業では有機溶媒で処理した固体材料から溶媒を除去回収する操作は少なくないが、このように除去物質が水でなくても蒸発(昇華)操作によって除去される場合も乾燥の範疇(はんちゅう)に含まれる。「絶縁油の乾燥」「乾燥空気」などというように、液体や気体中の水分の除去操作に対しても乾燥という語が用いられるが、単位操作の区分のうえでは前者は蒸発(または蒸留)に近い操作であり、後者は調湿(ちょうしつ)として取り扱われる。固体材料中の水分の除去操作ではあるが、直接液状のまま分離する圧搾や遠心分離操作は脱水(固液分離)操作として乾燥とは区別される(以下、記述の便宜上とくに断らない限り固体中の水分の除去として説明をするが、ほとんどの場合そのまま有機溶媒などにも適合する)。 固体中に含まれている水分の状態は、固体の構造と水分量とによって大幅に異なる。材料自体が水を含まない非親水性材料では、水は素材間隙(かんげき)を液状水として満たし、毛細管内の水と類似した挙動をとる。構造が微細になると当然毛管力を受けることとなる。水分が少なくなると、水は固体構造の接点などの凹入部に散在するようになり、他の部分では固体内部表面に吸着状態で存在することになる。さらに乾燥させると吸着水分のみとなる。親水性材料では素材と水とは分子構造的に種々な結合をもち、均質的なものとなる。生体内では細胞液として細胞構造を形成し、あるいはゲル、ゾル、コロイドなどの状態となることも少なくない。 [河村祐治] 乾燥の機構的要素(1)材料内水分の蒸発面への移動 蒸発面は多くの場合、材料外面であるが、内部にあることもある。 (2)蒸発潜熱の供給 材料外部よりの対流伝熱、放射伝熱または材料内部の伝導伝熱およびこれらの組合せによる。誘電加熱も利用される。 (3)蒸発蒸気の除去 通気や真空排気などによって系外へ排除する。材料表面から気流への蒸気移動が対象となるが、蒸発面が材料内部にある場合には、材料内部での蒸気移動も問題になる。 乾燥を遂行するためには、これらの因子を量的にすべて均衡させる必要があり、熱・物質同時移動操作と称されるゆえんである。 [河村祐治] 乾燥方法材料の特性に応じて、前記の乾燥機構を満足させ、効率よく乾燥を行わせるよう種々の方法が考案され実用化されている。乾燥速度を大きくすることは一般的には望ましいことであるが、ある限度を超えると材料によっては、ひずみや亀裂(きれつ)が発生したり、表面硬化(表面に緻密(ちみつ)な乾燥層ができ透水性が悪く乾燥に悪影響を与える)を生じるなどのことがあるので注意を要する。たとえば、木材の乾燥では変形防止のため外気の湿度を高めて乾燥速度を抑制する方法(調湿乾燥法)がよく用いられる。逆に、材料内部で沸騰を伴うような乾燥法(過熱蒸気乾燥法など)は一般論的には正常とはいえないが、急速乾燥ができ多孔性の製品が得られるため食品などの乾燥に用いられる。医薬品や食品などには高温では品質が劣化するため、常温以下、場合によっては氷点以下で乾燥する必要のあるものも少なくない。 [河村祐治] 『桐林良三著『乾燥装置』(1966・日刊工業新聞社)』 ©Shogakukan"> 乾燥装置の種類 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
<<: Licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra) - Licorice
>>: Perfect fluid - perfect fluid
Recommend
Hiruzen Plateau - Hiruzenkogen
A plateau that stretches across the northern part ...
Alpha Centauri C - Alpha Centauri C
…It reaches its zenith at 9 p.m. in mid-June. Pro...
Ordensburg - Oldensburg
…Munich was entrusted to H. Giesler, Dresden to W...
Tissé, E. (English spelling) TisseE
…In 1924, he supervised the editing of the Russia...
Megophrys
...The family Pipidae includes the African clawed...
Shinmei Mirror
A chronicle from Emperor Jimmu to Emperor Gohanazo...
Kinyukai - Kinyukai
...At first, the number of members was just over ...
Toll road
...a road on which a toll can be collected from t...
Masahiro Ouchi
Year of death: September 18, 4th year of Meiō (Oct...
Sea wisteria flower - Kaitouge
This refers to the eggs of the common octopus or ...
Rinchi - Rinchi
〘Noun〙① Looking into a pond. [Wang Rong - Preface ...
Photo - shashin (English spelling) photograph
Photography is a general term for the technology ...
Pseudophyllophora - Pseudophyllophora
...When this final developmental form is ingested...
Central [town] - Chuo
A former town in Kume County, central Okayama Pref...
Espata danza - Espata danza
...There are many other folk songs with beautiful...