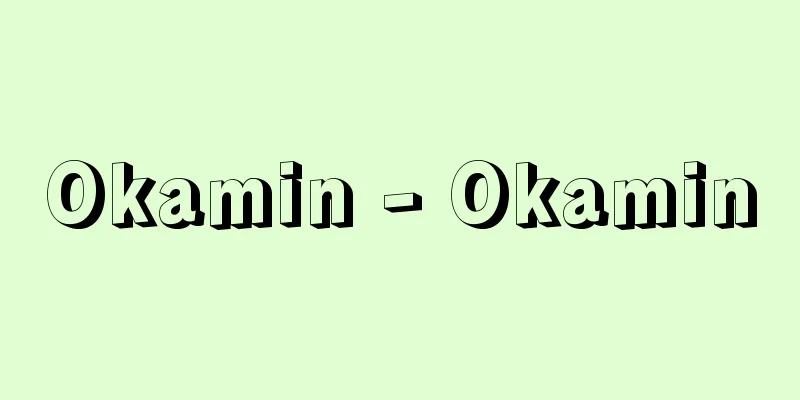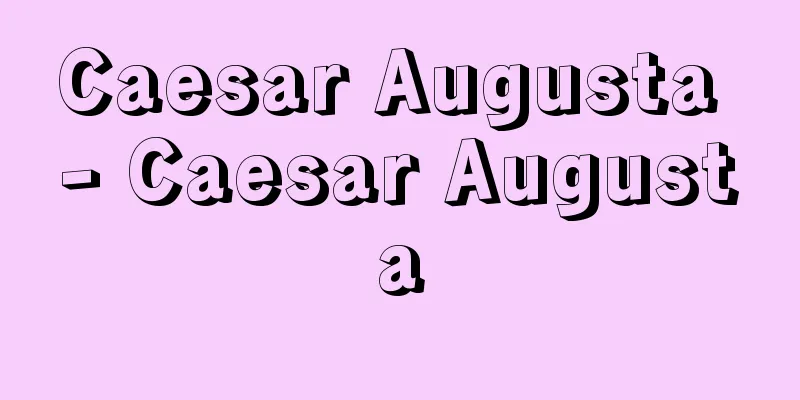Electronic Warfare

|
The US Department of Defense Military Dictionary (published in 2001) defines electronic warfare (EW) as "military operations using electromagnetic and directed energy to control the electromagnetic spectrum or attack an enemy," and lists three types of electronic warfare: electronic attack, electronic protection, and electronic warfare support. In traditional terms, electronic attack (EA) corresponds to electronic countermeasures (ECM), electronic protection (EP) corresponds to electronic counter-counter measures (ECCM), and electronic warfare support (EWS) or electronic support (ES) corresponds to electronic support measures (ESM). Electronic warfare is carried out not only in wartime but also in peacetime, and ES collects basic data useful for EA and EP. One type of ES is COMMINT (Communication Intelligence), which intercepts radio communications of a hypothetical enemy, detects the source of the communication, analyzes the content of the communication, and explores the enemy's intentions and actions. ELINT (Electronic Intelligence) searches for and monitors radar signals from hypothetical enemies, detects the location of the source, analyzes and processes the radio signals, and creates a data bank of their characteristics. These two are collectively called SIGINT (Signal Intelligence). There are rumors of the existence of Echelon (a communications interception organization) as a global SIGINT system, which is conducted by the Anglo-Saxon countries of the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand, but it has never been officially recognized. EA includes jamming, which disrupts the use of radio waves by enemy radar and communications, chaff, which scatters thread-like radio wave reflectors in the air, deception, which misleads enemy radars about distance and speed information, and decoys, which attract enemy radars. EP is a means of countering enemy ECM, and can be achieved by using a different antenna, changing the radar's transmission frequency or pulse repetition frequency (the interval between transmissions), or coding the transmitted radio waves. In addition, measures to avoid enemy infrared detection are sometimes called IRCM (Infra-Red Counter Measure). Today, many countries have specialized ES and EA units, aircraft, and ships, and radars and communication devices have EP capabilities built in. In addition, attack aircraft and bombers have EA systems built into the aircraft to avoid enemy detection and attack, or mounted on the outside in the form of an independent pod (container). [Keiichi Nogi] [References] | | |©Shogakukan "> Electronic Warfare Battle Example (1) ©Shogakukan "> Electronic Warfare Battle Example (2) Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
アメリカ国防総省の軍事用語事典(2001年発行)では電子戦(EW)を「電磁スペクトラムをコントロールし、あるいは敵を攻撃するために、電磁および指向エネルギーを利用する軍事行動」と定義し、電子戦には「電子攻撃Electronic Attack、電子防護Electronic Protection、電子戦支援Electronic Warfare Support」の三つがあるとしている。従来の用語では電子攻撃(EA)は電子対策ECM(Electronic Counter Measure)に、電子防護(EP)は対電子対策ECCM(Electronic Counter-Counter Measure)に、電子戦支援(EWS)あるいは電子支援(ES)は電子支援手段ESM(Electronic Support Measure)に、それぞれ対応すると考えてもよい。電子戦は戦時のみならず平時にも行われていて、ESによってEAやEPに役だつ基礎データを収拾している。ESの一つにコミントCOMMINT(Communication Intelligence通信情報収集)があって、仮想敵の無線通信を傍受し、発信源を探知し、通信内容を分析し、相手の意図や行動を探る。またエリントELINT(Electronic Intelligence電子情報収集)では、仮想敵のレーダー電波などを捜索、監視し、発信源の位置を探知し、電波の信号を分析処理して、その特性についてのデータバンクを作成する。この二つをまとめてシギントSIGINT(Signal Intelligence信号情報収集)とよんでいる。全地球的規模でシギントを行っているシステムとして、アメリカを中心にイギリス、カナダ、オーストラリア、ニュージーランドのアングロサクソン諸国が参加しているエシュロンEchelon(通信傍受機関)の存在が噂(うわさ)されるが、公式に認められたことはない。EAには、敵のレーダーや通信の電波使用を妨害するジャミング、糸のような電波反射体を空中にばらまくチャフ、敵レーダーの距離や速度情報を誤らせる欺瞞(ぎまん)deception、敵レーダーを引き付けるおとりdecoyなどがある。EPは敵によるECMに対抗する手段で、別のアンテナを使用したり、レーダーの発信周波数やパルス繰り返し周波数(発信の間隔)を変えたり、発信電波をコード化しておいたりする方法がある。なお、敵の赤外線探知などを避ける手段を、IRCM(Infra-Red Counter Measure)とよぶこともある。現代では多くの国がESやEA専門の部隊や航空機、艦船を保有しており、レーダーや通信機にはEP能力が組み込まれている。また攻撃機や爆撃機は、相手の探知や攻撃を避けるEAシステムを機体に内蔵したり、独立したポッド(容器)の形で機外に搭載する。 [野木恵一] [参照項目] | | |©Shogakukan"> 電子戦の戦闘例(1) ©Shogakukan"> 電子戦の戦闘例(2) 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
Recommend
Orbital period - orbital period
…In addition, with normal launch methods, it is n...
Regeneration
This is the phenomenon in which, when a part of a...
Elgani - Elgani
The Turkish side of the Tigris and Euphrates rive...
Suzhou
A prefecture-level city in the southern part of J...
Abira - Abira
…Originally, Krishna was a warrior strategist and...
Hironori Iyoshi - The child of life
Year of birth: Unknown An official from the late 7...
Poème (English spelling)
…However, the Japanese verse art has not traditio...
Mugi [town] - Mugi
A former town in Mugi County in the central-southe...
Forced labor - Kyoseiroudou
Labor that is forced through violence or other me...
Chikyu - Chikyu
[1] The earth will continue to exist without chang...
Sakai merchant
They were merchants who held sway mainly in Sakai ...
Turtle ship
A military ship from the Joseon Dynasty of Korea....
Andean Region
This refers to the region where the Andes run vert...
chromoplast
The mechanism by which chloroplast development an...
Agreed tariff - Kyotei kanzei
The Uruguay Round was a critical juncture for the...