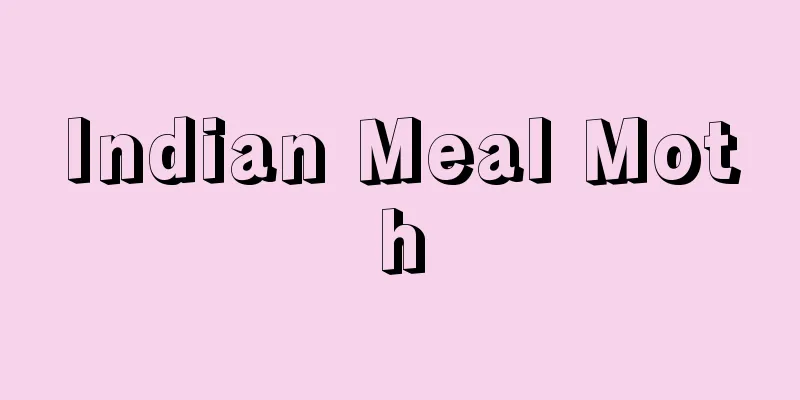Horizontal coordinates

|
A type of celestial coordinate system, which is a coordinate system that shows the position of a celestial body on the celestial sphere. The position of a celestial body is expressed by the angle a (altitude) measured perpendicularly from the horizon, and the azimuth angle Z (the azimuth angle is often measured eastward from the north point N). To explain in detail with , the reference point for horizontal coordinates is the vertical line ZO (the direction of the Earth's gravity), the plane that is perpendicular to it (intersects at a right angle) and passes through the observer O is the earth's horizon, and the great circle where this plane intersects with the celestial sphere is the horizon. The intersection point of the vertical line and the celestial sphere is the zenith Z, and the point P where the extension of the Earth's axis of rotation intersects with the celestial sphere is the celestial north pole. The great circle that passes through the zenith and the celestial north pole is the meridian, and the horizontal coordinate system is a coordinate system based on the horizon and meridian. The great circle that passes from Z through the celestial body S is called the azimuth circle. Let's call the intersection point of the azimuth circle and the horizon H. The altitude a of a celestial body is the angle ∠SOH measured along the azimuth circle, and the azimuth angle Z is usually measured as ∠NOH. Horizontal coordinates are used in surveying, celestial navigation, geodesy, etc. [Naoaki Owaki] "Calculating Sunrise and Sunset: How to Calculate the Times of Rising and Setting of Celestial Bodies" by Nagasawa Takumi (1999, Chijin Shokan) [Reference items] | | | |Note: The north point is the point where the meridian and the horizon intersect that is closest to the north celestial pole. The south point is the point where the meridian and the horizon intersect that is closest to the south celestial pole. ©Shogakukan "> Horizontal coordinates (diagram) Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
天球上の天体の位置を表す座標、すなわち天球座標の一種。天体の位置を、地平線から垂直に測った角a(高度)と、方位角Zで表す(方位角は北点Nを基点とし東回りに測ることが多い)。詳しくで説明すると、地平座標で基準となるのは鉛直線ZO(地球重力の方向)で、これに垂直(直角に交わる)で観測者Oを通る平面が地平面、この面と天球と交わる大円が地平線である。また鉛直線と天球との交点が天頂Z、地球自転軸の延長が天球と交わる点Pが天の北極である。天頂と天の北極を通る大円が子午線で、地平座標系は、地平線と子午線とを基準とした座標系である。Zから天体Sを通る大円を方位圏という。方位圏と地平線との交点をHとしよう。天体の高度aとは方位圏に沿って測った角∠SOH、方位角Zは普通∠NOHで測る。地平座標は、測量、天文航法、測地学などで用いられる。 [大脇直明] 『長沢工著『日の出・日の入りの計算――天体の出没時刻の求め方』(1999・地人書館)』 [参照項目] | | | |注:北点とは、子午線と地平線が交わる点のうち、天の北極に近い点をいう。南点とは、同じく天の南極に近い点をいう©Shogakukan"> 地平座標〔図〕 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
Recommend
Gaesimsa Temple Site Stone Pagoda
A two-tiered, four-cornered, five-story stone pago...
Kasane -
A mining term. Used to describe the cross-sectiona...
Housekeeping - Sculpin
...The educational goal through these was to teac...
Nanyo Japanese Town - Nanyo Japanese Town
From the beginning of the 17th century to the end ...
Kakiuchi - Kaito
Depending on the region, Kakiuchi is also called ...
Iekakebayashi - Iekakebayashi
...Recently, with the decline in the number of fa...
Anointing of the sick - byoshanotyu
One of the sacraments of the Catholic Church. A pr...
Basilisk (English spelling)
An imaginary monster that lives in the desert. Als...
Veronica (English spelling) Veronica; brooklime; speedwell
A general term for the genus Veronica (Scrophulari...
Theory of regulations - jorei riron (English spelling) teoria della statuta [Italy]
The word "ordinance" originally meant th...
Vampyrum spectrum
…Many species have nasal lobes, but in rare cases...
Now the Emperor
〘 noun 〙 The temporary imperial palace that was us...
Fixed term deposit
A general term for deposits that, in principle, ca...
Procyon (English spelling)
The proper name of the alpha star in the constell...
Trophy - trophy
Originally, the term referred to a victory plaque...