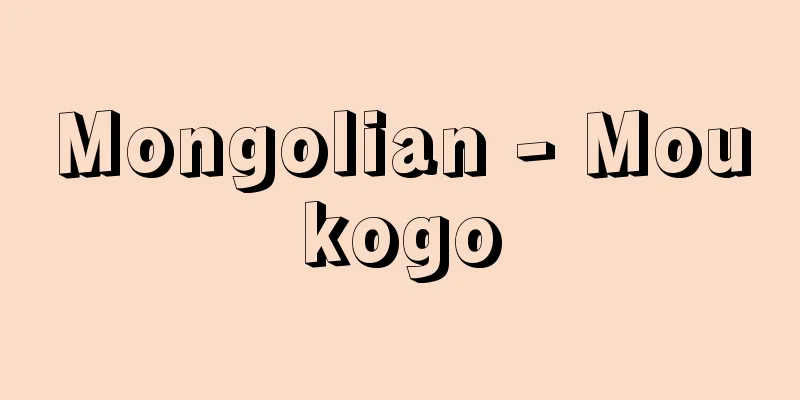Mr. Sakakibara

|
A fudai daimyo (feudal lord) from Mikawa. Said to be a descendant of Niki Yoshinaga, the guardian of Ise Province during the Muromachi period, he lived in Sakakibara Village, Ichishi County, Ise Province (Tsu City, Mie Prefecture) and called himself the Sakakibara clan. Later, during the time of Kiyonaga, he moved to Mikawa Province (Aichi Prefecture) and lived in Ueno Shimo Village, located in the northwest of Okazaki Castle, and served Matsudaira Hirotada, the father of Tokugawa Ieyasu. Kiyonaga's grandson Yasumasa became a trusted vassal of Ieyasu, and after the Mikawa Ikko Ikki uprising, he was promoted to samurai taisho (commander of the Hatamoto clan). Sakakibara Yasumasa was called one of the three great men and became a senior vassal of the Tokugawa clan. He was active as a bannerman during the period when the Tokugawa clan ruled over five provinces, and after entering the Kanto region, he was given 100,000 koku in Tatebayashi, Kozuke Province (Gunma Prefecture) and became a daimyo. His descendants were transferred to Shirakawa, Mutsu Province (Fukushima Prefecture), Himeji, Harima Province (Hyogo Prefecture), Murakami, Echigo Province (Niigata Prefecture), before being transferred back to Himeji, and finally to Takada, Echigo Province, with a fief of 150,000 koku by the time of the Meiji Restoration. Since Yasumasa, the official title has been Shikibu Taifu, a hereditary position, and the family is a prestigious family within the hereditary lineage of the Tokugawa clan. [Masuo Inorimoto] [References] | | |Note: In the diagram, biological children are indicated with | and adopted children with ‖ ©Shogakukan Sakakibara Family / Brief Family Tree Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
三河(みかわ)出身の譜代大名(ふだいだいみょう)。室町時代の伊勢国(いせのくに)守護仁木義長(にきよしなが)の子孫といわれ、伊勢国一志(いちし)郡榊原村(三重県津市)に住し榊原氏を称した。のち清長(きよなが)のとき三河国(愛知県)に移り、岡崎城北西部に位置する上野下(うえのしも)村に居住し、徳川家康の父松平広忠(まつだいらひろただ)に仕えた。清長の孫康政(やすまさ)は家康の近臣となり、三河一向一揆(いっこういっき)のあと旗本一手の侍大将に取り立てられた。榊原康政は三傑の一人と称せられ徳川氏重臣となった。五か国領有時代も旗本部将で活躍し、関東入部後は上野国(こうずけのくに)(群馬県)館林(たてばやし)で10万石を与えられ大名となった。子孫は陸奥国(むつのくに)(福島県)白河、播磨国(はりまのくに)(兵庫県)姫路、越後国(えちごのくに)(新潟県)村上に移封ののちふたたび姫路に転封され、最後は越後国高田15万石で明治維新に至る。官名は康政以来、式部大輔(しきぶたいふ)を世襲し、徳川氏の譜代筋(すじ)では名門である。 [煎本増夫] [参照項目] | | |注:図では実子を|で、養子を‖で示した©Shogakukan"> 榊原氏/略系図 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
>>: Sakakibara [Hot Spring] - Sakakibara
Recommend
Hot spring heat release amount - Onsen Hounetsuryo
…Iceland is a good example of this. [Heat dissipa...
Squid fishing - Ikatsuri
…A type of lure used for squid fishing. A cylindr...
Kamarinskaya - Kamarinskaya
…These two operas became models for later Russian...
Sweet - Sweet
〘Adj.-kochi〙 sweet/sweet 〘Adj.-ku〙[1] Used in refe...
Erythrocruorin
A red pigmented protein found in the blood cells o...
Astronomy - Tenmon Gaku (English spelling) astronomy English
Astronomy, simply put, is the study of celestial ...
Mount Hiei
This mountainous area forms the border between Ky...
Balilla
…In Germany, the Hitler Youth (1926) under the Na...
Cat's Story - Neko no Soushi
Otogi-zoshi. One of the Shibukawa editions. It was...
Good fortune - qǐ yùn (English spelling)
In China during the Ming and Qing dynasties, this ...
Kui people - Kui (English spelling)
In Thai, they are called Soai. They are a Mon-Khme...
Larsson, C.
...These include Martin Szanzer, who wrote the mu...
Diplomatic corps
The diplomats of the various countries' diplo...
World Federation of Labor - Sekairouren
Abbreviation for "World Trade Union Confedera...
miliaria crystallina (English spelling) miliaria crystallina
…Depending on where sweat accumulates, it can be ...