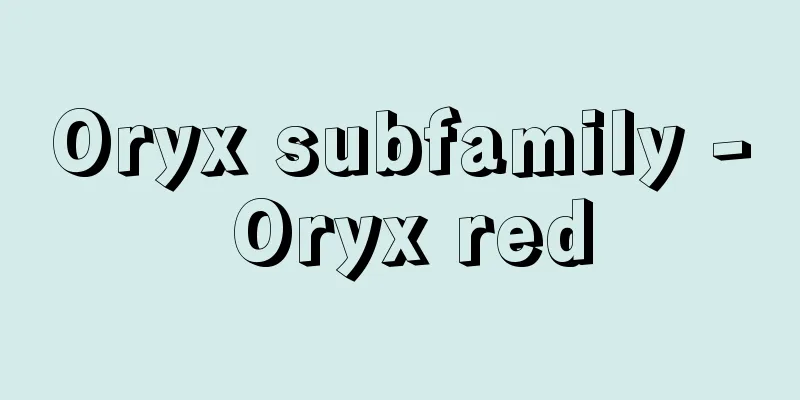pneumothorax

|
What kind of disease is it? ●Main symptoms and progression This is a disease in which a hole appears in the pleura that surrounds the lungs, causing sudden chest pain and difficulty breathing. Normally, the lungs expand and contract to breathe. When you have this disease, air leaks from the surface of the lungs into the chest cavity (inside the chest), causing the lungs to remain contracted and unable to expand sufficiently. If the amount of air leaking out increases, the lungs may be compressed to the other side, pushing against the heart and blood vessels. This is called tension pneumothorax, and if left untreated, it can lead to breathing difficulties and cyanosis, resulting in a dangerous condition. If it affects both lungs it can be life-threatening, but this is rare and most cases occur in one lung only. It is also known that approximately half of patients who have experienced pneumothorax will experience a recurrence. ● Causes of the disease and how symptoms develop Pneumothorax is a condition in which air gets into the thoracic cavity (between the parietal and visceral pleura) and the lungs are damaged. There are various causes, and it can be broadly divided into three types: spontaneous pneumothorax, traumatic pneumothorax, and iatrogenic pneumothorax. Of these, spontaneous pneumothorax can be divided into primary spontaneous pneumothorax, which occurs when an emphysematous cyst (bulla), a thin air sac formed on the surface of the lung, or a subpleural cyst (bleb) ruptures, and secondary pneumothorax, which occurs secondary to other lung diseases. Traumatic pneumothorax is caused by chest compression or rib fractures. Iatrogenic pneumothorax can occur following percutaneous lung biopsy, subclavian vein puncture, transbronchial lung biopsy, etc. ●Characteristics of the disease Spontaneous pneumothorax tends to occur in young, tall, thin men, while secondary pneumothorax occurs in conjunction with underlying diseases such as emphysema or emphysematous cystosis after recovery from tuberculosis, and is therefore more common in elderly people. EBM checks on common treatments and care [Treatment and care] In mild cases, keep at rest [Evaluation] ☆☆☆ [Key points] Observational studies have shown that with rest alone, collapsed (shrunken) lungs expand by 1.25 percent per day. (1) [Treatment and care] Perform needle degassing therapy and continuous degassing therapy [Evaluation] ☆☆☆ [Evaluation points] Needle deaeration therapy involves inserting a needle into the pleura to remove the accumulated air, while continuous deaeration therapy involves inserting a tube into the pleura and leaving it in place to allow the air to be removed continuously. The effectiveness of these treatments has been confirmed by clinical studies. It is recommended to first perform needle deaeration therapy, and then perform continuous deaeration therapy only if no improvement is seen. (2)-(4) [Treatment and care] Performing lung cystectomy through thoracoscopic surgery [Rating] ☆☆☆☆ [Evaluation points] In cases where recurrences occur repeatedly, or in young patients who wish to avoid recurrence, thoracoscopic surgery is performed from the first treatment. Reliable clinical studies have shown that this can prevent recurrence. (2)(5) [Treatment and care] Pleurodesis therapy [Evaluation] ☆☆☆ [Evaluation points] Pleurodesis therapy involves injecting a drug into the pleural cavity to artificially induce inflammation, bonding the lungs to the chest wall, and preventing air leakage. Clinical studies have reported that pleurodesis therapy using tetracycline antibiotics has the same effect as thoracoscopic surgery. However, since its effectiveness and risks for simple spontaneous pneumothorax, which often occurs in young people, are unclear, it should only be performed in cases where air leaks from a chest drain continue or in cases of secondary pneumothorax or pneumothorax due to other causes. (2)(7)(8) Checking commonly used drugs with EBM Injection solution for pleurodesis [Drug name] Tetracycline antibiotic (2)(7)(8) [Rating] ☆☆☆ [Evaluation points] Clinical studies have reported that pleurodesis therapy using tetracycline antibiotics has the same effect as thoracoscopic surgery, but its effectiveness and risk for simple spontaneous pneumothorax, which often occurs in young people, is unclear. It should be limited to cases where air leakage from a chest drain continues or where there is a secondary pneumothorax or a pneumothorax due to other causes. Overall, it is currently the most reliable treatment method .<br /> If the degree of collapse is 25 percent or less, rest alone Pneumothorax is a condition in which air leaks out of the lungs, causing them to shrink and not be able to fully expand, resulting in sudden chest pain and difficulty breathing. Treatment depends on the degree of lung collapse (how much the lungs have shrunk). If the degree of collapse is 25 percent or less of the total lung volume and is not progressing, rest alone is all that is needed to monitor the condition. As the lung shrinks, the ruptured area will heal and you can expect natural healing. If the lung is only 10% collapsed or less, it will usually heal naturally within 1 to 2 weeks. In cases where air has accumulated in the chest is removed, if the degree of collapse is 50 percent or more, or there is an underlying condition such as a chronic lung disease, and the collapsed lung does not re-expand with rest therapy alone, then puncture deaeration therapy or continuous deaeration therapy will be performed using a trocar tube, a thin tube that removes the air that has accumulated in the chest. Thoracoscopic surgery is performed for severe cases. Patients in their 20s and 30s who have repeated recurrences of the disease, have had spontaneous pneumothorax in both lungs, have had long-term lung collapse, or have several abnormal tissues called bullae or blebs on the surface of the lungs may be treated with thoracoscopic surgery to remove the bullae and blebs. Do not use pleurodesis for simple spontaneous pneumothorax In addition, pleurodesis, which uses tetracycline antibiotics to cause inflammation in the thoracic cavity and adhere the lung to the chest wall to prevent air leakage, has not been shown to be effective for simple spontaneous pneumothorax. Therefore, this treatment should not be used for spontaneous pneumothorax, but should be used for pneumothorax caused by other reasons. (1)Light RW. Pleural Diseases, 4th ed. Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, 2001. Source: "EBM: A book that explains correct treatment" Information about the book "EBM: A book that explains correct treatment" |
|
どんな病気でしょうか? ●おもな症状と経過 肺を包んでいる胸膜(きょうまく)(肋膜(ろくまく))に穴があき、突然の胸痛(きょうつう)(胸の痛み)に襲われて呼吸が苦しくなる病気です。通常、肺は大きく膨らんだり縮んだりして呼吸作用をしています。この病気になると、肺の表面から胸腔(きょうくう)(胸のなか)に空気が漏れだし、肺が縮んだままになって、十分に膨らむことができません。 漏れでる空気の量が多くなると、肺が反対側に圧迫されて心臓や血管まで押されてしまうことがあります。これを緊張性気胸(きんちょうせいききょう)といい、放置すると呼吸困難やチアノーゼをきたして危険な状態となります。 両側の肺におこると命にかかわりますが、両側におこるのはまれで、ほとんどは片方の肺におきます。 また、気胸をおこしたことのある患者さんの約半分は再発することが知られています。 ●病気の原因や症状がおこってくるしくみ 気胸とは胸腔内(壁側胸膜(へきそくきょうまく)と臓側胸膜(ぞうそくきょうまく)との間)に空気が入り、肺がダメージを受けた状態です。原因はさまざまで、自然気胸、外傷性気胸、医原性気胸の三つに大きく分けられます。このうち自然気胸は、肺の表面に薄い空気の袋ができる気腫性(きしゅせい)のう胞(ほう)(ブラ)や、胸膜下(きょうまくか)のう胞(ブレブ)の破裂によって生じる原発性自然気胸と、ほかの肺の病気に続発して生じる続発性気胸に分けられます。外傷性気胸は胸部圧迫や肋骨骨折などによって生じます。医原性気胸は経皮肺生検(けいひはいせいけん)、鎖骨下静脈穿刺(さこつかじょうみゃくせんし)、経気管支肺生検(けいきかんしはいせいけん)などに引き続いて生じることがあります。 ●病気の特徴 自然気胸は、若年のやせ型で長身の男性に発症することが多く、続発性気胸は基礎疾患である肺気腫(はいきしゅ)、結核(けっかく)が治った後の気腫性肺(きしゅせいはい)のう胞(ほう)症などに併発しておこるため、高齢者に多く発症します。 よく行われている治療とケアをEBMでチェック [治療とケア]軽症例では安静を保つ [評価]☆☆☆ [評価のポイント] 安静のみで、虚脱(縮んだ状態)した肺が1日あたり1.25パーセントずつ拡張することを示した観察研究があります。(1) [治療とケア]穿刺脱気療法(せんしだっきりょうほう)・持続脱気療法(じぞくだっきりょうほう)を行う [評価]☆☆☆ [評価のポイント] 胸膜に針を刺してたまった空気を抜くのが穿刺脱気療法、胸膜にチューブを入れ、そのままにしておき持続的に空気を抜けるようにするのが持続脱気療法です。これらの治療の効果は臨床研究によって確認されています。まずは穿刺脱気療法を行い、改善がみられない場合に限って、持続脱気療法を行うことが勧められます。(2)~(4) [治療とケア]胸腔鏡下手術(きょうくうきょうかしゅじゅつ)で肺(はい)のう胞切除術(ほうせつじょじゅつ)を行う [評価]☆☆☆☆ [評価のポイント] 再発をくり返す場合、または若年者で再発を避けたい患者さんには初回から胸腔鏡下手術を行います。それによって再発を予防できることが、信頼性の高い臨床研究によって報告されています。(2)(5) [治療とケア]胸膜癒着療法(きょうまくゆちゃくりょうほう)を行う [評価]☆☆☆ [評価のポイント] 胸腔内に薬剤を注入して、人工的に炎症をおこし、肺と胸壁(きょうへき)を癒着させ空気の漏れを防ぐのが胸膜癒着療法です。テトラサイクリン系抗菌薬による胸膜癒着療法では胸腔鏡下手術と同等の効果を得られることを報告した臨床研究があります。しかし、若年者に発生することが多い単純な自然気胸に対する効果や危険性は明らかではないため、胸腔ドレーンからの空気の漏れが持続する場合や、続発性気胸やほかの原因による気胸に限って行うべきでしょう。(2)(7)(8) よく使われている薬をEBMでチェック 胸膜癒着療法のための注入液 [薬名]テトラサイクリン系抗菌薬(2)(7)(8) [評価]☆☆☆ [評価のポイント] テトラサイクリン系抗菌薬による胸膜癒着療法では、胸腔鏡下手術と同等の効果を得られると臨床研究によって報告されていますが、若年者に発生することが多い単純な自然気胸に対する効果や危険性は明らかではありません。胸腔ドレーンからの空気の漏れが持続する場合や続発性気胸やほかの原因による気胸に限って行うべきでしょう。 総合的に見て現在もっとも確かな治療法 虚脱度25パーセント以下なら安静のみ 気胸は肺内の空気が漏れだして肺が縮み、十分に膨らむことができなくなる状態で、突然の胸痛や呼吸困難に見舞われます。治療は肺の虚脱(肺の縮み具合)の度合いに応じて対応します。虚脱度が肺全体の25パーセント以下で、進行性でなければ安静のみでようすをみます。 肺が縮むと破れた部分が癒着して、自然治癒が期待できます。とくに虚脱度合が10パーセント以下なら、ふつうは1~2週間で自然に治ります。 胸にたまった空気を抜く場合も 虚脱度50パーセント以上、慢性の肺の病気などの基礎疾患がある場合で、安静療法だけでは虚脱肺の再拡張がみられない場合は、細いチューブで胸のなかにたまった空気を抜くトロッカーチューブで、穿刺脱気療法や持続脱気療法を行います。 重症者は胸腔鏡下手術を 20歳~30歳代で再発をくり返す、両側の肺で自然気胸になったことがある、肺虚脱が長期間続く、肺の表面にブラやブレブと呼ばれる異常な組織がいくつかできている、などの患者さんでは胸腔鏡下手術でブラやブレブを切除する肺のう胞切除術を行うこともあります。 単純な自然気胸に胸膜癒着療法はしない また、テトラサイクリン系の抗菌薬を使って胸腔内に炎症をおこすことで、肺と胸壁を癒着させて空気の漏れを防ぐ胸膜癒着療法は、単純な自然気胸での効果は明らかになっていません。そこで、この治療は自然気胸については行わず、ほかの原因による気胸に対して行うべきでしょう。 (1)Light RW. Pleural Diseases, 4th ed. Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, 2001. 出典 法研「EBM 正しい治療がわかる本」EBM 正しい治療がわかる本について 情報 |
>>: Platycodon grandiflorum; balloonflower
Recommend
Sanage Shrine - Sanage Shrine
The main shrine is located in Sanage-cho, Toyota C...
Popular novel - tsuuzokushosetsu
It refers to books that are highly entertaining a...
Barriera (English spelling) Peruvian wild grape
A genus of woody climbing plants in the Menisperma...
Galidia elegans (English spelling)
...the yellow mongoose, Cynictis penicillata (sou...
Bitter Sea
〘Noun〙 (also "kugai") A Buddhist term. A...
Vicq d'Azyr, F. (English spelling) VicqdAzyrF
…Medicine has a history dating back to ancient Gr...
Prosh'yan, PP (English spelling) ProshyanPP
...In addition to old cadres like Nathanson, the ...
Cultural ecology
...The view of culture as an adaptive system sees...
Udaya - Udaya
…It is located near Patna, the capital of Bihar, ...
Lake Kitagata
A long, narrow lake formed in a dissected valley ...
NS Lenin
...It completed its mission in 1970 and was laid ...
Brown Pelican - Brown Pelican
A seabird of the Pelecanidae family of the order ...
Vacuum - Shinkuu (English spelling)
A vacuum is a space that is completely devoid of ...
gold key
…During the 18th and 19th centuries, many Europea...
Eigenshipa - Eigenshipa
…Shogun Yoshimitsu made Eigen-ji a place of praye...