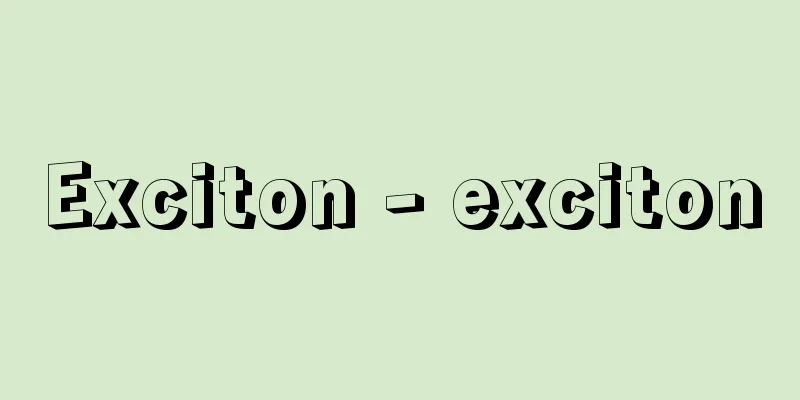Saikyoji Temple

|
This is the head temple of the Tendai Shinsei sect, located in Sakamoto Honmachi, Otsu City, Shiga Prefecture. It is also called Kaikozan Kenhossho Saikyo-ji Temple. The principal image is Amida Nyorai. It is said to have been founded in 618 (the 26th year of the reign of Empress Suiko) by Prince Shotoku for his mentor, the Korean monks Eji and Esou. As the Tendai sect became more popular, its teachings spread to this temple, located north of Mount Hiei. During the Tenryaku era (947-957), Gansanjie Daishi Ryogen restored and rebuilt the temple, making it the central training center for Nembutsu. In 1486 (Bunmei 18), the founder, Shinsei Shonin, entered the temple, restored over 40 buildings and teachings, and began the practice of chanting Buddhist prayers, a tradition that is still carried on today. In 1571 (Genki 2), the temple was burned down when Oda Nobunaga burned down Mount Hiei, but Akechi Mitsuhide, who became the lord of Sakamoto Castle, became a parishioner and the temple was rebuilt in 1574 (Tensho 2). In 1590, the temple merged with Hossho-ji Temple in Awataguchi, Yamashiro (Kyoto Prefecture). In 1878 (Meiji 11), the temple became the head temple of the Shinsei school of Tendai Buddhism, and currently has over 400 branch temples across the country. The guest hall, known as the Momoyama Palace, is a shoin-style building that was relocated from Fushimi Castle, and is a national important cultural property along with the principal image of the seated Amida Buddha (late Heian period), the temple bell (Heian period), and the seated Yakushi Buddha (hidden Buddha, handed down from Kyoto's Hossho-ji Temple). Within the grounds is the grave of Akechi Mitsuhide's family. [Nakayama Kiyota] "Ancient Temple Pilgrimage: Omi 5, Saikyoji Temple" (1980, Tankosha) Main hall (nationally designated important cultural property). Otsu City, Shiga Prefecture © Lake Biwa Visitors Bureau Saikyoji Temple Source: Shogakukan Encyclopedia Nipponica About Encyclopedia Nipponica Information | Legend |
|
滋賀県大津市坂本本町にある天台真盛宗(しんせいしゅう)の総本山。戒光山兼法勝(かいこうざんけんほっしょう)西教寺と称する。本尊は阿弥陀如来(あみだにょらい)。618年(推古天皇26)聖徳太子が恩師の高麗(こま)僧慧慈(えじ)、慧聡(えそう)のために創建したと伝えられる。その後、天台宗が盛んになるに及び、比叡山(ひえいざん)北方にあたる当寺にもその教線が及んだ。天暦(てんりゃく)年間(947~957)に元三慈恵(がんさんじえ)大師良源が復興再建して念仏の中央道場とした。1486年(文明18)中興開山の真盛上人(しんせいしょうにん)が入寺し、40余の堂塔と教法を再興して不断念仏を始め、いまなおその伝統が受け継がれている。1571年(元亀2)織田信長の比叡山焼打ちによって焼失したが、坂本城主となった明智光秀(あけちみつひで)が檀徒(だんと)となって1574年(天正2)に再建され、90年には山城(やましろ)(京都府)粟田口(あわたぐち)にあった法勝寺(ほっしょうじ)と合併した。1878年(明治11)天台宗真盛派本山となり、現在では全国に400余りの末寺をもつ。桃山御殿とよばれる客殿は、伏見(ふしみ)城から移築された書院造の建物で、本尊阿弥陀如来坐像(ざぞう)(平安後期)、梵鐘(ぼんしょう)(平安時代)、薬師(やくし)如来坐像(京都法勝寺伝来、秘仏)などとともに国の重要文化財。境内には明智光秀一族の墓がある。 [中山清田] 『『古寺巡礼 近江5 西教寺』(1980・淡交社)』 本堂(国指定重要文化財)。滋賀県大津市©公益社団法人びわこビジターズビューロー"> 西教寺 出典 小学館 日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)日本大百科全書(ニッポニカ)について 情報 | 凡例 |
<<: Saikyozuka (English spelling) Ch'ae hyǒp-ch'ong
>>: Saigyo Sakura - Saigyo Sakura
Recommend
Visit to Italy - Italiahomon
…The fruits of this period were the poetry collec...
Killard - Killard
…They reject interest (riba), in which one party ...
Ammonia - ammonia
A compound of nitrogen and hydrogen, it is a colo...
Adiantum pedatum (English spelling) Adiantumpedatum
…[Shigeyuki Mitsuda]. … *Some of the terminology ...
Yellow-bellied bell frog - Yellow-bellied bell frog
...Sometimes they turn over with the red ventral ...
Ship type - Senkei
(1) The three-dimensional shape of a ship. It mai...
Akebonozasa - Akebonozasa
...Distichus (also called Kirinchiku) is used for...
Otsu Primeval Flower Garden
...The main industries are field crops, mainly be...
Adrasteia
…Kronos, the father of Zeus, was born. It was a s...
Chapel (English spelling) chapel; cappella
A chapel. A house or room where Christian worship ...
Ocean Acoustic Tomography
…The time required for each path is determined by...
Ponape Island (English spelling)
A volcanic island in the eastern part of the Carol...
Meat - carnivores
A general term for animals belonging to the order...
fillstrath terrace
...Terraces are also classified into erosional te...
Chitragupta
… Yama, the Indian god of death, governs the unde...